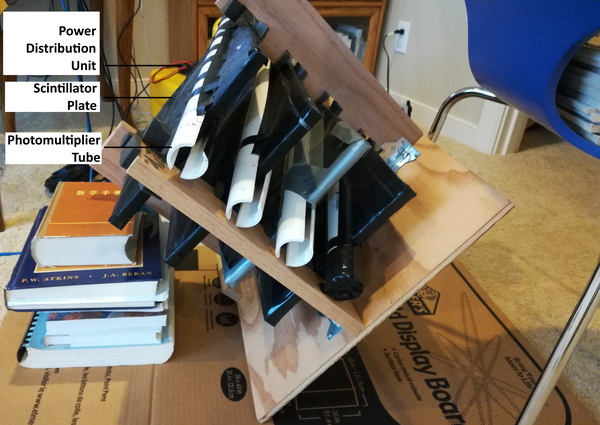
Here, the authors considered the stretching behavior of rubber bands by exposing the rubber bands to increasing loads and measuring their stretch response. They found that a linear stretch response was observed for intermediate loading steps, but this behavior was lost at lower or higher loads, deviating from Hooke's Law. The authors suggest that studies such as these can be used to evaluate other visco-elastic structures.
Read More...

.jpg)

