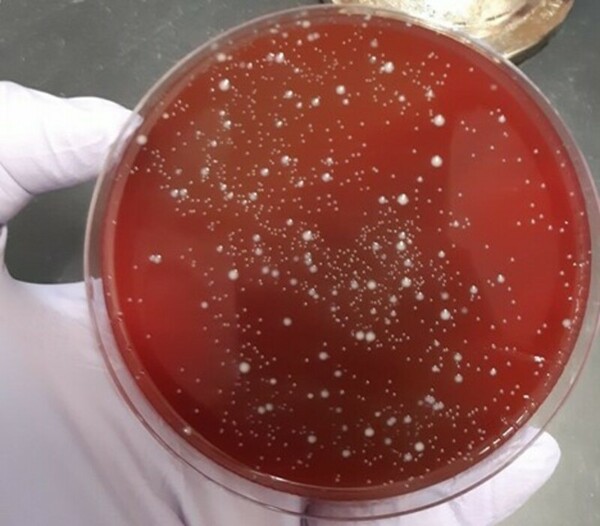
In this study, the authors investigate the effects of acidity on the survival of commercial probiotic Lovebug bacterial strains.
Read More...Pediatric probiotic culture survival study in acidic pH using an in vitro model

In this study, the authors investigate the effects of acidity on the survival of commercial probiotic Lovebug bacterial strains.
Read More...Enhancing activity of antibiotics against Staphylococcus aureus with Shuang-Huang-Lian
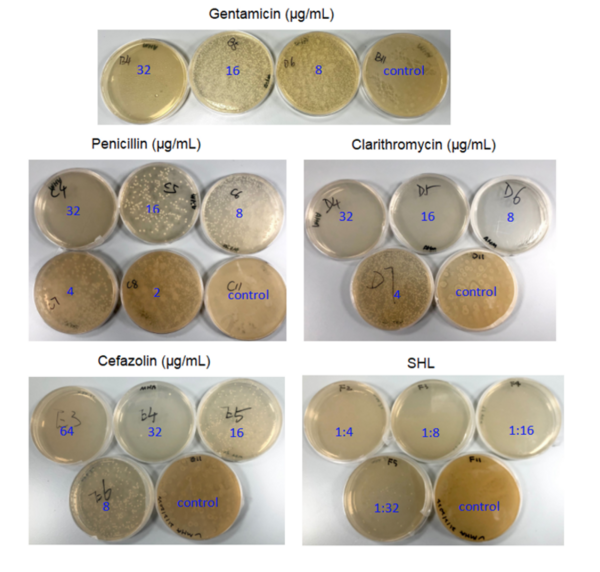
Staphylococcus aureus is a major pathogen in both hospitals and the community and can cause systemic infections such as pneumonia. Multi-drug resistant strains, such as Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) are particularly worrisome. In order to reduce the development of bacterial resistance, we hypothesized that two selected traditional Chinese medicines, Shuang-Huang-Lian (SHL) and Lan-Qin, would be effective against S. aureus. The results showed that SHL had a synergistic effect with gentamicin as well as additive effects with penicillin and cefazolin against S. aureus compared with using antibiotics alone.
Read More...The effects of UV-C and ionizing radiation on the functions of Escherichia Coli

In this study, the authors send E. coli cultures to space via the Cubes in SpaceTM program to determine if ultraviolet C and ionizing radiation negatively affect bacterial growth.
Read More...Characterizing Quorum Sensing-Induced Bioluminescence in Variable Volumes With Vibrio fischeri Using Computer Processing Methods
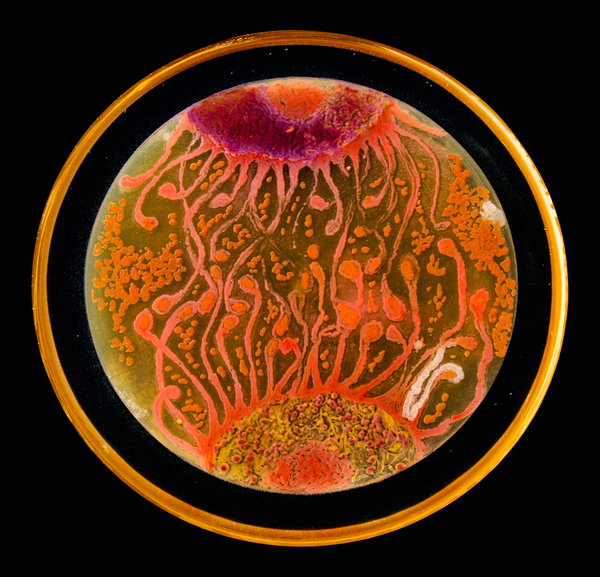
Understanding how bacteria respond to other bacteria could facilitate their ability to initiate and maintain their infectiousness. The phenomenon by which bacteria signal to each other via chemical signals is called quorum sensing, which could be targeted to deter bacterial infection in some cases if better understood. In this article, the authors study how a bacterium called V. fischeri uses quorum sensing to change bioluminescence, an easy readout that facilitates studying quorum sensing in this strain.
Read More...Disk Diffusion Tests Show Ginger to be Ineffective as an Antibacterial Agent
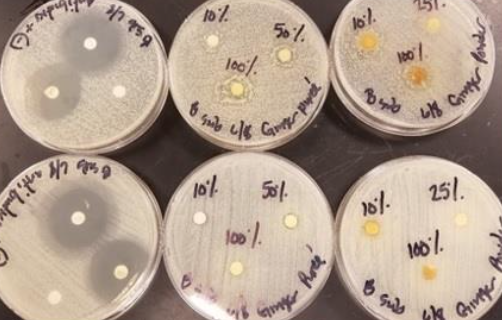
In this study, preparations of ginger were tested for an effect on the growth of four common bacterial species.
Read More...The Effects of Ultraviolet Light on Escherichia coli
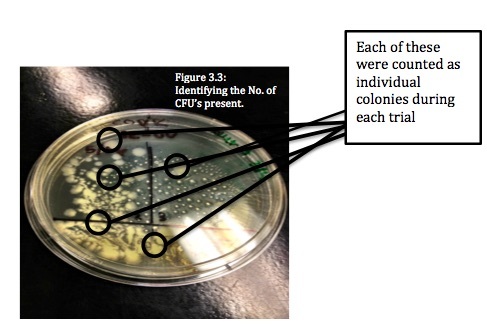
In this study E. coli bacteria was exposed to small UV lights currently used in school laboratories to see the effect on colony growth. This project explores how UV radiation methods could be applied in common households to inhibit bacterial growth.
Read More...Antibacterial properties of household spices and toothpaste against oral bacteria
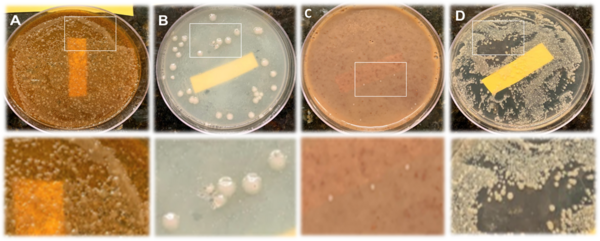
Bacteria cause tooth decay, plaque, bad breath, and other diseases. Despite being cleaned with water and toothpaste, oral bacteria live on our toothbrushes. Bacterial growth has been shown to be inhibited by different toothpastes and common household spices. This study tested how different toothpastes and common household spices, including cinnamon, cumin, nutmeg, and ground white pepper, can inhibit bacteria from growing on toothbrushes
Read More...Effect of heme vs. non-heme iron supplements on gut microbiome fitness

Here, based on identification of iron deficiencies of a majority of people around the world, the authors sought to understand how the two main forms of dietary iron, heme and non-heme, affect the bacteria found in the human gut. by using a cell plate study, they found that bacterial growth increased with increasing concentration os either form of iron, up until the point where the high iron content resulted in cytotoxicity. They suggest this evidence points to the potential dangers of overconsumption of iron.
Read More...Strain-specific and photochemically-activated antimicrobial activity of berberine and two analogs
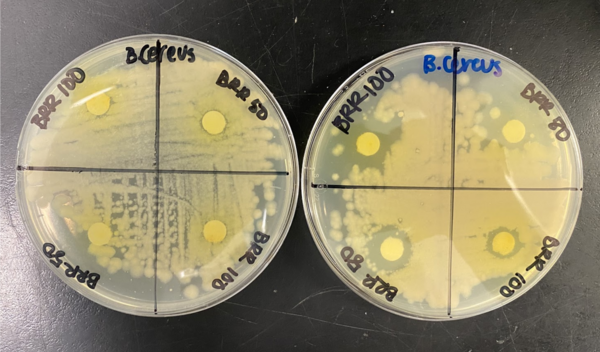
In this study, the authors investigate the antimicrobial effects of berberine and berberine analogs. Berberine is extracted from plants and is a naturally occurring alkaloid, and is also excited photochemically. Using three different assays, the authors tested whether these compounds would inhibit bacterial growth. They found that these compounds were antibacterial and even more so when used with photoirradiation. This study has important antibacterial implications.
Read More...The effects of early probiotic supplementation on the germination of Arabidopsis thaliana
The use of fertilizers is associated with an increase in soil degradation, which is predicted to lead to a decrease in crop production within the next decade. Thus, it is critical to find solutions to support crop production to sustain the robust global population. In this study, the authors investigate how probiotic bacteria, like Rhizobium leguminosarum, Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas fluorescens, can impact the growth of Arabidopsis thaliana when applied to the seeds.They hypothesized that solutions with multiple bacterial species compared to those with only a single bacterial species would promote seed germination more effectively.
Read More...