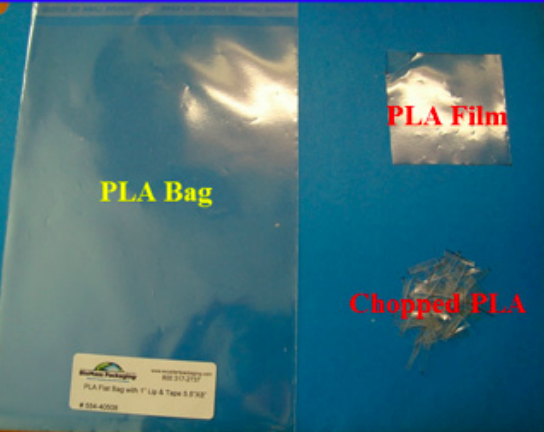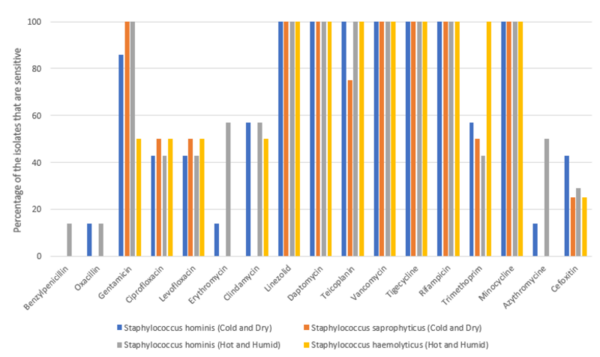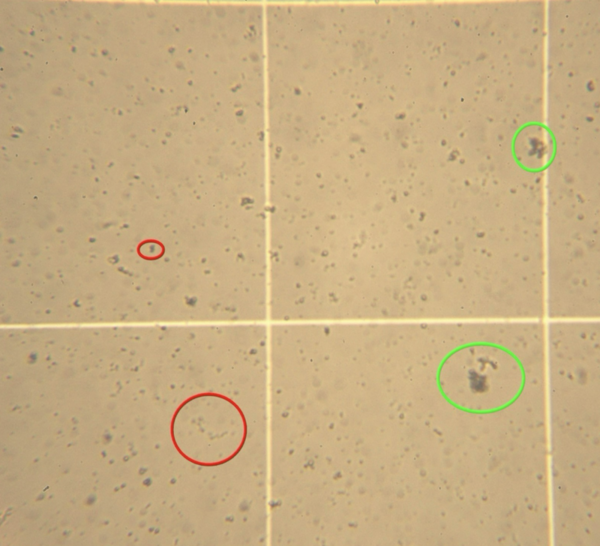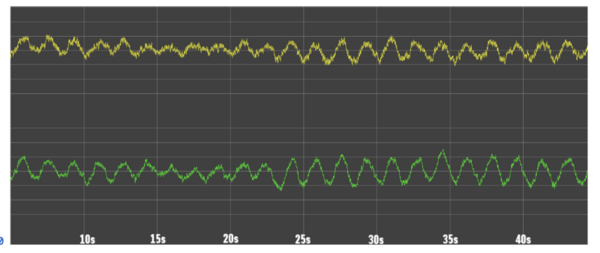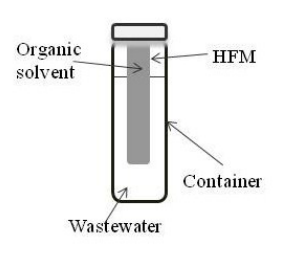
The water we use must be treated and cleaned before we release it back into the environment. Here, the authors investigate two new techniques for purifying dissolved impurities from waste water. Their findings may give rise to more cheaper and more efficient water treatment and help keep the planet greener.
Read More...