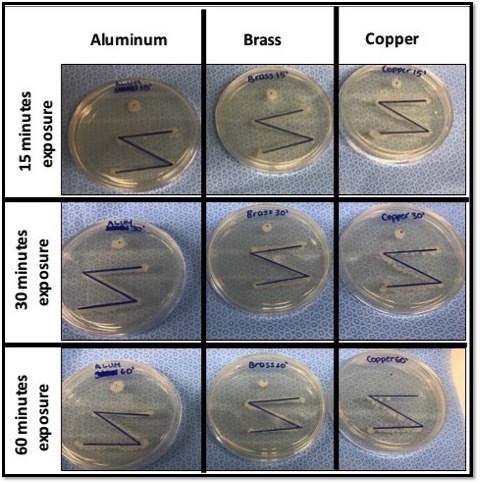
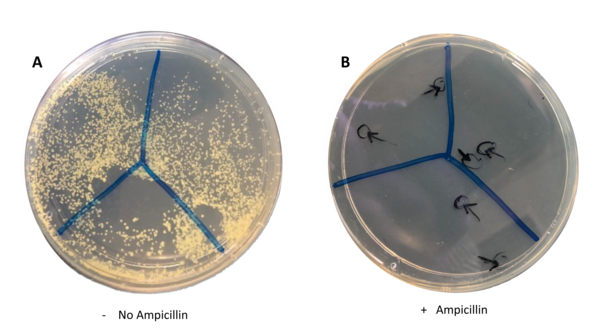
In South Asian countries, the major cause of oral cancer is reported to be chewing paan, which is comprised of betel leaf daubed with slaked lime paste and areca nut. To investigate how paan may contribute to the onset of cancer, the authors treated two immortalized cell lines with extracts of betel leaf, areca nut, and lime and evaluated how these treatments affected cell proliferation and cell death. Initial results indicate that while betel leaf alone may inhibit cell growth, areca nut promoted cancer cell survival and proliferation, even when co-treated with betel leaf. These data suggest that areca nut could exacerbate the progression of oral cancer in humans.
Read More...

.jpg)