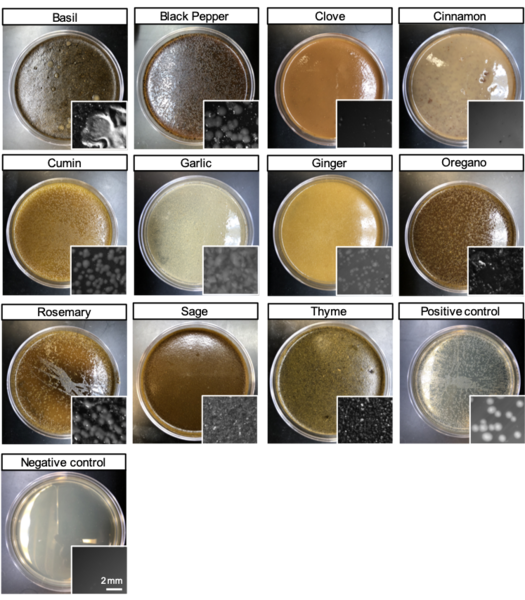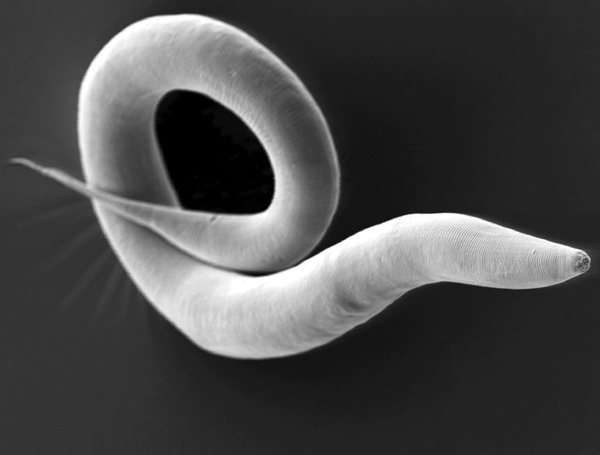
Cilia are little hair-like protrusions on many cells in the human body, including those lining the trachea where they play a role in clearing our respiratory tract of mucous and other irritants. Genetic mutations that impair ciliary function have serious consequences on our well-being making it important to understand how ciliary function is regulated. By using a simple organism, such as the worm C. elegans that use cilia to move, the authors explore the effect of certain genetic mutations on the cilia of the worms by measuring their ability to move towards or away from certain odorants.
Read More...