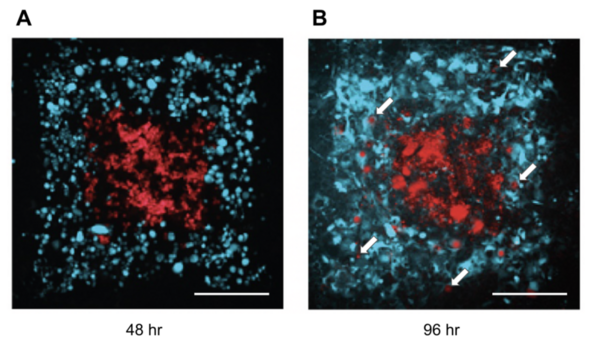
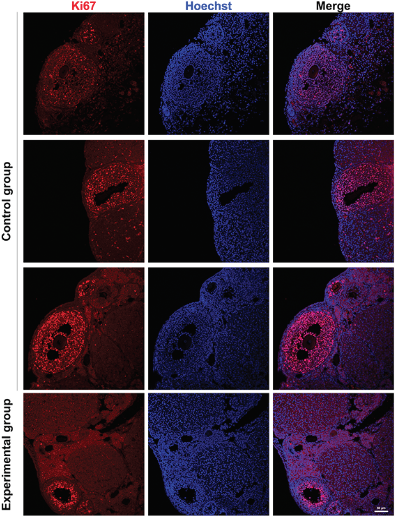
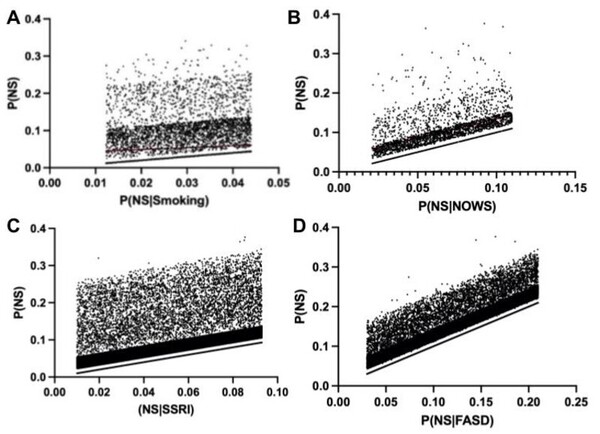
Neural machine translation (NMT) is a software that uses neural network techniques to translate text from one language to another. However, one of the most famous NMT models—Google Translate—failed to give an accurate English translation of a famous Korean nursery rhyme, "Airplane" (비행기). The authors fine-tuned a pre-trained model first with a dataset from the lyrics domain, and then with a smaller dataset containing the rhythmical properties, to teach the model to translate rhythmically accurate lyrics. This stacked fine-tuning method resulted in an NMT model that could maintain the rhythmical characteristics of lyrics during translation while single fine-tuned models failed to do so.
Read More...