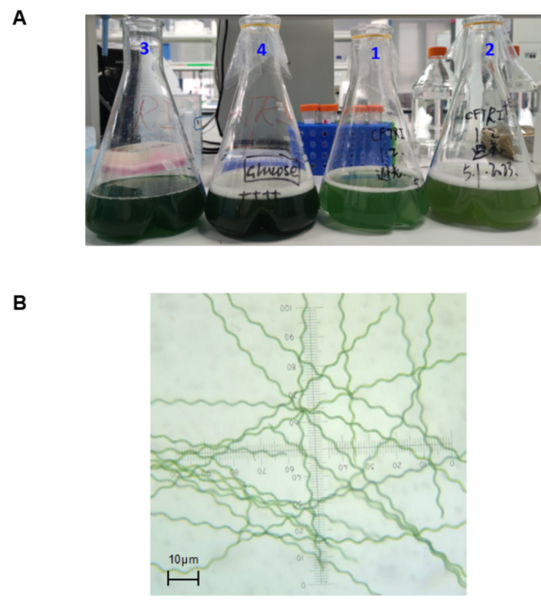
Nosocomial infections acquired in hospitals pose a risk to patients, a risk compounded by resistant microorganisms. To combat this problem, researchers have turned to bioactive compounds from medicinal plants such as the widely used neem. In the present study, researchers sought to determine the effectiveness of different neem preparations against several hospital acquired human pathogens. Neem powder in water successfully inhibited microorganism growth making it a potential agent to combat these infections.
Read More...