The authors investigate how improper disposal of medication can be mitigated through community education efforts.
Read More...Survey of medication disposal: Patient views and awareness

The authors investigate how improper disposal of medication can be mitigated through community education efforts.
Read More...Behavioral Longevity: The Impact of Smoking, Alcohol Consumption, and Obesity on Life Expectancy
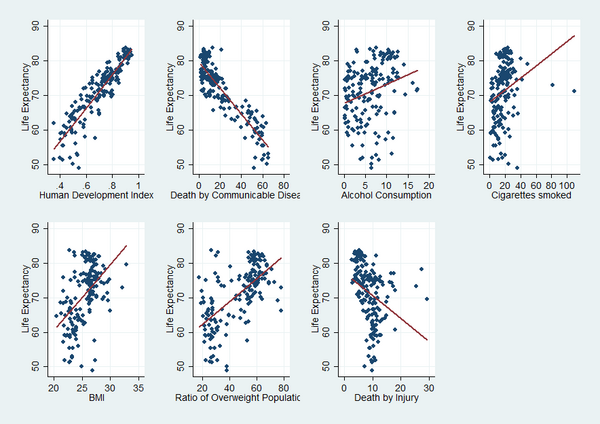
In this article, the authors look into what is already known about the factor affecting longevity and determine the importance of behavioral factors including alcohol consumption, smoking, and obesity on longevity. The authors quantify data from over 150 countries and, interestingly, find that the impact each factor has on longevity is at least in part dependent on the country's economic development status. Overall, they conclude that an average person’s life expectancy can increase by more than 3 years if smoking and alcohol consumption is reduced by a half and weight is decreased by 10%.
Read More...Lung cancer AI-based diagnosis through multi-modal integration of clinical and imaging data
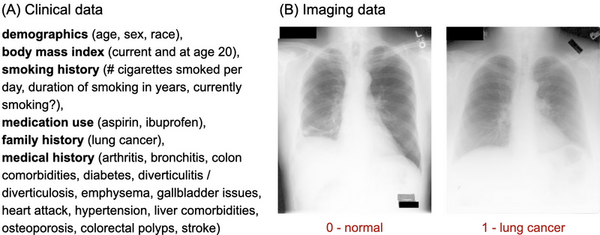
Lung cancer is highly fatal, largely due to late diagnoses, but early detection can greatly improve survival. This study developed three models to enhance early diagnosis: an MLP for clinical data, a CNN for imaging data, and a hybrid model combining both.
Read More...The effect of youth marijuana use on high-risk drug use: Examining gateway and substitution hypothesis
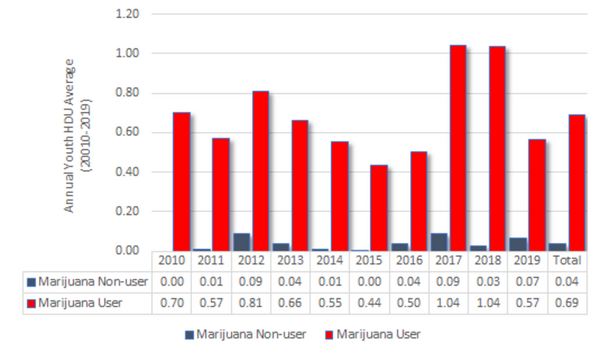
The authors looked at whether youth use of marijuana related to later high-risk drug use. Using survey data from 2010-2019 they found that youth marijuana use did correlate to an increased risk of high-risk drug use.
Read More...Increasing CO2 levels in water decrease the hatching success of brine shrimp

As atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) levels rise, ocean acidification poses a growing threat to marine ecosystems. To better understand these changes, this study investigates how varying CO2 levels influence the growth of brine shrimp. The findings offer important insights into the resilience of aquatic life and the broader implications of environmental change.
Read More...How planarians are affected by mouthwash and cough syrup

Since cough syrup and mouthwash are commonly used items and often end up flushed down the drain or toilet, they can eventually find their way into into freshwater waterways which can be harmful to many marine organisms, such as planarians (aquatic flatworms). To investigate the effects of these substances on planarians, the authors considered different concentrations of Listerine mouthwash and Robitussin syrup along with their active ingredients. By using a behavioral assay, they identified that the active ingredients of cough syrup detrimentally affect planarian behavior. They suggest that these findings could be used to guide disposal methods to lessen detrimental effects on aquatic life.
Read More...From Waste to Wealth: Making Millivolts from Microbes!
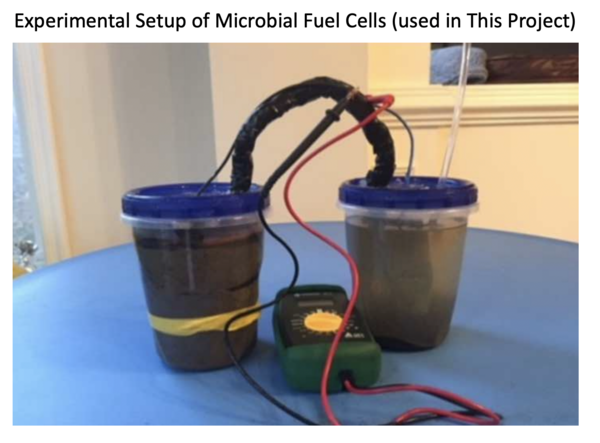

In this study, the authors report their successful efforts to increase voltage production in a Microbial Fuel Cell (MFC), which is a system in which microorganisms produce electricity while performing their normal metabolism.
Read More...How does light affect the distribution of Euglena sp. and Tetrahymena pyriformis

In this article, the authors explored the locomotory movement of Euglena sp. and Tetrahymena pyriformis in response to light. Such research bears relevance to the migration and distribution patterns of both T. pyriformis and Euglena as they differ in their method of finding sustenance in their native environments. With little previous research done on the exploration of a potential response to photostimulation enacted by T. pyriformis, the authors found that T. pyriformis do not bias in distribution towards areas of light - unlike Euglena, which displayed an increased prevalence in areas of light.
Read More...Converting SiO2 wafers to hydrophobic using chlorotrimethylsilane
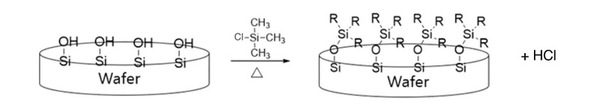
Semiconductors are the center of the fourth industrial revolution as they are key components for all electronics. Exposed wafers made of silicon (Si), which can easily oxidize, convert to silicon dioxide (SiO2). The surface of SiO2 wafers consists of many Si-OH bonds, allowing them to easily bond with water, resulting in a “wet” or hydrophilic condition. We sought to determine a way to modify the surface of SiO2 wafers to become hydrophobic to ensure safe wet cleaning.
Read More...An in vitro comparative analysis of the growth factors present in FBS vs PLAY®

Here the authors performed a comparative analysis to investigate the viability of using PLAY® instead of fetal bovine serum (FBS) as a growth medium to culture cells with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Read More...