
This study investigates the presence of alkaloids in a variety of medicinal plants using the Marquis reagent. They reveal some surprising results and how useful the Marquis reagent is.
Read More...Alkaloids Detection in Commonly Found Medicinal Plants with Marquis Reagent

This study investigates the presence of alkaloids in a variety of medicinal plants using the Marquis reagent. They reveal some surprising results and how useful the Marquis reagent is.
Read More...Effect Of SMC On The Growth Of Bean, Cherry Tomato And Roma Tomato Plant

Mushroom compost, also called Spent Mushroom Substrate or Spent Mushroom Compost (SMC), is suitable for a variety of plants. Previous research has found that the application of SMC will increase plant growth. However, it is unclear which exact proportions of SMC and soil will maximize tomato and bean plant growth. We showed that the hypothesized growth media with 30% SMC optimizes seed germination, plant height, number of leaves, and survival rate compared to other combinations of growth media. Our research suggests that SMC is a useful alternative for conventional fertilizers.
Read More...Taft linear free-energy relationships in the biocatalytic hydrolysis of sterically hindered nitrophenyl ester substrates
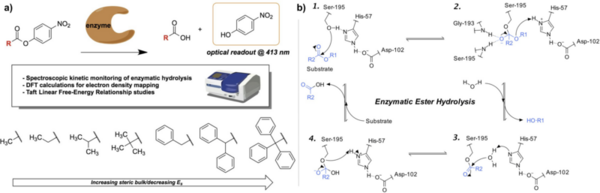
This study applies Taft linear free-energy relationships to study kinetic trends in the enzymatic hydrolysis of sterically hindered substrates.
Read More...How does light affect the distribution of Euglena sp. and Tetrahymena pyriformis

In this article, the authors explored the locomotory movement of Euglena sp. and Tetrahymena pyriformis in response to light. Such research bears relevance to the migration and distribution patterns of both T. pyriformis and Euglena as they differ in their method of finding sustenance in their native environments. With little previous research done on the exploration of a potential response to photostimulation enacted by T. pyriformis, the authors found that T. pyriformis do not bias in distribution towards areas of light - unlike Euglena, which displayed an increased prevalence in areas of light.
Read More...Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy analysis of seven wisconsin biosolids

The authors analyzed biosolids from five Wisconsin wastewater treatment plants and suggest using KBr pellet FTIR as a simple and rapid method to start characterizing P species in biosolids.
Read More...The Effect of Cobalt Biomineralization on Power Density in a Microbial Fuel Cell
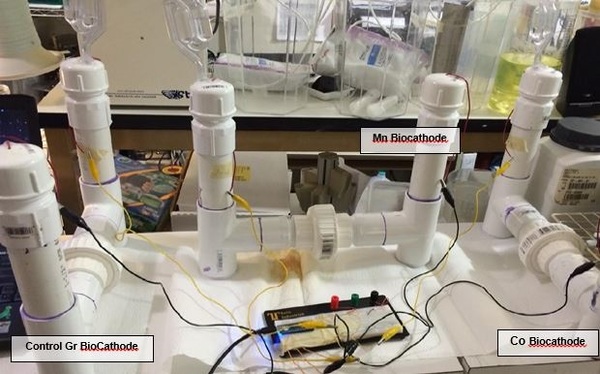
A microbial fuel cell is a system to produce electric current using biochemical products from bacteria. In this project authors operated a microbial fuel cell in which glucose was oxidized by Shewanella oneidensis in the anodic compartment. We compared the power output from biomineralized manganese or cobalt oxides, reduced by Leptothrix cholodnii in the cathodic compartment.
Read More...Enhanced soil fertility through seaweed-derived biochar: A comparative analysis with commercial fertilizers
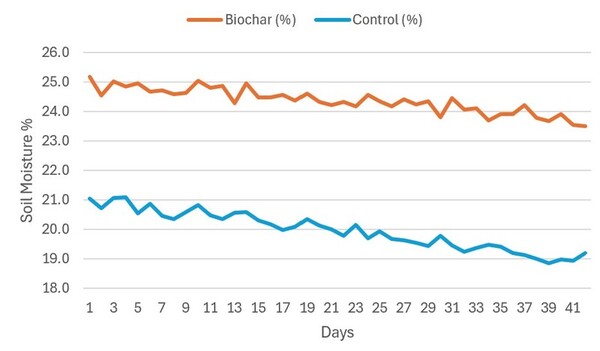
The study explored converting Gracilaria seaweed waste—known for releasing toxic hydrogen sulfide when decomposed—into biochar as a sustainable solution for waste management and soil improvement.
Read More...Efficacy of natural coagulants in reducing water turbidity under future climate change scenarios

Here the authors investigated the effects of natural coagulants on reducing the turbidity of water samples from the Tennessee River Watershed. They found that turbidity reduction was higher at lower temperatures for eggshells. They then projected and mapped turbidity reactions under two climate change scenarios and three future time spans for eggshells. They found site-specific and time-vary turbidity reactions using natural coagulants could be useful for optimal water treatment plans.
Read More...Voltage, power, and energy production of a Shewanella oneidensis biofilm microbial fuel cell in microgravity
.PNG)
The authors looked at the ability of Shewanella oneidensis to generate energy in a microbial fuel cell under varying conditions. They found that the S. Onedensis biofilm was able to produce energy in microgravity and that one of the biggest factors that limited energy production was a decrease in growth medium present.
Read More...Effects of spices on rice spoilage

In this work, based on centuries of history where spices have been used and thought to have antimicrobial properties that prolong the shelf life of food, the authors investigated if several spices used in Indian cooking could delay the spoilage of cooked white rice. Based on changed in appearance and smell, as well as growth on agar plates, they found that cinnamon was the most effective in delaying spoilage, followed by cumin, pepper, garlic, and ginger. Their findings suggest the ability to use spices rather than chemical food preservatives to prolong the shelf life of foods.
Read More...