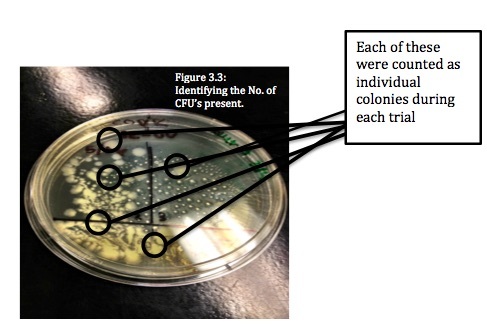
In this study E. coli bacteria was exposed to small UV lights currently used in school laboratories to see the effect on colony growth. This project explores how UV radiation methods could be applied in common households to inhibit bacterial growth.
Read More...