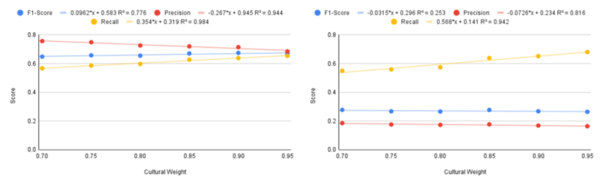
The authors develop a new method for training machine learning algorithms to differentiate between hate speech and cultural speech in online platforms.
Read More...Battling cultural bias within hate speech detection: An experimental correlation analysis

The authors develop a new method for training machine learning algorithms to differentiate between hate speech and cultural speech in online platforms.
Read More...High school students’ perceptions of third-party tracking and personalization
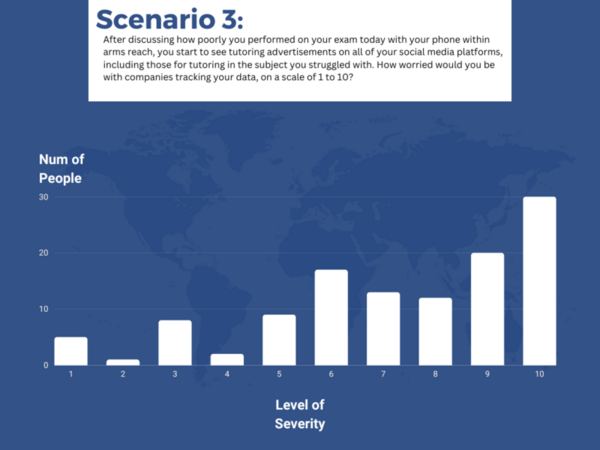
The authors looked at student perception on various situations involving third-party tracking to personalize recommendations.
Read More...Psychosocial impact of home-based learning among students during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Singapore

In this study, the authors surveyed a number of students in Singapore to determine how their experiences changed after the implementation of home-based learning during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Read More...OLED Screens Better Exhibit the Color Black than LCD Screens

There are two types of competing TV screens on the market, organic light emitting diode (OLED) and liquid crystal display (LCD). The better capability to exhibit black results in higher contrast images. Here, authors compared the ability of the two types of screens to show black in an environment eliminating external light.
Read More...Impact of length of audio on music classification with deep learning
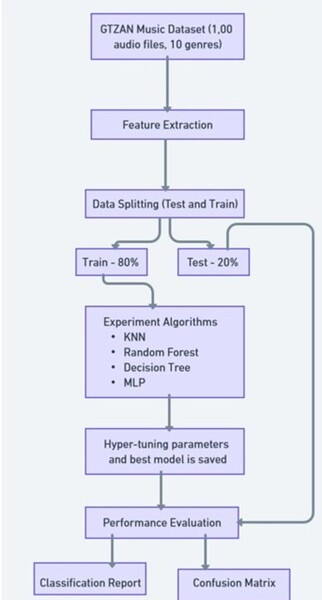
The authors looked at how the length of an audio clip used of a song impacted the ability to properly classify it by musical genre.
Read More...SeniorConnect: A low-cost, app-based real-time alert system to connect seniors with their caregivers
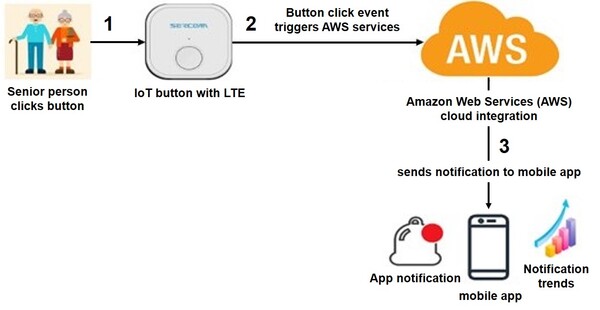
The authors design and test an easy-to-use and cost-effective mobile app-based alert system to help senior citizens rapidly communicate with caregivers in emergencies or when in need of assistance.
Read More...SmartZoo: A Deep Learning Framework for an IoT Platform in Animal Care
Zoos offer educational and scientific advantages but face high maintenance costs and challenges in animal care due to diverse species' habits. Challenges include tracking animals, detecting illnesses, and creating suitable habitats. We developed a deep learning framework called SmartZoo to address these issues and enable efficient animal monitoring, condition alerts, and data aggregation. We discovered that the data generated by our model is closer to real data than random data, and we were able to demonstrate that the model excels at generating data that resembles real-world data.
Read More...Exploring the Wonders of the Early Universe: Green Pea Galaxies and Light Flux

Studying other galaxies can help us understand the origins of the universe. Here, the authors study a type of galaxies known as Green Peas gaining insights that could help inform our understanding of Lyman alpha emitters, one of the first types of galaxies that existed in the early universe.
Read More...Characterizing Quorum Sensing-Induced Bioluminescence in Variable Volumes With Vibrio fischeri Using Computer Processing Methods
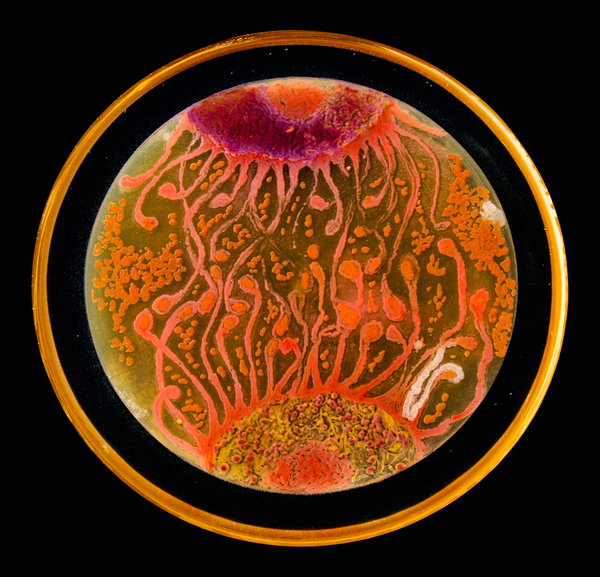
Understanding how bacteria respond to other bacteria could facilitate their ability to initiate and maintain their infectiousness. The phenomenon by which bacteria signal to each other via chemical signals is called quorum sensing, which could be targeted to deter bacterial infection in some cases if better understood. In this article, the authors study how a bacterium called V. fischeri uses quorum sensing to change bioluminescence, an easy readout that facilitates studying quorum sensing in this strain.
Read More...A comparison of use of the mobile electronic health record by medical providers based on clinical setting

The electronic health record (EHR), along with its mobile application, has demonstrated the ability to improve the efficiency and accuracy of health care delivery. This study included data from 874 health care providers over a 12-month period regarding their usage of mobile phone (EPIC® Haiku) and tablet (EPIC® Canto) mEHR. Ambulatory and inpatient care providers had the greatest usage levels over the 12-month period. Awareness of workflow allows for optimization of mEHR design and implementation, which should increase mEHR adoption and usage, leading to better health outcomes for patients.
Read More...