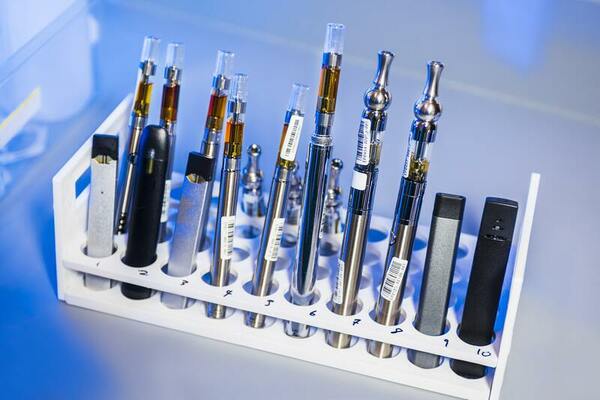
Here, recognizing the significant growth of electronic cigarettes in recent years, the authors sought to test a hypothesis that three main components of the liquid solutions used in e-cigarettes might affect lung cancer cell viability. In a study performed by exposing A549 cells, human lung cancer cells, to different types of smoke extracts, the authors found that increasing levels of nicotine resulted in improve lung cancer cell viability up until the toxicity of nicotine resulted in cell death. They conclude that these results suggest that contrary to conventional thought e-cigarettes may be more dangerous than tobacco cigarettes in certain contexts.
Read More....jpg)