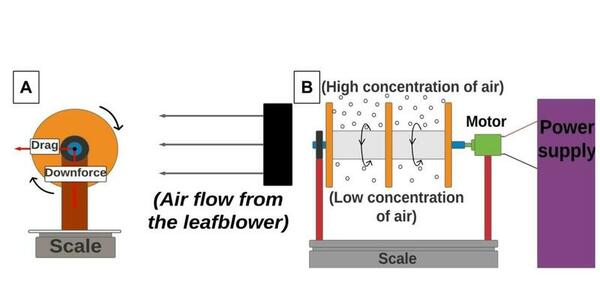
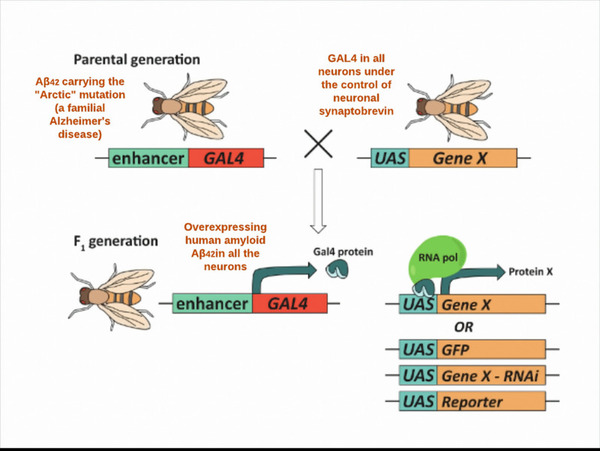
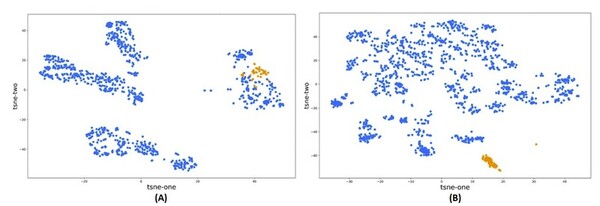
Here in an effort to better understand how our brains process and remember different categories of information, the authors assessed working memory capacity using an operation span task. They found that individuals with higher working memory capacity had higher overall higher task accuracy regardless of the type of category or the type of visual distractors they had to process. They suggest this may play a role in how some students may be less affected by distracting stimuli compared to others.
Read More...