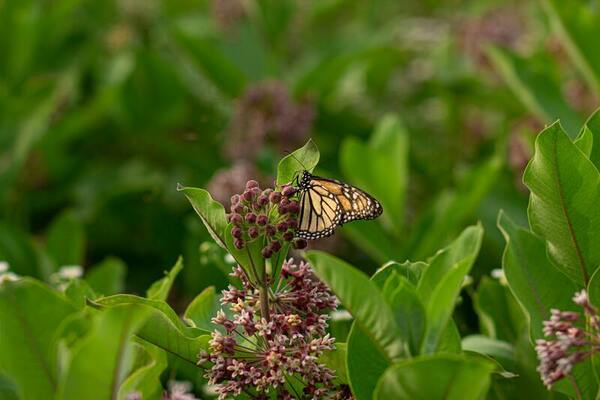

This study assesses the capacity for milkweed species, an important host plant for Monarch butterflies, to grow in desert environments with different water levels.
Read More...Milkweed sustainability in the Sonoran Desert: A. erosa is more water-efficient compared to two other species

This study assesses the capacity for milkweed species, an important host plant for Monarch butterflies, to grow in desert environments with different water levels.
Read More...Motion tracking and analysis of spray water droplets studied by high-speed photography using an iPhone X
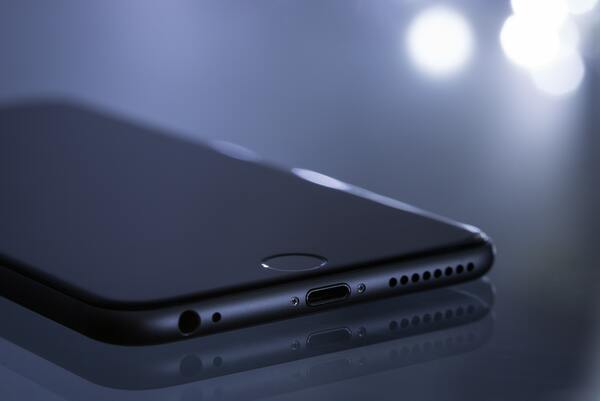

Smartphones are not only becoming an inseparable part of our daily lives, but also a low-cost, powerful optical imaging tool for more and more scientific research applications. In this work, smartphones were used as a low-cost, high-speed, photographic alternative to expensive equipment, such as those typically found in scientific research labs, to accurately perform motion tracking and analysis of fast-moving objects. By analyzing consecutive images, the speed and flight trajectory of water droplets in the air were obtained, thereby enabling us to estimate the area of the water droplets landing on the ground.
Read More...The relationship between macroinvertebrates, water quality, and the health of Stevens Creek
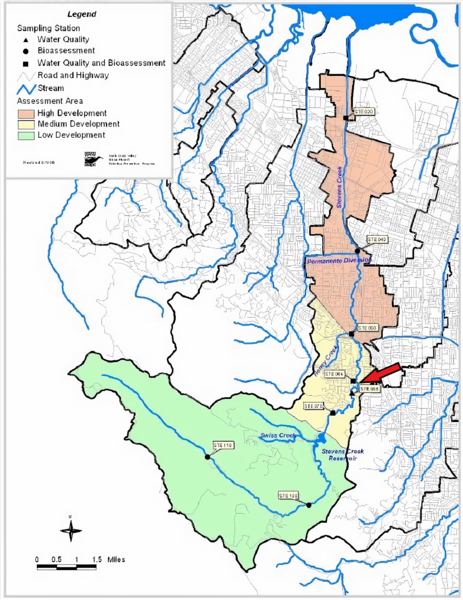
Stevens Creek, which flows through Santa Clara County in California, provides a crucial habitat for federally designated threatened steelhead trout, with a portion of the trout’s diet being dependent on the presence and abundance of macroinvertebrates that inhabit the creek. In this article, the authors investigate how the water chemistry within the creek was associated with the abundance and diversity of macroinvertebrates, and subsequently the creek’s health. They conduct qualitative analysis of macroinvertebrates and water quality to obtain a general understanding of the health of Stevens Creek.
Read More...Effects of airport runoff pollution on water quality in bay area sites near San Francisco and Oakland airports
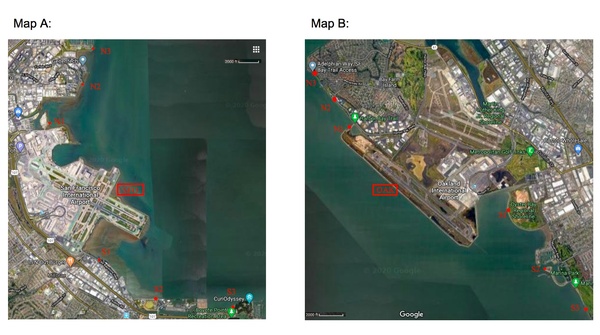
In this study, the authors sample water at different points closer and closer to two different airports to determine if these airports may be contributing to water pollution, specifically by measuring metals, nitrates, and pH.
Read More...The external presence of running water influences the root growth of pea plants (Phaselous vulgaris)
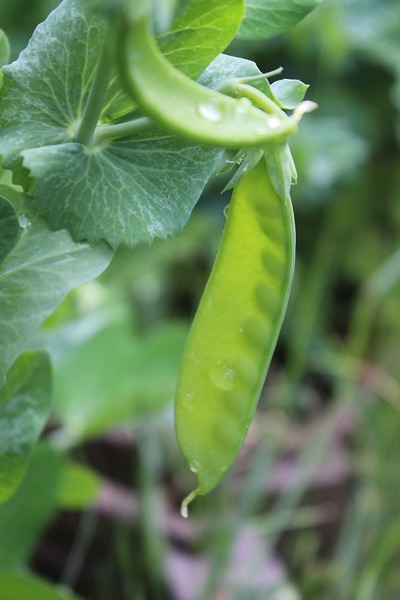

Each year, invasive tree roots cause large amounts of damage to underground pipes. While this is usually due to leaks and cracks, tree roots can also invade pipes that are structurally sound. We are interested in investigating whether plant roots have an affinity towards flowing water, measured through mass, even when the running water is not in direct contact with soil. We tested this by creating a choice chamber with water running under one end and no stimulus on the other end. Overall, the masses of the roots growing towards flowing water were greater than the masses of the roots growing towards the end with no stimulus, showing that plant roots did have an affinity towards flowing water.
Read More...Comparing the Voltage Output of Water in Drop and Flow Form Using a Piezoelectric Sensor and Hydroelectric Turbine
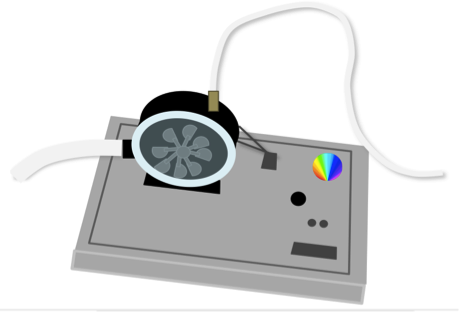
This study compares the voltage output of two potential alternative energy sources: water drops hitting a piezoelectric surface and water flowing through a hydroelectric turbine. The findings of this study suggest that harnessing kinetic energy from falling raindrops may be a viable alternative energy source.
Read More...Towards an Integrated Solution for Renewable Water and Energy
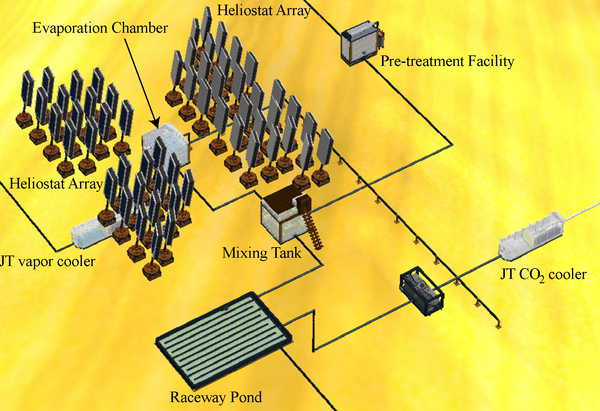
An integrated plant that would generate energy from solar power and provide clean water would help solve multiple sustainability issues. The feasibility of such a plant was investigated by looking at the efficacy of several different modules of such a plant on a small scale.
Read More...The optimization of high-protein duckweed cultivation in eutrophicated water with mutualistic bacteria
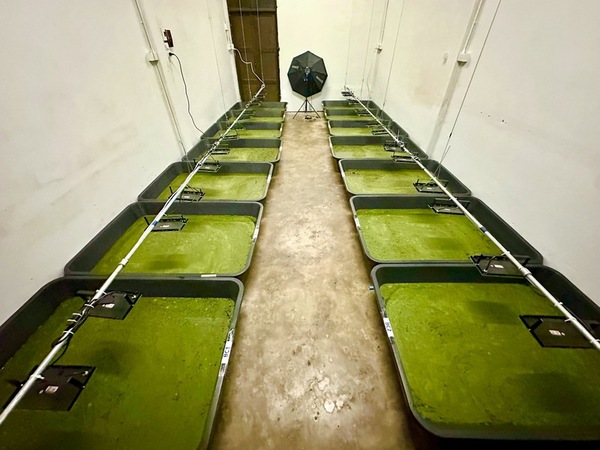

he rapid growth of the human population is driving food crises in Thailand and Southeast Asia, while contributing to global food insecurity and a larger carbon footprint. One potential solution is cultivating duckweed (Wolffia globosa) for consumption, as it grows quickly and can provide an alternative protein source. This research explored two methods to optimize duckweed cultivation: using phosphorus- and nitrogen-rich growing media and plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB).
Read More...The Dependence of CO2 Removal Efficiency on its Injection Speed into Water
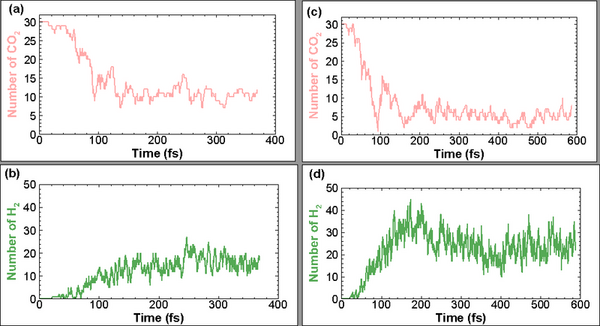
Recent research confirms that climate change, driven by CO2 emissions from burning fossil fuels, poses a significant threat to humanity. In response, authors explore methods to remove CO2 from the atmosphere, including breaking its molecular bonds through high-speed collisions.
Read More...Examination of the underlying chemical physics of the Mpemba effect in water and other liquids

Counterintuitive in nature, the Mpemba effect asserts that hot liquid freezes faster than cold liquid. While noted throughout history by scientific minds like Aristotle, the phenomenon remains in contention with varying hypotheses for the effect proposed alongside the effect’s rise in popularity. Contributing to the research efforts surrounding the Mpemba effect, the authors in this article explore the effect in different liquids ranging in physical properties and intermolecular forces to determine potential parameters attributable to producing the Mpemba effect.
Read More...