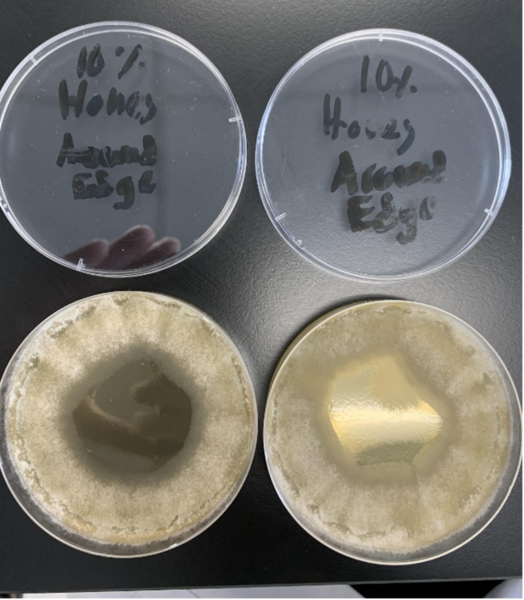
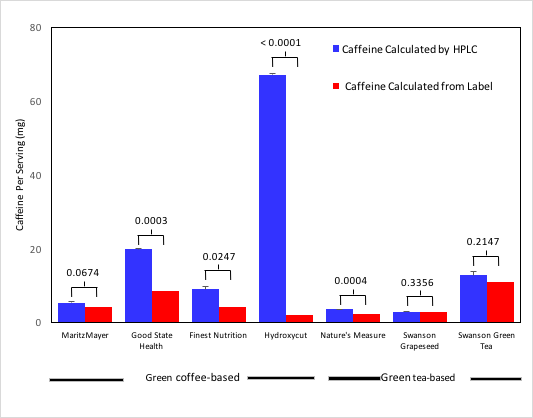
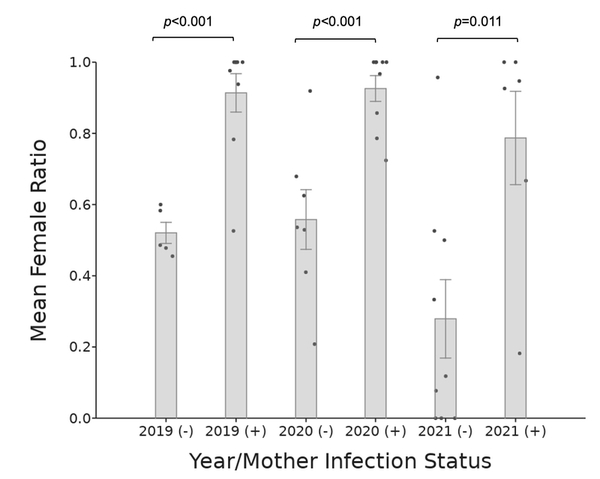
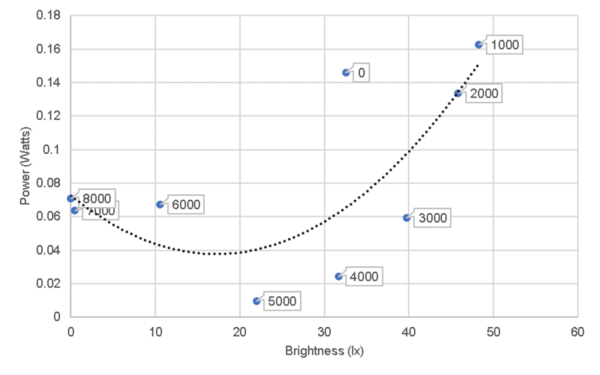
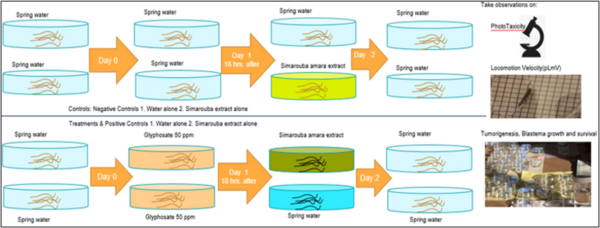
In the modern world, communication and mobility are no longer obstacles. A natural consequence is that people from all over the world are mixing like never before and national identity can no longer be determined simply by a person's appearance or manner of speech. In this article, the authors study how a person's accent interferes with the perception of a their national identity and proposes ways to eliminate such biases.
Read More...