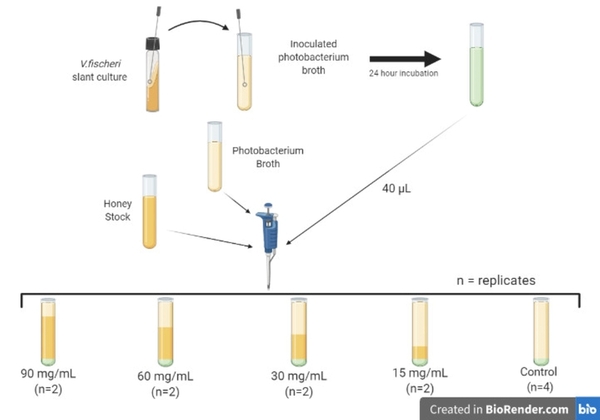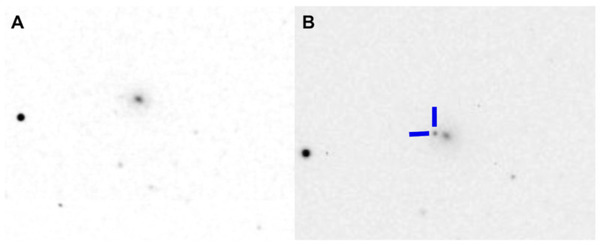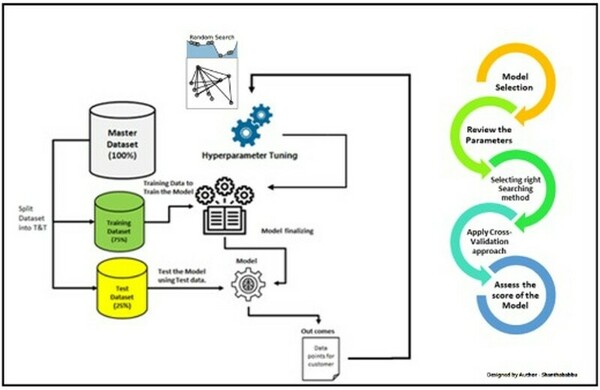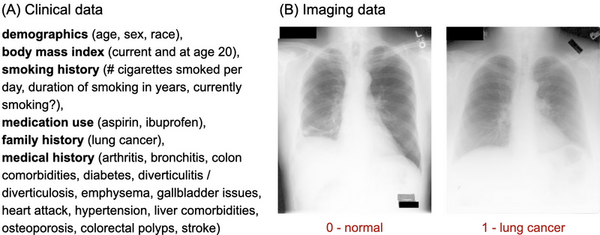
Lung cancer is highly fatal, largely due to late diagnoses, but early detection can greatly improve survival. This study developed three models to enhance early diagnosis: an MLP for clinical data, a CNN for imaging data, and a hybrid model combining both.
Read More...