
In this study a student uses Daphnia magna, or water fleas, to assay the purity of local soil samples. Daphnia magna are a helpful organism to detect potentially harmful levels of toxins in water.
Read More...Monitoring Local Soil Toxicity by Daphnia magna Viability

In this study a student uses Daphnia magna, or water fleas, to assay the purity of local soil samples. Daphnia magna are a helpful organism to detect potentially harmful levels of toxins in water.
Read More...Development of Two New Efficient Means of Wastewater Treatment
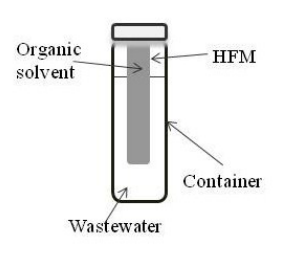
The water we use must be treated and cleaned before we release it back into the environment. Here, the authors investigate two new techniques for purifying dissolved impurities from waste water. Their findings may give rise to more cheaper and more efficient water treatment and help keep the planet greener.
Read More...Correlation between trihalomethane concentrations and various cancers in Massachusetts counties
.png)
The authors assess incidence and mortality rates of two cancer types in relation to trihalomethane pollutant concentrations in drinking water.
Read More...Which fruit peel helps retain the most soil moisture?

Here, the authors investigated the ability to use fruit peels to help soil retain moisture, a property that is essential to agriculture. Across a 96-hour observation period, orange, banana, and kiwi peel water emulsions were evaluated for their effects on soil moisture. They found that orange peels retained the most moisture, but banana and kiwi peels also offered improvements over their control sample.
Read More...Investigation of the correlation between trihalomethane concentrations and socioeconomic factors in NY State
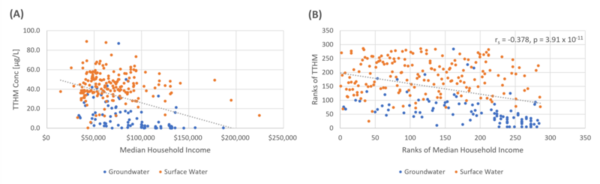
Trihalomethanes, probable human carcinogens, are commonly found disinfection by-products (DBPs) in public water systems (PWS). The authors investigated the correlation between trihalomethane concentrations and socioeconomic factors in New York State, finding a negative correlation between median household income and trihalomethane concentrations. The inverse association between trihalomethanes and household income may indicate socioeconomic disparity regarding drinking water quality and the need for improved efforts to assist small- and medium-sized community water systems to lower DBP levels in New York State.
Read More...From trash to treasure: A sustainable approach to oil spill clean-up
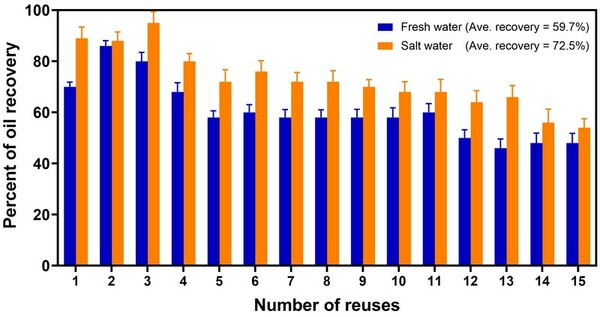
In this study the authors looked at sustainable ways to clean up oil spills that harm marine life. Using water spangle leaves and milk week the authors looked at the ability to recovery oil from both fresh and salt water and the ability to reuse the organic material to clean up spills. Their results show promise to help find a sustainable, eco-friendly way to clean up oil spills and protect marine life and habitats.
Read More...Impact of dams in Santa Clara County on the nitrification of the surrounding ecosystem
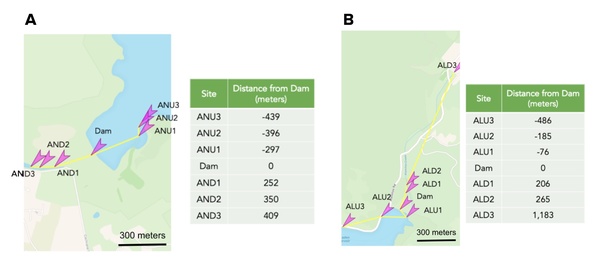
Two dams in Santa Clara County were evaluated for water and soil nitrate levels in order to determine whether nitrification rates were higher upstream than downstream of the dam. This could indicate a detrimental effect of dams on the nitration cycle in the environment.
Read More...Probiotic biosorption as a way to remove heavy metal in seawater

In this study, the authors address the concerns of heavy metal contamination in industrial and feedlot water waste. They test whether added probiotics are capable of taking up heavy metals in water to attenuate pollution.
Read More...Exploring Unconventional Growing Methods to Promote Healthy Growth in Common Household Plants: Tagetes patula L. and Lepidium sativum

This study focused on finding more sustainable growing methods that reduce chemical fertilizer or water usage and can be used at the household level for garden plants. Metrics for healthy plant growth were height at first bloom, growing time, and survival rate. The Deep Water Culture (DWC) treatment for garden cress plants significantly increased the height at first bloom compared to the control group. For rates of surviving plants, the treatments had little effect on garden cress, but the Eggshell Grounds, Wick System, and DWC system groups outperformed the control group for marigolds.
Read More...Estimating the liquid jet breakdown height using dimensional analysis with experimental evidence
These authors mathematically deduce a model that explains the interesting (and unintuitive) physical phenomenon that occurs when water falls.
Read More...