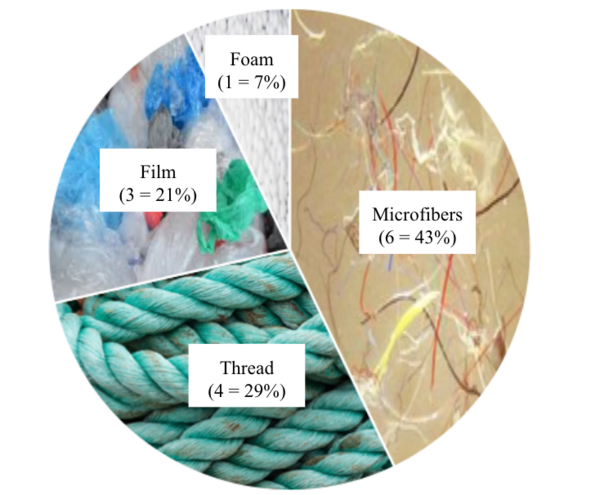
Does the overuse of plastic in Japan poses an ecological risk to marine species and their consumers? Using visual and chemical dissection, all fish in this study were found to have microplastics present in their gastrointestinal tract, including two species that are typically eaten whole in Japan. Overall, these results are concerning as previous studies have found that microplastics can carry persistent organic pollutants. It is presumed that the increasing consumption of microplastics will have negative implications on organ systems such as the liver, gut, and hormones.
Read More...
![Alterations of the [Fe/H] Values Modulate Light Curves by Absolute Magnitude in non-Blazhko RRab Lyraes](/rails/active_storage/representations/proxy/eyJfcmFpbHMiOnsibWVzc2FnZSI6IkJBaHBBallHIiwiZXhwIjpudWxsLCJwdXIiOiJibG9iX2lkIn19--7d8b84074a7b504657e6acd5ed4f66e4b84daf63/eyJfcmFpbHMiOnsibWVzc2FnZSI6IkJBaDdCem9MWm05eWJXRjBTU0lJY0c1bkJqb0dSVlE2QzNKbGMybDZaVWtpRFRZd01IZzJNREErQmpzR1ZBPT0iLCJleHAiOm51bGwsInB1ciI6InZhcmlhdGlvbiJ9fQ==--33b2b080106a274a4ca568f8742d366d42f20c14/Figure_4.png)

_(35622760083).jpg)