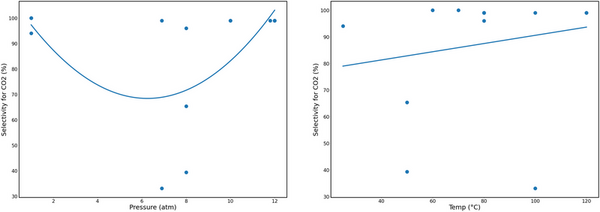
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are promising new nanomaterials for use in the fight against climate change that can efficiently capture and convert CO2 to other useful carbon products. This research used computational models to determine the reaction conditions under which MOFs can more efficiently capture and convert CO2. In a cost-efficient manner, this analysis tested the hypothesis that pressure and temperature affect the efficacy of carbon capture and conversion, and contribute to understanding the optimal conditions for MOF performance to improve the use of MOFs for controlling greenhouse CO2 emissions.
Read More...
.jpg)