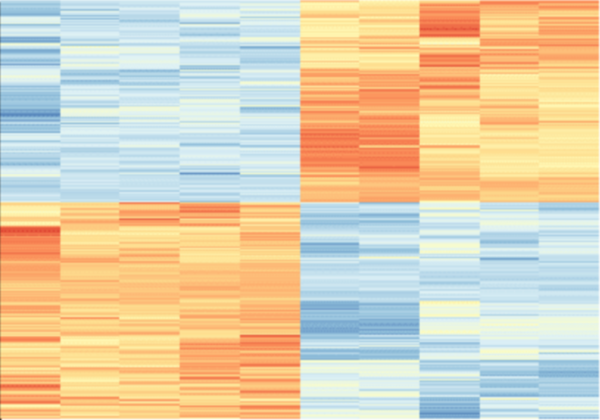
The authors compare RNA expression profiles across three human cell types following infection with MERS-CoV
Read More...Differential MERS-CoV response in different cell types

The authors compare RNA expression profiles across three human cell types following infection with MERS-CoV
Read More...Manipulation of extracellular matrix mechanical cues to stimulate oligodendrocytes to promote remyelination
Oligodendrocytes are specialized brain cells that can change to cells that produce myelin and protect nerves. This study investigates the capacity for different extracellular matrix cues to induce this effect in culture.
Read More...Analysis of complement system gene expression and outcome across the subtypes of glioma
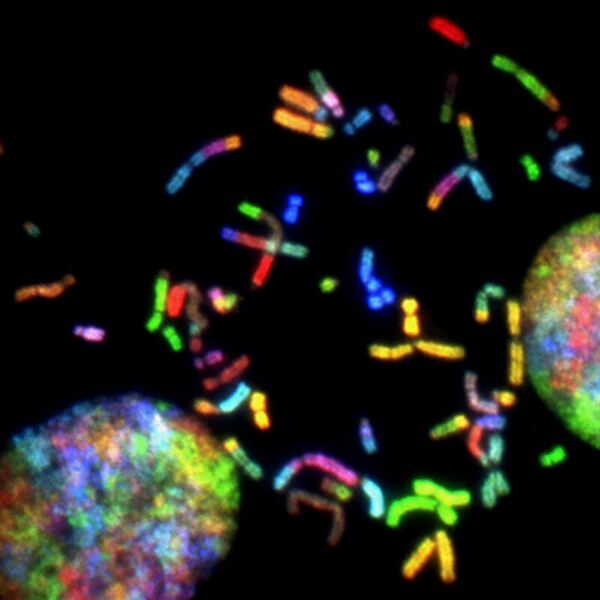
Here the authors sought to better understand glioma, cancer that occurs in the glial cells of the brain with gene expression profile analysis. They considered the expression of complement system genes across the transcriptional and IDH-mutational subtypes of low-grade glioma and glioblastoma. Based on their results of their differential gene expression analysis, they found that outcomes vary across different glioma subtypes, with evidence suggesting that categorization of the transcriptional subtypes could help inform treatment by providing an expectation for treatment responses.
Read More...The Effects of Antioxidants on the Climbing Abilities of Drosophila melanogaster Exposed to Dental Resin
Dental resins can be a source of reactive oxygen species (ROS) which in unruly amounts can be toxic to cellular and overall health. In this report, the authors test whether the consumption of antioxidant rich foods like avocado and asparagus can protect against the effect of dental resin-derived ROS. However, rather than testing humans, they use fruit flies and their climbing abilities as an experimental readout.
Read More...The analysis of the viral transmission and structural interactions between the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein and the lymphocyte receptor integrin α4β7
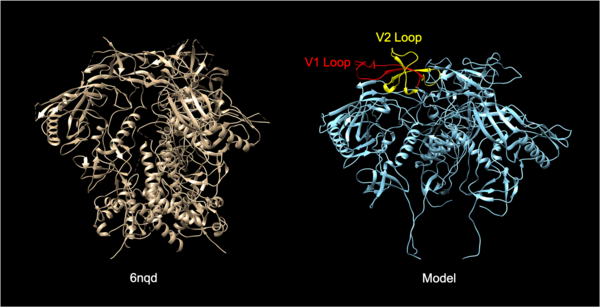
The Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) infects approximately 40 million people globally, and one million people die every year from Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS)-related illnesses. This study examined the interactions between the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein gp120 and the human lymphocyte receptor integrin α4β7, the putative first long-range receptor for the envelope glycoprotein of the virus in mucosal tissues. Presented data support the claim that the V1 loop is involved in the binding between α4β7 and the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein through molecular dockings.
Read More...Investigating Lymphocytic Involvement in Minimal Change Nephrotic Syndrome
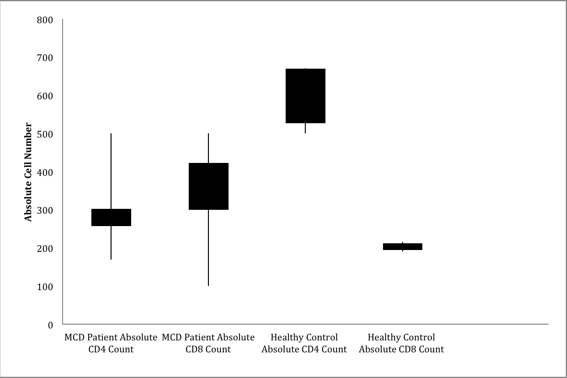
Minimal Change Disease (MCD) is a degenerative kidney disease. Researchers know very little about the cause of this disorder, however some research has suggested that T lymphocytes may be involved. In this study, the authors measure CD4 and CD8 T cell subpopulations in patients with MCD to investigate whether irregular T lymphocyte populations may be involved in MCD pathogenesis.
Read More...Reactivity-informed design, synthesis, and Michael addition kinetics of C-ring andrographolide analogs
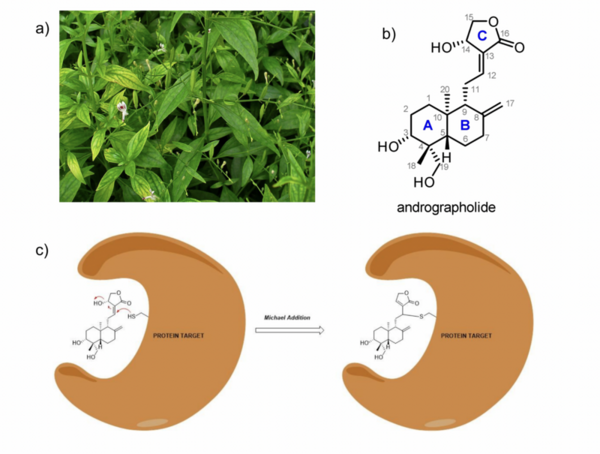
Here, based on the identification of androgapholide as a potential therapeutic treatment against cancer, Alzheimer's disease, diabetes, and multiple sclerosis, due to its ability to inhibit a signaling pathway in immune system function, the authors sought ways to optimize the natural product human systems by manipulating its chemical structure. Through the semisynthesis of a natural product along with computational studies, the authors developed an understanding of the kinetic mechanisms of andrographolide and semisynthetic analogs in the context of Michael additions.
Read More...Protein kinases in phagocytosis (phagocytotic kinome): A promising biomarker set in cancer therapeutics
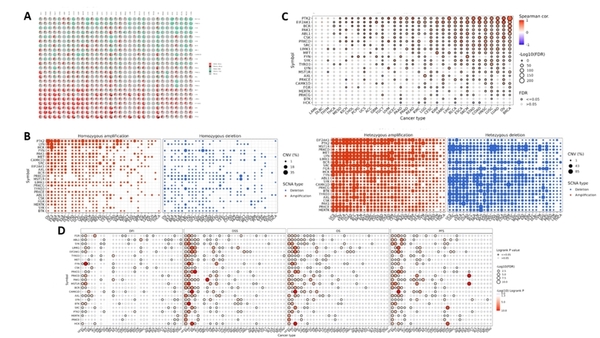
This study analyzes genetic alterations and expression patterns of protein kinases involved in phagocytosis across multiple cancers using TCGA data.
Read More...Design and in silico screening of analogs of rilpivirine as novel non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) for antiretroviral therapy
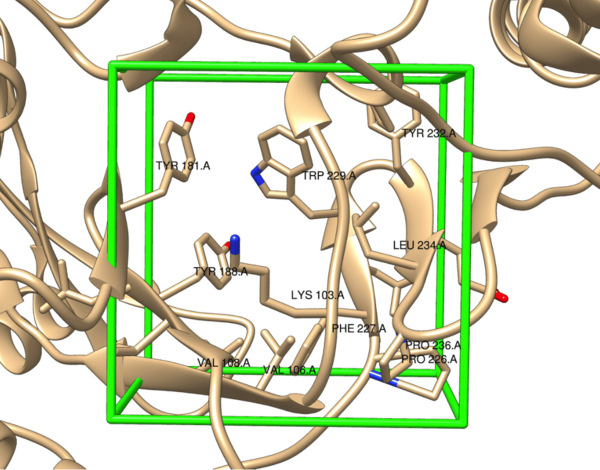
In this study, the authors use high-throughput virtual screening to design and evaluate a set of non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors for binding affinity to the protein reverse transcriptase. These studies have important applications toward HIV therapies.
Read More...Investigating the Role of the Novel ESCRT-III Recruitment Factor CCDC11 in HIV Budding: A Potential Target for Antiviral Therapy
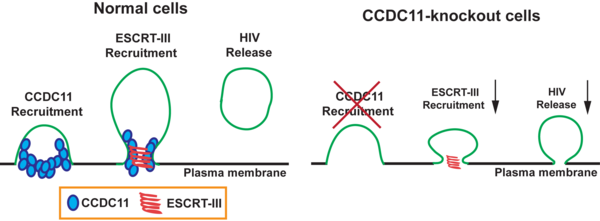
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) is a life-threatening condition caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). In this work, Takemaru et al explored the role of Coiled-Coil Domain-Containing 11 (CCDC11) in HIV-1 budding. Their results suggest that CCDC11 is critical for efficient HIV-1 budding, potentially indicating CCDC11 a viable target for antiviral therapeutics without major side effects.
Read More...