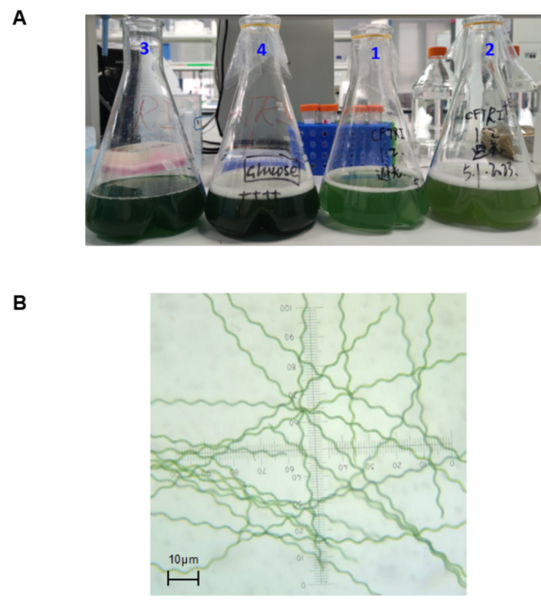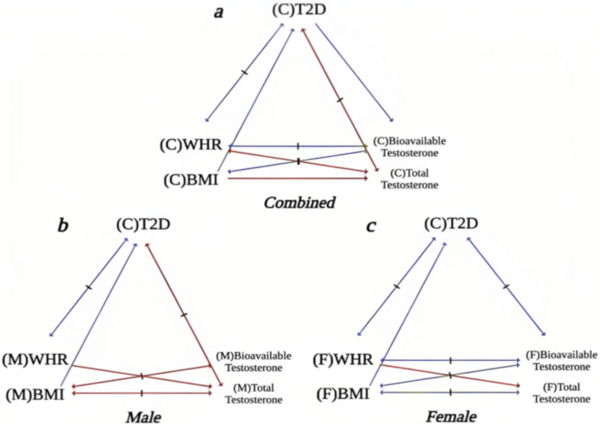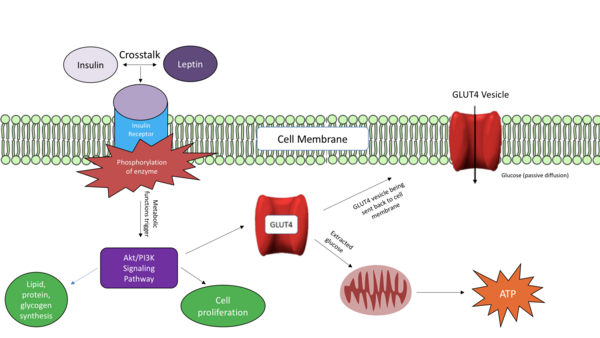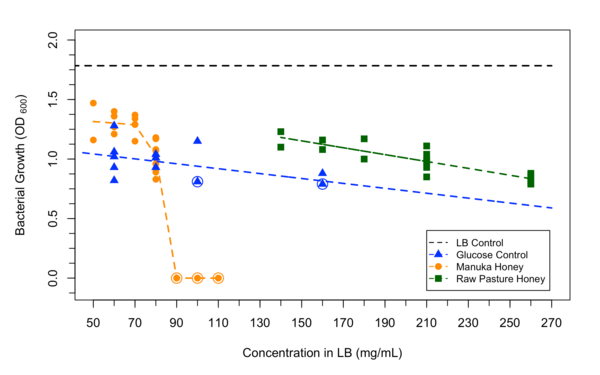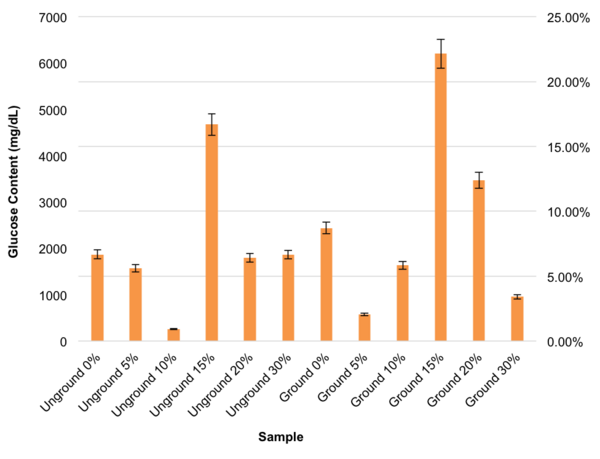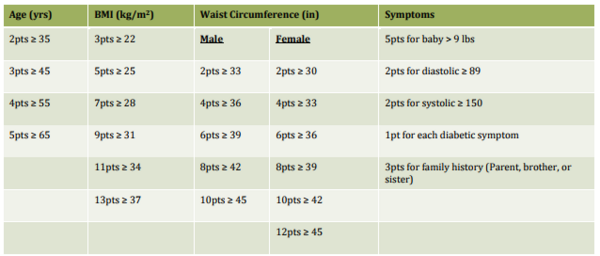
Here the authors sought to investigate whether and how cerebral stroke and other health-related variables are influenced together and amongst each other by using statistical analyses. Their analysis suggested relations between nearly all variables considered, with the strongest association between having heart disease and a cerebral stroke.
Read More...