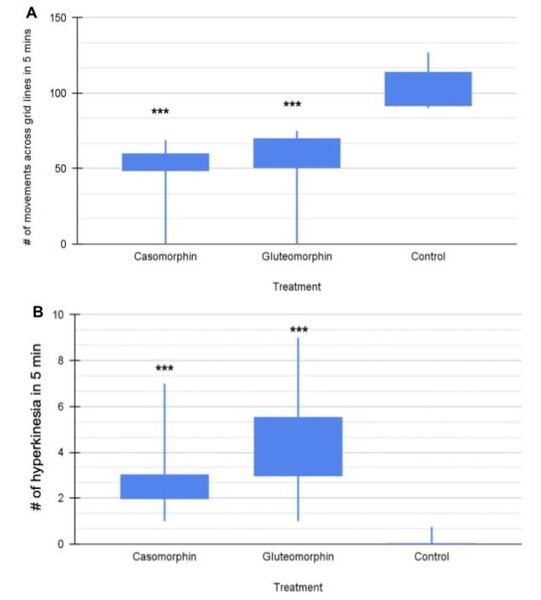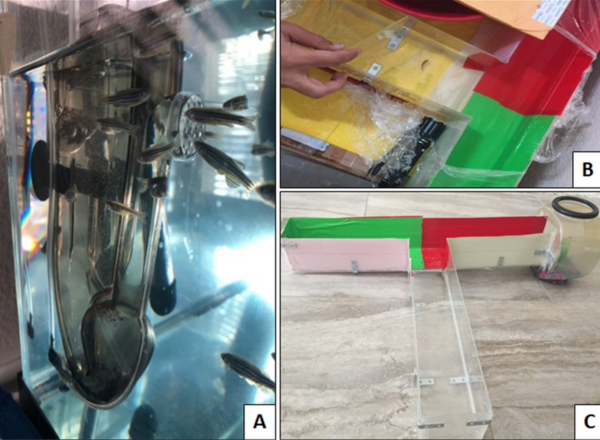
The authors compared the short-term effects of processed versus unprocessed food on spatial learning and survival in zebrafish, given the large public concern regarding processed foods. By randomly assigning zebrafish to a diet of brine shrimp flakes (processed) or live brine shrimp (unprocessed), the authors show while there is no immediate effect on a fish's decision process between the two diets, there are significant correlations between improved learning and stress response with the unprocessed diet.
Read More...

.png)