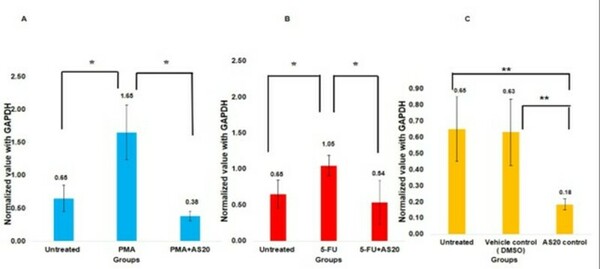
The authors found that treatment with AS20 suppressed phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and 5-flurouracil (5-FU) induction of COX2 expression. We also observed AS20 treated cells showed DNA fragmentation in HeLa cells.
Read More...Apoptosis induction and anti-inflammatory activity of polyherbal drug AS20 on cervical cancer cell lines

The authors found that treatment with AS20 suppressed phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and 5-flurouracil (5-FU) induction of COX2 expression. We also observed AS20 treated cells showed DNA fragmentation in HeLa cells.
Read More...Integrating microbial fuel cell with sedum green roof for stormwater retention and renewable energy generation
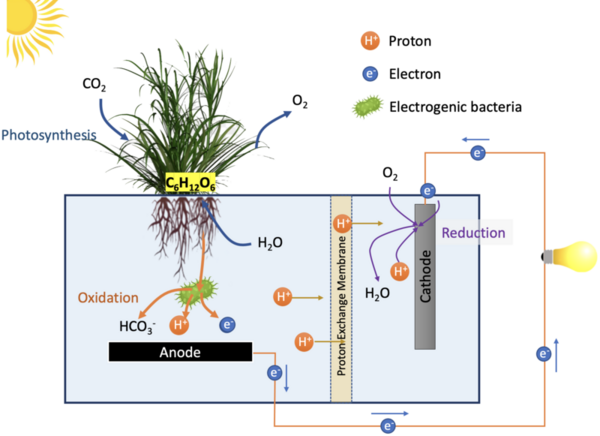
The authors looked at renewable energy generators and the ability to utilize green roofs as a solution to climate change.
Read More...Uncovering mirror neurons’ molecular identity by single cell transcriptomics and microarray analysis
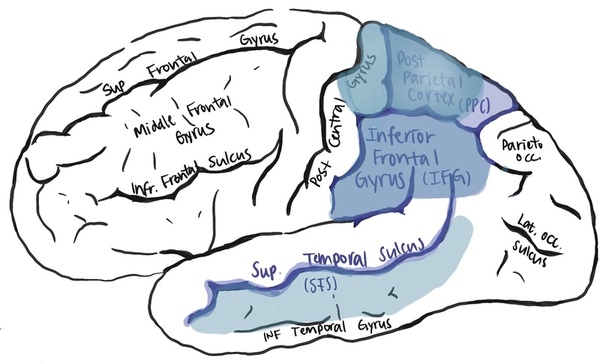
In this study, the authors use bioinformatic approaches to characterize the mirror neurons, which are active when performing and seeing certain actions. They also investigated whether mirror neuron impairment was connected to neural degenerative diseases and psychiatric disorders.
Read More...Protective effect of bromelain and pineapple extracts on UV-induced damage in human skin cells

In this study, the authors tested whether the compound bromelain extracted from pineapples could protect skin cells from UV damage.
Read More...The effects of food type on mediator-less microbial fuel cell electricity output
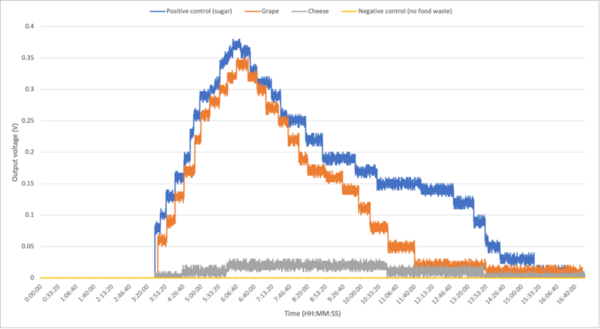
The authors look at how different food types impact the ability of bacteria to produce electricity.
Read More...Combinatorial treatment by siNOTCH and retinoic acid decreases A172 brain cancer cell growth
Treatments inhibiting Notch signaling pathways have been explored by researchers as a new approach for the treatment of glioblastoma tumors, which is a fast-growing and aggressive brain tumor. Recently, retinoic acid (RA) therapy, which inhibits Notch signaling, has shown a promising effect on inhibiting glioblastoma progression. RA, which is a metabolite of vitamin A, is very important in embryonic cellular development, which includes the regulation of multiple developmental processes, such as brain neurogenesis. However, high doses of RA treatment caused many side effects such as headaches, nausea, redness around the injection site, or allergic reactions. Therefore, we hypothesized that a combination treatment of RA and siRNA targeting NOTCH1 (siNOTCH1), the essential gene that activates Notch signaling, would effectively inhibit brain cancer cell proliferation. The aim of the study was to determine whether inhibiting NOTCH1 would inhibit the growth of brain cancer cells by cell viability assay. We found that the combination treatment of siNOTCH1 and RA in low concentration effectively decreased the NOTCH1 expression level compared to the individual treatments. However, the combination treatment condition significantly decreased the number of live brain cancer cells only at a low concentration of RA. We anticipate that this novel combination treatment can provide a solution to the side effects of chemotherapy.
Read More...siRNA-dependent KCNMB2 silencing inhibits lung cancer cell proliferation and promotes cell death
Here, seeking to better understand the genetic associations underlying non-small cell lung cancer, the authors screened hundreds of genes, identifying that KCNMB2 upregulation was significantly correlated with poor prognoses in lung cancer patients. Based on this, they used small interfering RNA to decrease the expression of KCNMB2 in A549 lung cancer cells, finding decreased cell proliferation and increased lung cancer cell death. They suggest this could lead to a new potential target for lung cancer therapies.
Read More...A comparison study in the expansion of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
.png)
In this study, the effects of different sources of serum on growing mesenchymal stem cells are compared with the goal of identifying one more suitable for clinical use.
Read More...Ribosome distribution affects stalling in amino-acid starved cancer cells
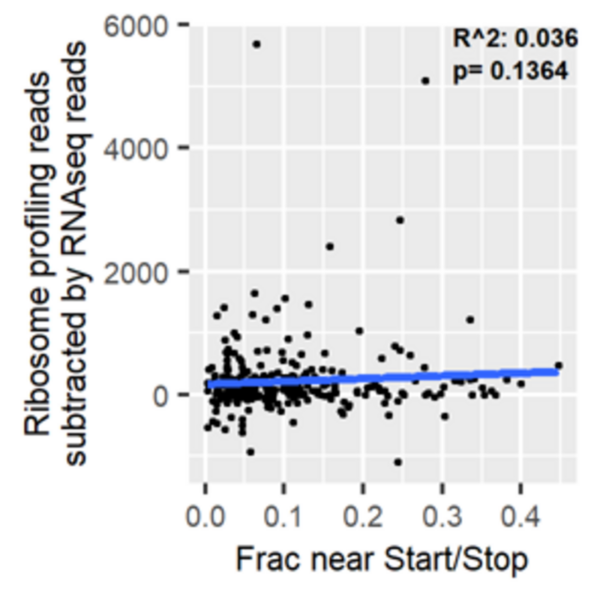
In this article, the authors analyzed ribosome profiling data from amino acid-starved pancreatic cancer cells to explore whether the pattern of ribosome distribution along transcripts under normal conditions can predict the degree of ribosome stalling under stress. The authors found that ribosomes in amino acid-deprived cells stalled more along elongation-limited transcripts. By contrast, they observed no relationship between read density near start and stop and disparities between mRNA sequencing reads and ribosome profiling reads. This research identifies an important relationship between read distribution and propensity for ribosomes to stall, although more work is needed to fully understand the patterns of ribosome distribution along transcripts in ribosome profiling data.
Read More...Discovery of novel targets for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
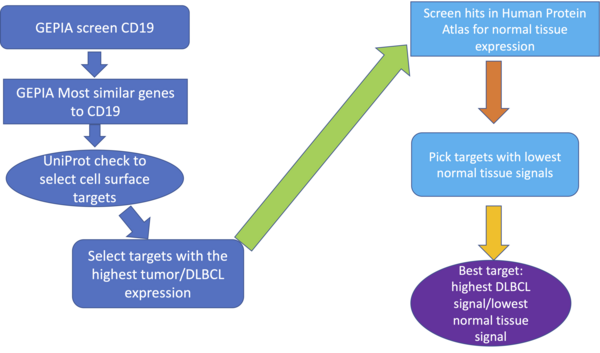
In this study, the authors identify new potential targets to treat advanced diffuse large B-cell lymphoma after treatment relapse and loss of CD19 expression.
Read More...