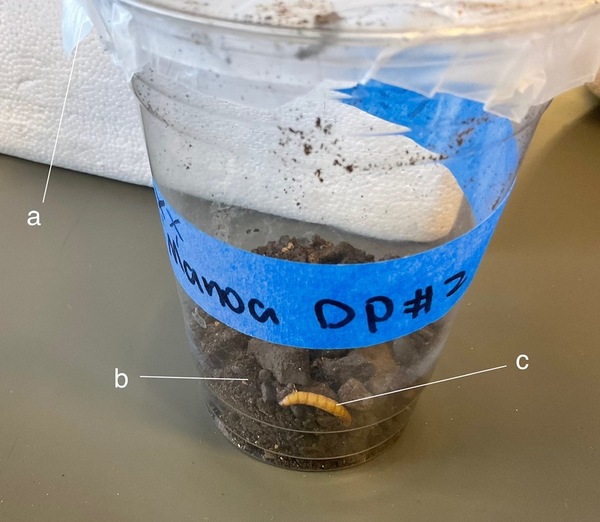
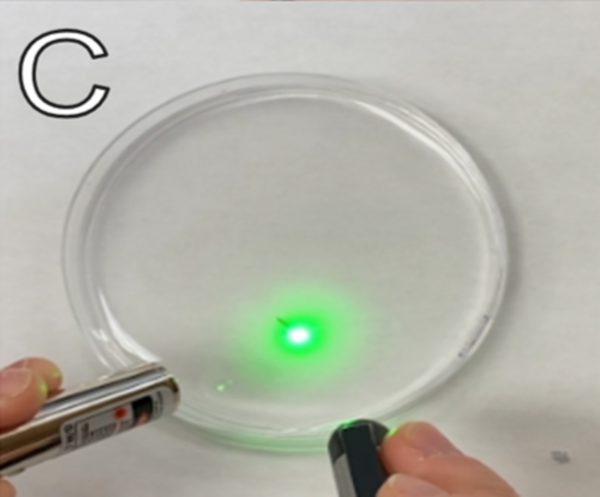
Fungi that attack and kill insects have promise for targeting mosquitoes without the harmful environmental impacts of chemicals like DDT. To find out whether fungi might be effective in controlling mosquitoes in Hawaii, Jiang and Chan test the effects of Hawaiian fungal isolates on mosquito larvae.
Read More...