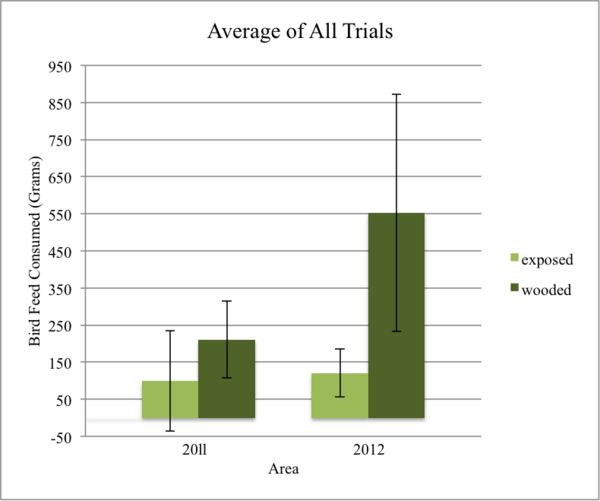
The phenomenon of dying trees and plants in areas affected by acid rain has become increasingly problematic in recent times. Is there any method to efficiently utilize the rainwater and reduce the harmfulness of acid rain or make it beneficial to plants? This study aimed to investigate the potential of neutralizing acid rainwater infiltrating the soil to increase soil pH, produce beneficial salts for plants, and support better plant growth. To test this hypothesis, precipitation samples were collected from six states in the U.S. in 2022, and the pH of the acid rain was measured to obtain a representative pH value for the country. Experiments were then conducted to simulate the neutralization of acid rain and the subsequent change in soil pH levels. To evaluate the effectiveness and feasibility of this method, cat grass was planted in pots of soil soaked with solutions mimicking acid rain, with control and experimental groups receiving neutralizing agents (ammonium hydroxide) or not. Plant growth was measured by analyzing the height of the plants. Results demonstrated that neutralizing agents were effective in improving soil pH levels and that the resulting salts produced were beneficial to the growth of the grass. The findings suggest that this method could be applied on a larger agricultural scale to reduce the harmful effects of acid rain and increase agricultural efficiency.
Read More...