
In this study, the authors test the longevity of a anti-mite compound, amitraz, in commercially-sold strips and the age-dependent efficacy of these strips in preventing honey bee colony collapse by ectoparasitic mite Varroa destructor.
Read More...A chemical and overwintering honey bee apiary field study comparing new and expired amitraz miticide

In this study, the authors test the longevity of a anti-mite compound, amitraz, in commercially-sold strips and the age-dependent efficacy of these strips in preventing honey bee colony collapse by ectoparasitic mite Varroa destructor.
Read More...Photometric analysis and light curve modeling of apparent transient 2020pni
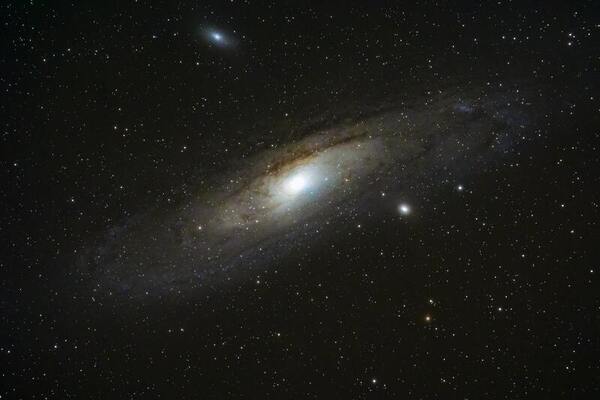

Supernovas are powerful explosions that result from gravitational collapse of a massive star. Using photometric analysis Arora et al. set out to investigate whether 2020pni (located in galaxy UGC 9684) was a supernova. They were ultimately able to identify 2020pni as a Type II-L supernova and determine it's distance from earth.
Read More...Cocktail therapy to inhibit multispecies biofilm in cystic fibrosis patients
Here, recognizing the important role of bacterial biofilms in many life-threatening chronic infections, the authors investigated the effectiveness of a combination treatment on biofilms composed of up to three different common species within the lungs of cystic fibrosis patients with computational analysis. They found that a triple cocktail therapy targeting three different signaling pathways has significant potential as both a treatment and prophylaxis.
Read More...Examining the Growth of Methanotrophic Bacteria Immersed in Extremely Low-Frequency Electromagnetic Fields
Scientist are investigating the use of methane-consuming bacteria to aid the growing problem of rising greenhouse gas emissions. While previous studies claim that low-frequency electromagnetic fields can accelerate the growth rate of these bacteria, Chu et al. demonstrate that this fundamental ideology is not on the same wavelength with their data.
Read More...Herbal formulation, HF1 diminishes tumorigenesis: a cytokine study between MCF-7 and BM-MSCs.

The authors use HF-1, an herbal formation, on bone marrow derived cells as well as breast cancer cells to assess HF-1's ability to prevent tumorigenesis. As metastasis requires coordination of multiple cells in the tumor microenvironment, their findings that HF-1 augments cytokine expression such as VEGF & TGF-B show that HF-1 has potential application to therapeutics.
Read More...Reducing levels of C-Reactive Protein: An eight-week, open-label clinical trial of three oral supplements
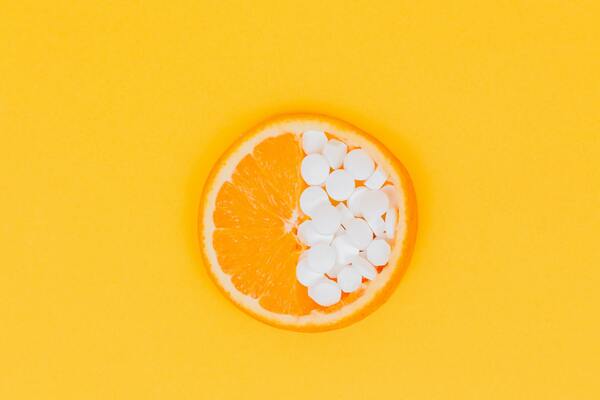

In this study, the effects of vitamin C, ginger, or curcumin supplements on C-reactive protein levels in healthy participants are determined in an eight-week open-label trial.
Read More...Validation of impact-absorbing football helmet facemask for head injury prevention with simulation
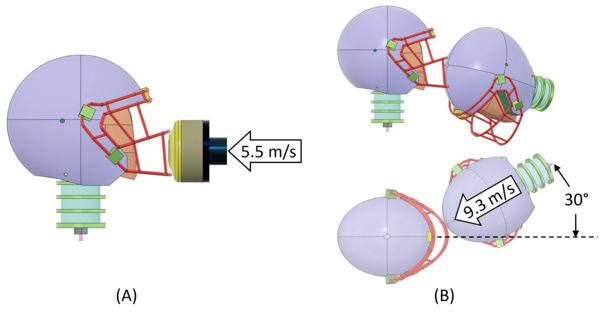
Head injuries are common in American football and the facemasks found on football helmets receive a lot of impact during contacts. This study investigates how effective they are at reducing concussion risk.
Read More...Ladder Fuel Treatments Effect Burn Area of Forest Fires in Semi-Arid High Elevation Climates

In this study, the authors investigate a timely and important topic: forest fires. More specifically, they use a wildfire simulator to test how ladder fuels effect the burn area of a forest fire. Ladder fuels are fuels that cause a forest fire to rise up from the forest floor to the canopy, which may affect the overall spread. They simulated fire spread with different levels of ladder fuel treatment and found that the spread of a burn area would indeed decrease with increased ladder fuel treatment. These findings have important implications for forest and forest fire management.
Read More...Analysis of the effects of positive ions and boundary layer temperature at various hypersonic speeds on boundary layer density
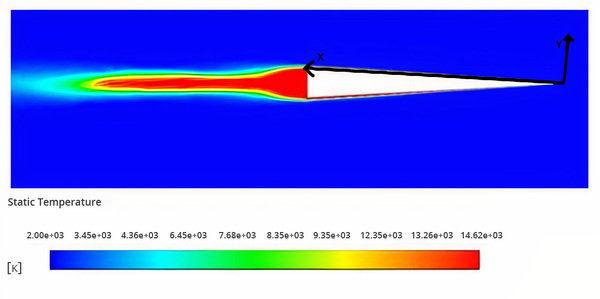
This study's goal was to identify the Mach numbers for which electrostatic drag and heat transfer manipulation would be most applicable inside the stratosphere. The experiments were conducted using computational fluid dynamics software. The study demonstrated that, on average, higher Mach speeds resulted in a considerably higher potential decrease in density. The study highlights that further research on the surface charge method is warranted to explore higher hypersonic speeds within the stratosphere.
Read More...Analysis of reduction potentials to determine the most efficient metals for electrochemical cell alternatives
In this study, the authors investigate what metals make the most efficient electrochemical cells, which are batteries that use the difference in electrical potential to generate electricity. Calculations predicted that a cell made of iron and magnesium would have the highest efficiency. Construction of an electrochemical cell of iron and magnesium produced voltages close to the theoretical voltage predicted. These findings are important as work continues towards making batteries with the highest storage efficiency possible.
Read More...