The authors looked into eco-friendly alternatives for insulating material. They ultimately found that a polyurethane derived from eggshells was an effective insulator and further research into it is warranted.
Read More...Investigating sustainable insulation materials: Analysis of biofoams and petroleum-derived foams

The authors looked into eco-friendly alternatives for insulating material. They ultimately found that a polyurethane derived from eggshells was an effective insulator and further research into it is warranted.
Read More...Development of novel biodegradable bioplastics for packaging film using mango peels

Here the authors explored the development of biodegradable bioplastic films derived from mango peels as a sustainable solution to plastic pollution and greenhouse gas emissions from fruit waste. They optimized the film's mechanical properties and water resistance through adjusting processing conditions and incorporating plasticizers and a hydrophobic coating, ultimately demonstrating its potential as a bacteriostatic and biodegradable alternative to conventional plastic food wrap.
Read More...Lactic acid bacteria protect the growth of Solanum lycopersicum from Sodium dodecyl sulfate
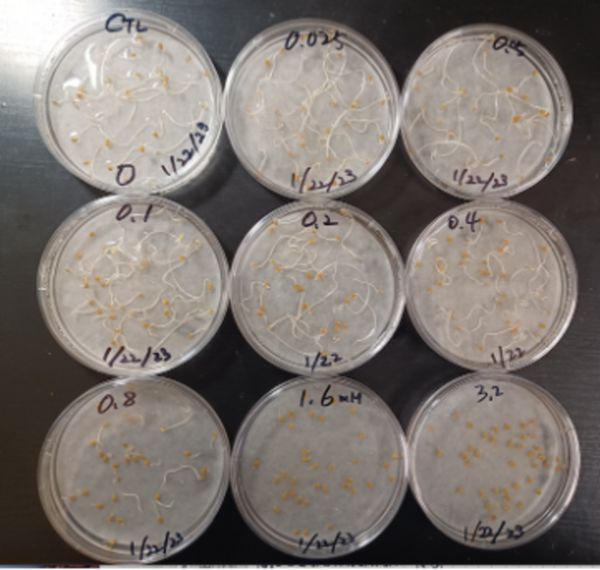
Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), a detergent component, can harm plant growth when it contaminates soil and waterways. Authors explored the potential of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) to mitigate SDS-induced stress on plants.
Read More...Slowing ice melting from thermal radiation using sustainable, eco-friendly eggshells
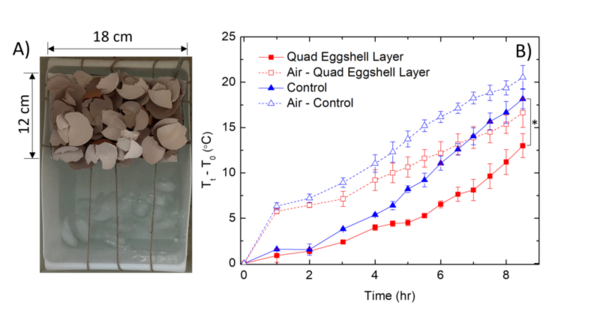
The authors looked at the ability of eggshells to slow ice melting. They found that eggshells were able to increase ice melting time when crushed showing that they were an effective thermal barrier.
Read More...Polluted water tested from the Potomac River affects invasive species plant growth

Here recognizing the potential for pollution to impact the ecosystems of local waterways, the authors investigated the growth of tiger lilies, which are invasive to the Potomac River, in relation to the level of pollution. The authors report that increasing levels of pollution led to increased growth of the invasive species based on their study.
Read More...From trash to treasure: A sustainable approach to oil spill clean-up
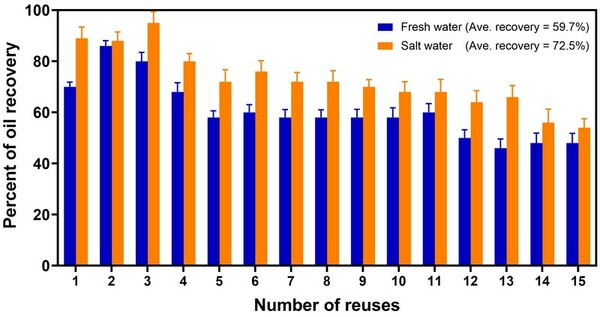
In this study the authors looked at sustainable ways to clean up oil spills that harm marine life. Using water spangle leaves and milk week the authors looked at the ability to recovery oil from both fresh and salt water and the ability to reuse the organic material to clean up spills. Their results show promise to help find a sustainable, eco-friendly way to clean up oil spills and protect marine life and habitats.
Read More...Pressure and temperature influence the efficacy of metal-organic frameworks for carbon capture and conversion
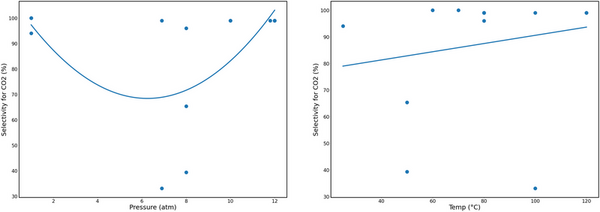
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are promising new nanomaterials for use in the fight against climate change that can efficiently capture and convert CO2 to other useful carbon products. This research used computational models to determine the reaction conditions under which MOFs can more efficiently capture and convert CO2. In a cost-efficient manner, this analysis tested the hypothesis that pressure and temperature affect the efficacy of carbon capture and conversion, and contribute to understanding the optimal conditions for MOF performance to improve the use of MOFs for controlling greenhouse CO2 emissions.
Read More...Efficacy of electrolytic treatment on degrading microplastics in tap water

Here seeking to identify a method to remove harmful microplastics from water, the authors investigated the viability of using electrolysis to degrade microplastics in tap water. Compared to control samples, they found electrolysis treatment to significantly the number of net microplastics, suggesting that this treatment could potentially implemented into homes or drinking water treatment facilities.
Read More...How planarians are affected by mouthwash and cough syrup

Since cough syrup and mouthwash are commonly used items and often end up flushed down the drain or toilet, they can eventually find their way into into freshwater waterways which can be harmful to many marine organisms, such as planarians (aquatic flatworms). To investigate the effects of these substances on planarians, the authors considered different concentrations of Listerine mouthwash and Robitussin syrup along with their active ingredients. By using a behavioral assay, they identified that the active ingredients of cough syrup detrimentally affect planarian behavior. They suggest that these findings could be used to guide disposal methods to lessen detrimental effects on aquatic life.
Read More...Estimating the Carcinogenic Risks of Major Pollutants Released into the Environment
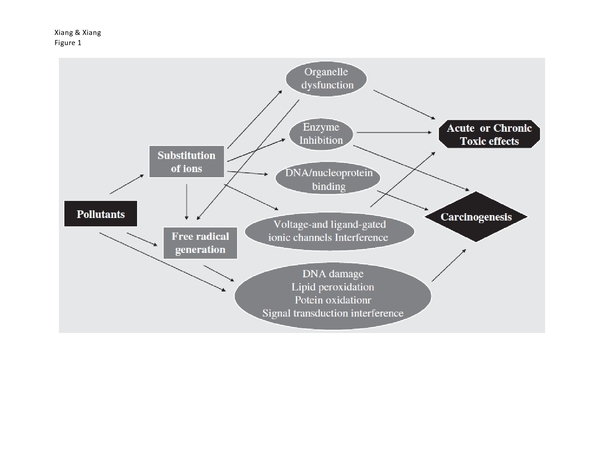
Each year, large amounts of carcinogenic pollutants are released into the environment, which negatively affects human health. This study ranks the major carcinogenic pollutants that are released into the air, water, and land by both the total released amounts and the potential carcinogenic risks.
Read More...