
The authors propose and test a method that would allow for the generation of a magnetic field on Mars sufficient to support future colonization.
Read More...Generation of a magnetic field on Mars

The authors propose and test a method that would allow for the generation of a magnetic field on Mars sufficient to support future colonization.
Read More...Simulation of cosmic rays in the presence of a magnetic field
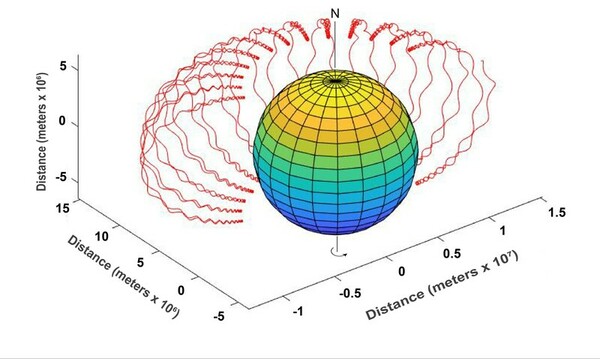
In this study the authors looked the trajectories of cosmic rays moving through a dipole field. They found that the trajectories of cosmic rays are determined by a particle's energy and interaction with Earth's B field.
Read More...Effects of Ocean Acidification on the Photosynthetic Ability of Chaetoceros gracilis in the Monterey Bay

In this article, Harvell and Nicholson hypothesized that increased ocean acidity would decrease the photosynthetic ability of Chaetoceros gracilis, a diatom prolific in Monterey Bay, because of the usually corrosive effects of carbonic acid on both seashells and cells’ internal structures. They altered pH of algae environments and measured the photosynthetic ability of diatoms over four days by spectrophotometer. Overall, their findings indicate that C. gracilis may become more abundant in Monterey Bay as the pH of the ocean continues to drop, potentially contributing to harmful algal blooms.
Read More...Managing CO2 levels through precipitation-based capture from seawater and electrochemical conversion
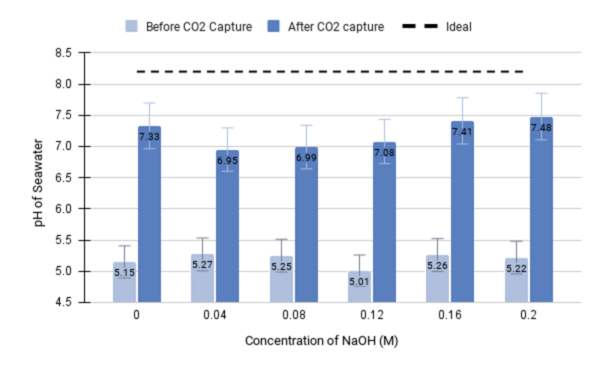
The authors set out to develop an electrochemical device that would have efficient and sustained carbon dioxide capture.
Read More...Methanotrophic bioremediation for the degradation of oceanic methane and chlorinated hydrocarbons

Seeking an approach to address the increasing levels of methane and chlorinated hydrocarbons that threaten the environment, the authors worked to develop a novel, low-cost biotrickling filter for use as an ex situ method tailored to marine environments. By using methanotrophic bacteria in the filter, they observed methane degradation, suggesting the feasibility of chlorinated hydrocarbon degradation.
Read More...The Effects of Atmospheric Attenuation on Cosmic Ray Muons: How is Surface Level Cosmic Ray Muon Flux Affected by Atmospheric Attenuation?
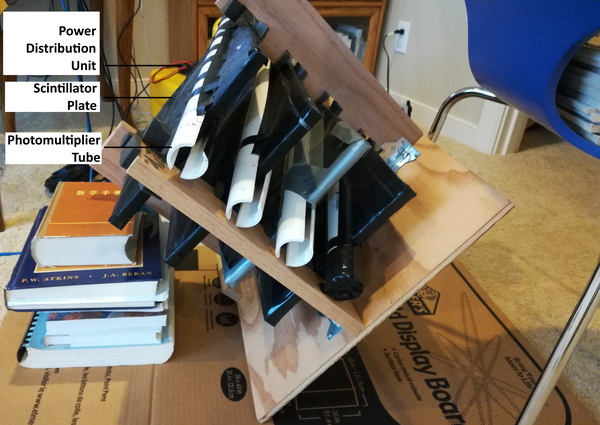

Cosmic rays are high-energy astronomical particles originating from various sources across the universe. Here, The authors sought to understand how surface-level cosmic-ray muon flux is affected by atmospheric attenuation by measuring the variation in relative muon-flux rate relative to zenith angle, testing the hypothesis that muons follow an exponential attenuation model. The attenuation model predicts an attenuation length of 6.3 km. This result implies that only a maximum of 24% of muons can reach the Earth’s surface, due to both decay and atmospheric interactions.
Read More...Low environmental pH inhibits phagosome formation and motility of Tetrahymena pyriformis
.jpg)
In this study, the authors look into some of the implications of rising carbon dioxide levels by studying the effects of acidic pH on the ability of T. pyriformis to feed by quantifying phagosome formation and motility.
Read More...Phytoplankton Plastid Proteomics: Cracking Open Diatoms to Understand Plastid Biochemistry Under Iron Limitation
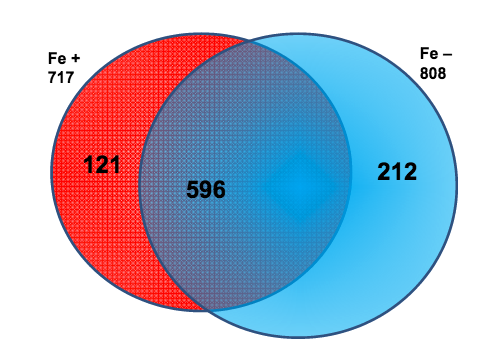
In many areas of the world’s oceans, diatoms such as Thalassiosira pseudonana are limited in growth by the availability of iron (Fe), which is an essential nutrient for diatoms. The authors of this study examined if Fe-limitation makes a significant difference in the proteins expressed within the chloroplast, the power source for diatoms, utilizing a new plastid isolation technique specific to diatoms and completing 14 mass spectrometry experiments.
Read More...Determining the Effect of Chemical and Physical Pretreatments on the Yield and Energy Output of Cellulosic Ethanol from Panicum Virgatum
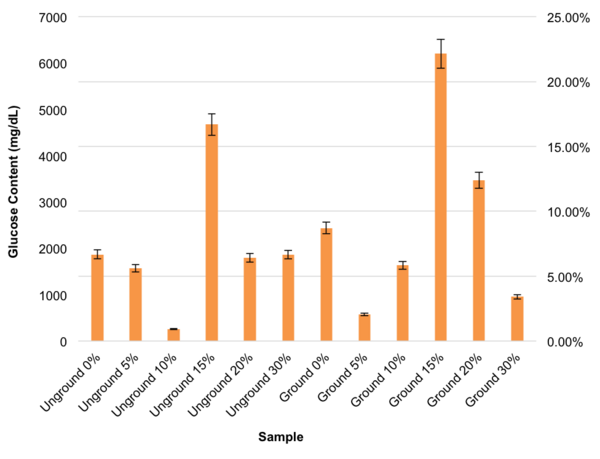
Fossil fuels are a limited resource; thus, it is important to explore new sources of energy. The authors examine the ability of switchgrass to produce ethanol and test the effects of pretreatment and grinding on ethanol yield.
Read More...The Effects of Ocean Acidification on the food location behavior and Locomotion of Pagurus Longicarpus
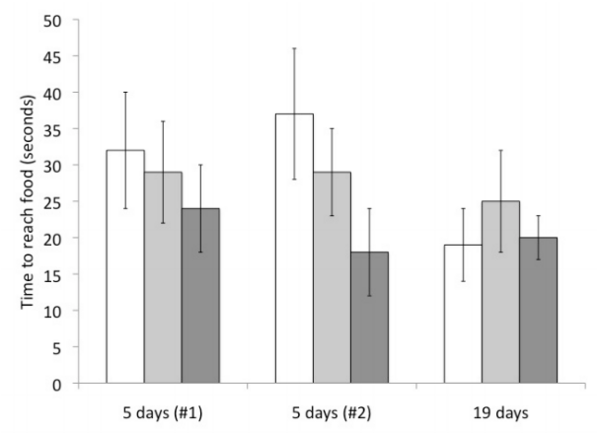
Increasing levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide is slowly acidifying our oceans. Here the authors test the effects of ocean acidification on the ability of hermit crabs (P. longicarpus) to find food. Though no statistically significant changes in food finding were observed, the data suggest a trend toward different activity.
Read More...