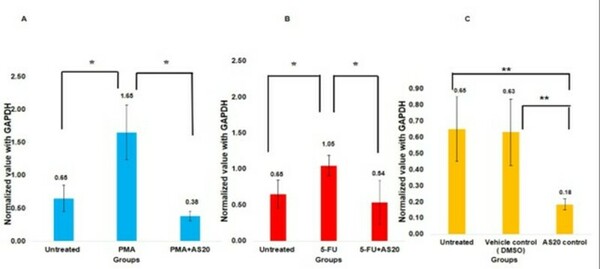
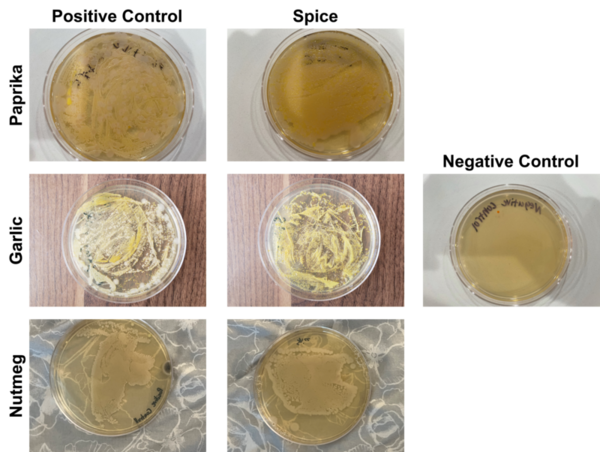
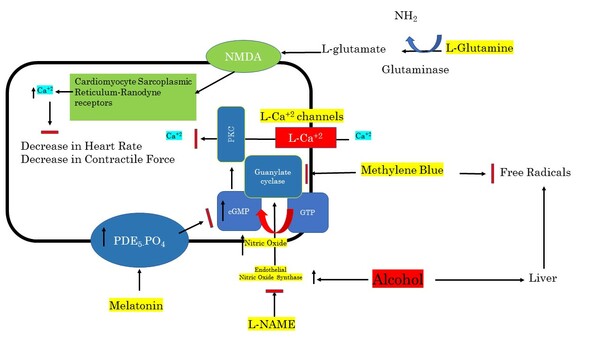
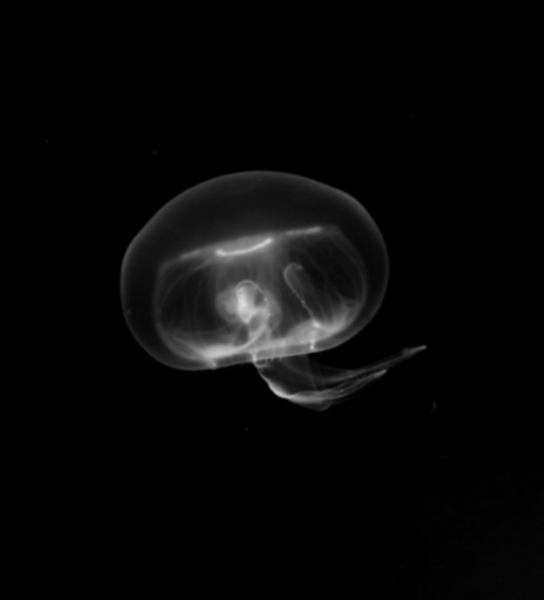
Chronic alcohol consumption can cause cardiac myopathy, which afflicts about 500,000 Americans annually. Gunturi et al. wanted to understand the effects of alcohol on heart rate and confirm the role of nitric oxide (NO) signaling in heart rate regulation. Using the model organism Daphnia magna, a water crustacean with a large, transparent heart, they found that the heart rate of Daphnia magna was reduced after treatment with alcohol. This depression could be reversed after treatment with inhibitors of NO synthesis and signaling. Their work has important implications for how we understand alcohol-induced effects on heart rate and potential treatments to reverse heart rate depression as a result of alcohol consumption.
Read More...

.PNG)