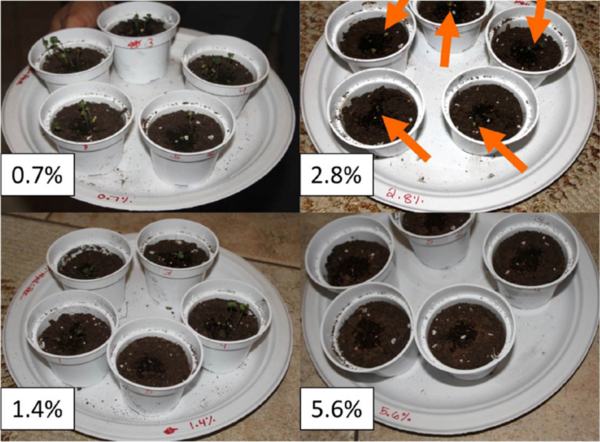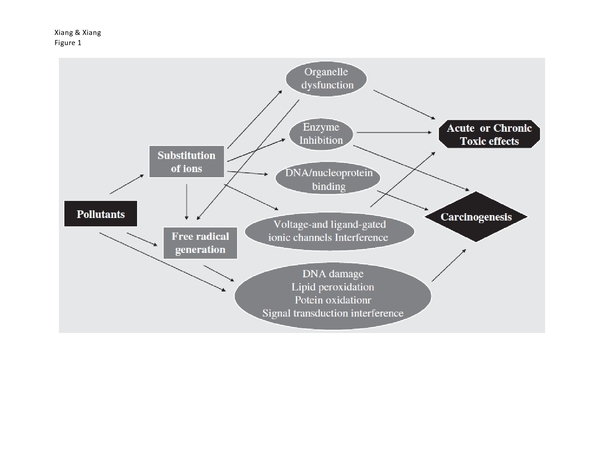
Each year, large amounts of carcinogenic pollutants are released into the environment, which negatively affects human health. This study ranks the major carcinogenic pollutants that are released into the air, water, and land by both the total released amounts and the potential carcinogenic risks.
Read More...