%20(1).png)
In this study, the authors identify transcripts and gene networks that are changed after infection with the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-related coronavirus (MERS-CoV).
Read More...Gene expression profiling of MERS-CoV-London strain
%20(1).png)
In this study, the authors identify transcripts and gene networks that are changed after infection with the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-related coronavirus (MERS-CoV).
Read More...PCR technology for screening genetically modified soybeans

In order to determine whether unmarked soybeans in the market were genetically modified crops, the authors developed a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) screen for DNA lectin.
Read More...Genomic Signature Analysis for the Strategic Bioremediation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Mangrove Ecosystems in the Gulf of Tonkin

Engineered bacteria that degrade oil are currently being considered as a safe option for the treatment of oil spills. For this approach to be successful, the bacteria must effectively express oil-degrading genes they uptake as part of an external genoming vehicle called a "plasmid". Using a computational approach, the authors investigate plasmid-bacterium compatibility to find pairs that ensure high levels of gene expression.
Read More...Comparing Virulence of Three T4 Bacteriophage Strains on Ampicillin-Resistant and Sensitive E. coli Bacteria
In this study, the authors investigate an alternative way to kill bacteria other than the use of antibiotics, which is useful when considering antibiotic-resistance bacteria. They use bacteriophages, which are are viruses that can infect bacteria, and measure cell lysis. They make some important findings that these bacteriophage can lyse both antibiotic-resistant and non-resistant bacteria.
Read More...Cathodal Galvanotaxis: The Effect of Voltage on the distribution of Tetrahymena pyriformis
.png)
The surface of the unicellular eukaryote, Tetrahymena pyriformis, is covered with thousands of hair-like cilia. These cilia are very similar to cilia of the human olfactory and respiratory tracts making them model organisms for studying cilia function and pathology. The authors of this study investigated the effect of voltage on T. pyriformis galvanotaxis, the movement towards an electrical stimulus. They observed galvanotaxis towards the cathode at voltages over 4V which plateau, indicating opening of voltage gated-ion channels to trigger movement.
Read More...TGFβ1 Codon 10 Polymorphism and its Association with the Prevalence of Low Myopia
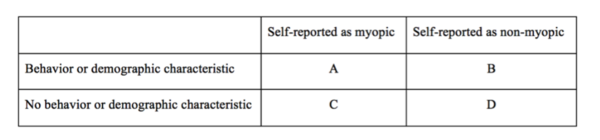
The goal of this project was to assess the relationships among low myopia, behavioral and demographic factors, and a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the TGFβ1 gene.
Read More...Lung cancer AI-based diagnosis through multi-modal integration of clinical and imaging data
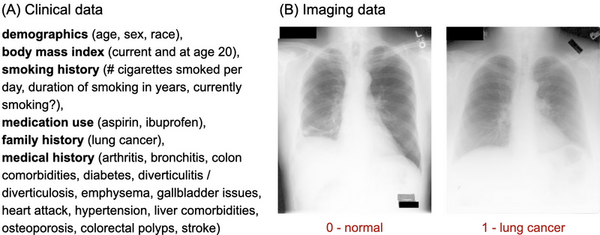
Lung cancer is highly fatal, largely due to late diagnoses, but early detection can greatly improve survival. This study developed three models to enhance early diagnosis: an MLP for clinical data, a CNN for imaging data, and a hybrid model combining both.
Read More...Contrasting role of ASCC3 and ALKBH3 in determining genomic alterations in Glioblastoma Multiforme
Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM) is the most malignant brain tumor with the highest fraction of genome alterations (FGA), manifesting poor disease-free status (DFS) and overall survival (OS). We explored The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and cBioportal public dataset- Firehose legacy GBM to study DNA repair genes Activating Signal Cointegrator 1 Complex Subunit 3 (ASCC3) and Alpha-Ketoglutarate-Dependent Dioxygenase AlkB Homolog 3 (ALKBH3). To test our hypothesis that these genes have correlations with FGA and can better determine prognosis and survival, we sorted the dataset to arrive at 254 patients. Analyzing using RStudio, both ASCC3 and ALKBH3 demonstrated hypomethylation in 82.3% and 61.8% of patients, respectively. Interestingly, low mRNA expression was observed in both these genes. We further conducted correlation tests between both methylation and mRNA expression of these genes with FGA. ASCC3 was found to be negatively correlated, while ALKBH3 was found to be positively correlated, potentially indicating contrasting dysregulation of these two genes. Prognostic analysis showed the following: ASCC3 hypomethylation is significant with DFS and high ASCC3 mRNA expression to be significant with OS, demonstrating ASCC3’s potential as disease prediction marker.
Read More...Elucidating the Genotoxicity of Synthetic Food Preservatives with the SOS Chromotest
.jpg)
Evidence suggests certain food preservatives may be genotoxic due to their ability to impair normal cellular pathways. The authors investigated the genotoxic potential and effects of commonly used synthetic food preservatives, specifically sodium nitrite, potassium sulfate, and hydrogen peroxide.
Read More...The Effect of the Human MeCP2 gene on Drosophila melanogaster behavior and p53 inhibition as a model for Rett Syndrome

In this study, the authors observe if the symptoms of Rett Syndrome, a neurodegenerative disease in humans, are reflected in Drosophila melanogaster. This was achieved by differentiating the behavior and physical aspects of wild-type flies from flies expressing the full-length MeCP2 gene and the mutated MeCP2 gene (R106W). After conducting these experiments, some of the Rett Syndrome symptoms were recapitulated in Drosophila, and a subset of those were partially ameliorated by the introduction of pifithrin-alpha.
Read More...