The authors looked at whether traditional Chinese medicine remedies that target the lungs and liver would reduce inflammation in a planaria model. They found that the two active compounds they tested were able to decrease induced inflammation by 97-98%.
Read More...Browse Articles
Computational development of aryl sulfone compounds as potential NNRTIs
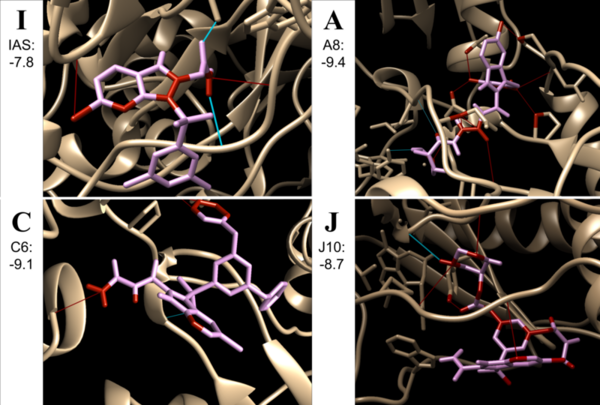
Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) are allosteric inhibitors that bind to the HIV reverse transcriptase and prevent replication. Indolyl aryl sulfones (IAS) and IAS derivatives have been found to be highly effective against mutant strains of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Here, we analyzed molecules designed using aryl sulfone scaffolds paired to cyclic compounds as potential NNRTIs through the computational design and docking of 100 novel NNRTI candidates. Moreover, we explored the specific combinations of functional groups and aryl sulfones that resulted in the NNRTI candidates with the strongest binding affinity while testing all compounds for carcinogenicity. We hypothesized that the combination of an IAS scaffold and pyrimidine would produce the compounds with the best binding affinity. Our hypothesis was correct as the series of molecules with an IAS scaffold and pyrimidine exhibited the best average binding affinity. Additionally, this study found 32 molecules designed in this procedure with higher or equal binding affinities to the previously successful IAS derivative 5-bromo-3-[(3,5-dimethylphenyl)sulfonyl]indole-2-carboxyamide when docked to HIV-1 reverse transcriptase.
Read More...Alkaloids Detection in Commonly Found Medicinal Plants with Marquis Reagent

This study investigates the presence of alkaloids in a variety of medicinal plants using the Marquis reagent. They reveal some surprising results and how useful the Marquis reagent is.
Read More...Bacteria and Antibiotic Resistance in School Bathrooms

Since school bathrooms are widely suspected to be unsanitary, we wanted to compare the total amount of bacteria with the amount of bacteria that had ampicillin or streptomycin resistance across different school bathrooms in the Boston area. We hypothesized that because people interact with the faucet, outdoor handle, and indoor handle of the bathroom, based on whether or not they have washed their hands, there would be differences in the quantity of the bacteria presented on these surfaces. Therefore, we predicted certain surfaces of the bathroom would be less sanitary than others.
Read More...Effect of Natural Compounds Curcumin and Nicotinamide on α-synuclein Accumulation in a C. elegans Model of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects over 10 million people worldwide. It is caused by destruction of dopamine-producing neurons, which results in severe motor and movement symptoms. In this study, the authors investigated the anti-Parkinsonian effects of two natural compounds curcumin and nicotinamide using C. elegans as a model organism.
Read More...Mutation of the Catalytic Cysteine in Anopheles gambiae Transglutaminase 3 (AgTG3) Abolishes Plugin Crosslinking Activity without Disrupting Protein Folding Properties
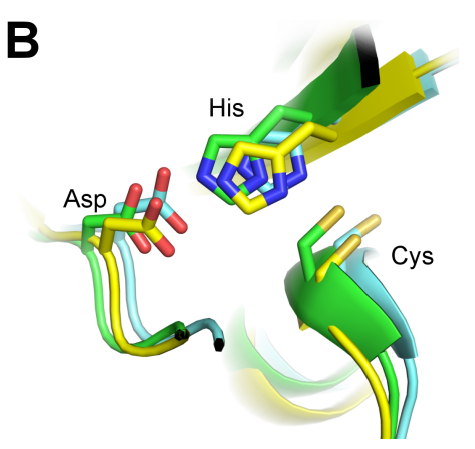
Malaria is a major public health issue, especially in developing countries, and vector control is a major facet of malaria eradication efforts. Recently, sterile insect technique (SIT), or the release of sterile mosquitoes into the wild, has shown significant promise as a method of keeping vector populations under control. In this study, the authors investigate the Anopheles gambiae transglutaminase 3 protein (AgT3), which is essential to the mating of the Anopheles mosquito. They show that an active site mutation is able to abolish the activity of the AgT3 enzyme and propose it as a potential target for chemosterilant inhibitors.
Read More...In silico design of novel acetylcholinesterase inhibitors as potential therapeutics for Alzheimer's disease
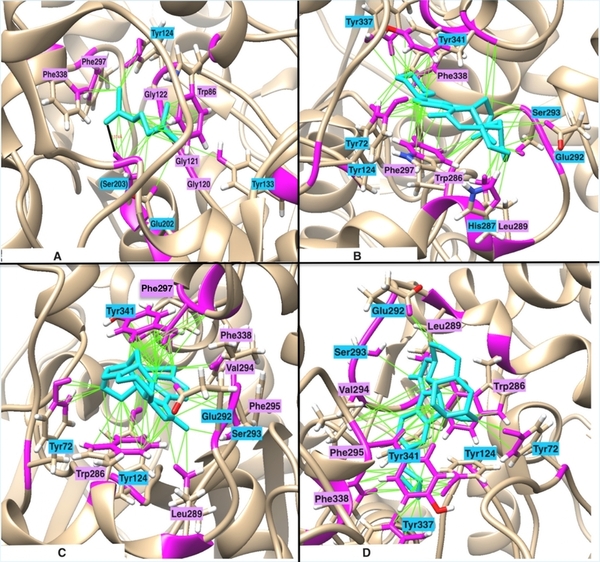
Elevated acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity contributes to cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s, motivating the search for more effective inhibitors with better bioavailability. This study used computational methods to design novel, non-toxic AChE inhibitors.
Read More...The effects of dysregulated ion channels and vasoconstriction in glioblastoma multiforme
The impact of genetic, drug, and procedural factors on cardiac xenograft survival days in non-human primates
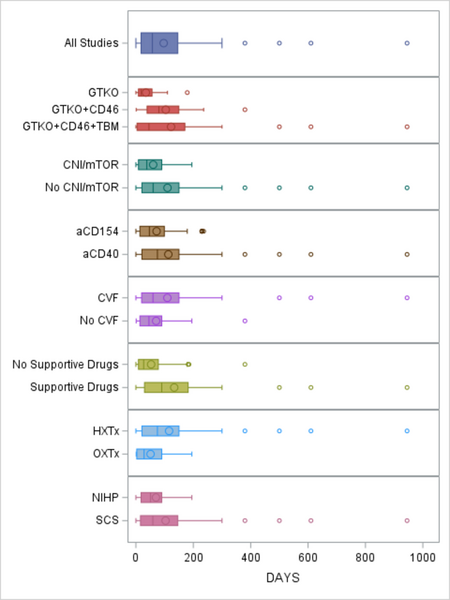
Due to a critical shortage of donor hearts, researchers are exploring cardiac xenotransplantation—transplanting animal hearts into humans—as a potential solution. This study synthesized nearly two decades of preclinical research to evaluate multiple factors affecting xenograft survival.
Read More...The effect of youth marijuana use on high-risk drug use: Examining gateway and substitution hypothesis
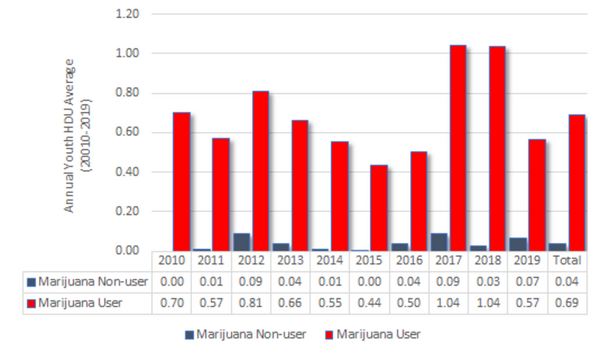
The authors looked at whether youth use of marijuana related to later high-risk drug use. Using survey data from 2010-2019 they found that youth marijuana use did correlate to an increased risk of high-risk drug use.
Read More...