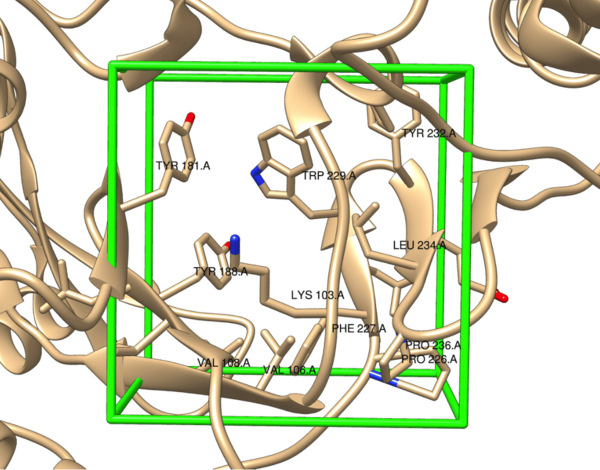
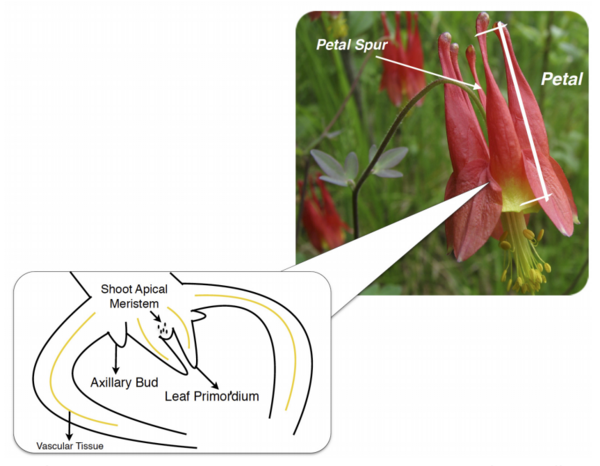
Plants, and all other multi-cellular organisms, develop through the coordinated action of many sets of genes. The authors here investigate the genes, in a class named KNOX, potentially responsible for organizing a certain part of Aquilegia (columbine) flowers called petal spurs. Through the technique Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR), they find that certain KNOX genes are expressed non-uniformly in petal spurs, suggesting that they may be involved, perhaps in a cell-specific manner. This research will help guide future efforts toward understanding how many beautiful flowers develop their unique shapes.
Read More...