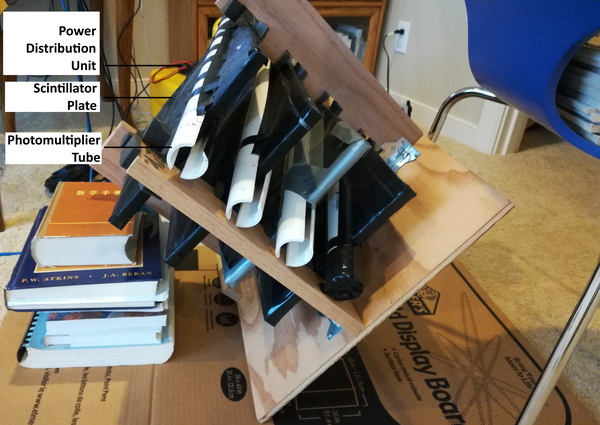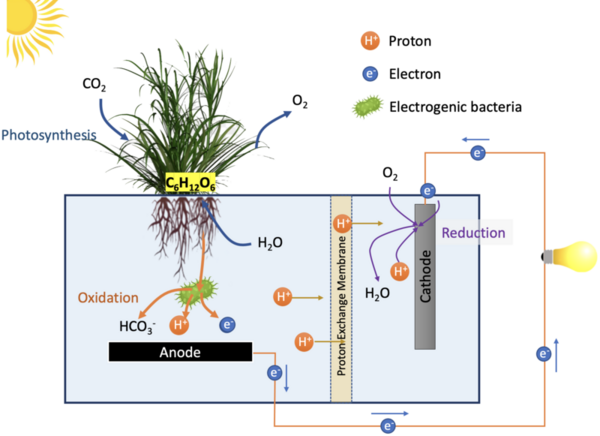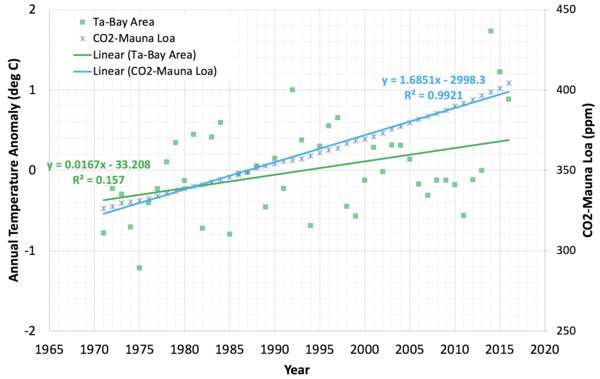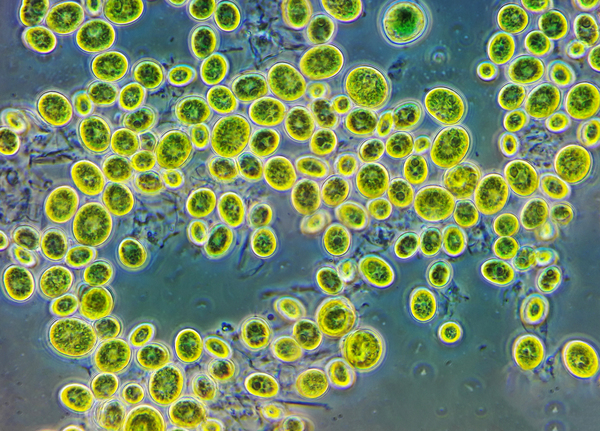
Chlorella sp. are unicellular green algae that use photosynthesis to reduce carbon dioxide into glucose. In this study, authors sought to determine the temperature that Chlorella sp. is maximally efficient at photosynthesis, and therefore removing the most carbon dioxide from the system. This activity could be harnessed to naturally remove carbon dioxide from the environment, fighting the effects of climate change.
Read More...