With low-temperature transportation being critical for the progress of research and medical services by preserving biological samples and vaccines, the optimization of cold storage materials is more critical now than ever. The exclusive use of dry ice has its limitations. Notably, it proves insufficient for cold storage during long-range transportation necessary for the delivery of specimens to rural areas. In this article, the authors have proposed a new means of cold storage through the combination of dry ice and ethanol. Upon thorough analysis, the authors have determined their new method as considerably better than the use of pure dry ice across many characteristics, including cold storage capacity, longevity of material, and financial and environmental feasibility.
Read More...Browse Articles
Can essential oils be allelopathic to Lolium multiforum without harming Solanum lycopersicum?

Seeking to investigate eco-friendly biological methods to control weeds and enhance food crop yields, here the authors considered the effects of three essential oils on seed germination and radicle length of both a weed and a common crop. They found that treatment with turmeric oil had phytotoxic potential, leading to a reduction in both seed germination and radicle length of the weed. In contrast, ginger oil possessed allelopathic properties towards both. The authors suggest that essential oils could be used as eco-friendly bio-herbicides.
Read More...Astragalus membranaceus Root Concentration and Exposure Time: Role in Heat Stress Diminution in C. elegans

In this study, the authors investigated the biological mechanism underlying the actions of a traditional medicinal plant, Astragalus membranaceus. Using C. elegans as an experimental model, they tested the effects of AM root on heat stress responses. Their results suggest that AM root extract may enhance the activity of endogenous pathways that mediate cellular responses to heat stress.
Read More...Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Periplasmic Proteins Interacting With the Peptidoglycan Layer of Escherichia coli
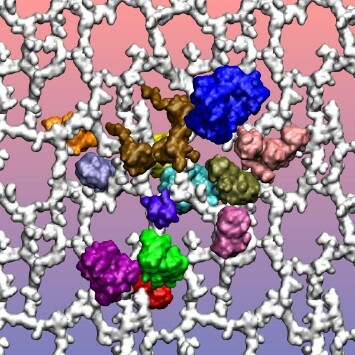
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations are a great tool to model and study complex biological systems. In this paper, the authors use MD simulations to construct and simulate a model of the periplasmic space, the peptidoglycan layer and its associated proteins, in an Escherichia coli cell.
Read More...Aberrant response to dexamethasone suppression test associated with inflammatory response in MDD patients
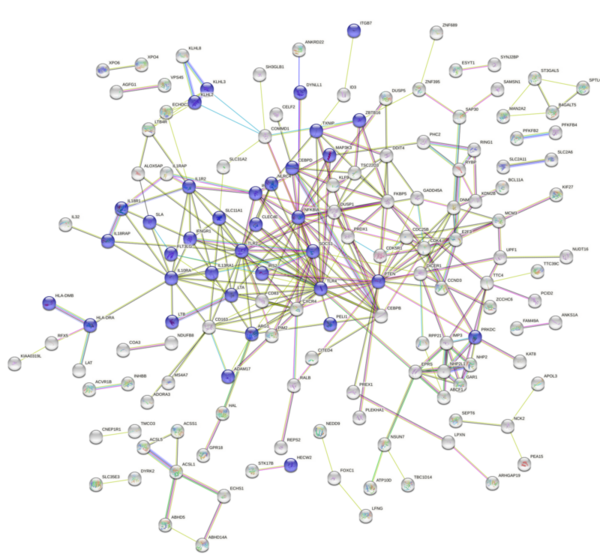
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a prevalent mood disorder. The direct causes and biological mechanisms of depression still elude understanding, though genetic factors have been implicated. This study looked to identify the mechanism behind the aberrant response to the dexamethasone suppression test (DST) displayed by MDD patients, in which they display a lack of cortisol suppression. Analysis revealed several pro-inflammatory genes that were significant and differentially expressed between affected and non-affected groups in response to the DST. Looking at ways to decrease the inflammatory response could have implications for treatment and may explain why some people treated for depression still display symptoms or may lead researchers to different classes of drugs for treatment.
Read More...The Protective Antioxidant Effects of Sulforaphane on Germinating Radish Seeds Treated with Hydrogen Peroxide
Free radical chain reactions result when atoms containing unpaired electrons bind with biomolecules and alter their biological functions, contributing to the progression of diseases such as atherosclerosis, cancer, and diabetes. Antioxidants, such as vitamin E and sulforaphane, are effective neutralizers of free radicals and prevent cellular damage. This present study is conducted to determine the relative effectiveness of sulforaphane against free radicals generated by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) compared with the known antioxidant vitamin E.
Read More...Transcriptomic profiling identifies differential gene expression associated with childhood abuse
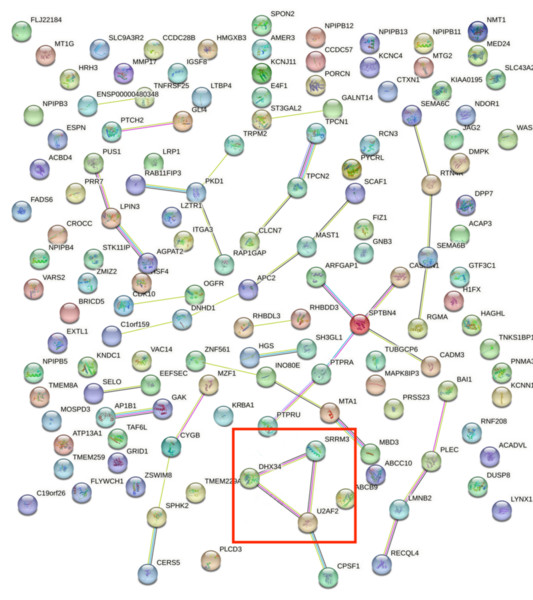
Childhood abuse has severe and lasting effects throughout an individual's life, and may even have long-term biological effects on individuals who suffer it. To learn more about the effects of abuse in childhood, Li and Yearwood analyze gene expression data to look for genes differentially expressed genes in individuals with a history of childhood abuse.
Read More...Comparative singlet oxygen photosensitizer efficiency of berberine, rose bengal, and methylene blue by time course nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) monitoring of a photochemical 4+2 cycloaddition endoperoxide formation

Berberine, a natural product alkaloid, has been shown to exert biological activity via in situ production of singlet oxygen when photo irradiated. Berberine utilizes singlet oxygen in its putative mechanism of action, wherein it forms an activated complex with DNA and photosensitizes triplet oxygen to singlet oxygen to specifically oxidize guanine residues, thereby halting cell replication and leading to cell death. This has potential application in photodynamic therapy, alongside other such compounds which also act as photosensitizers and produce singlet oxygen in situ. The quantification of singlet oxygen in various photosensitizers, including berberine, is essential for determining their photosensitizer efficiencies. We postulated that the singlet oxygen produced by photoirradiation of berberine would be superior in terms of singlet oxygen production to the aforementioned photosensitizers when irradiated with UV light, but inferior under visible light conditions, due to its strong absorbance of UV wavelengths.
Read More...Characterizing the association between hippocampal reactive astrogliosis, anhedonia-like behaviors, and neurogenesis in a monkey model of stress and antidepressant treatment
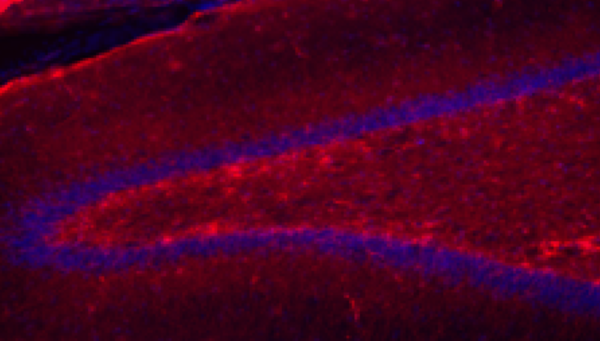
This study examined the effects of stress and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) on a measure of astrocyte reactivity in nonhuman primate (NHP) models of stress. Results showed that chronic separation stress in NHPs leads to increased signs of astrogliosis in the NHP hippocampus. The findings were consistent with the hypotheses that hippocampal astrogliosis is an important mechanism in stress-induced cognitive and behavioral deficits.
Read More...The Cilium- and Centrosome-Associated Protein CCDC11 Is Required for Cytokinesis via Midbody Recruitment of the ESCRT- III Membrane Scission Complex Subunit CHMP2A
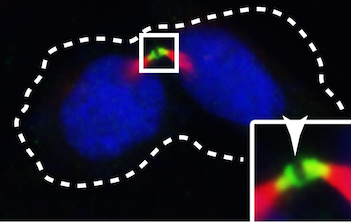
In order for cells to successfully multiply, a number of proteins are needed to correctly coordinate the replication and division process. In this study, students use fluorescence microscopy and molecular methods to study CCDC11, a protein critical in the formation of cilia. Interestingly, they uncover a new role for CCDC11, critical in the cell division across multiple human cell lines.
Read More...