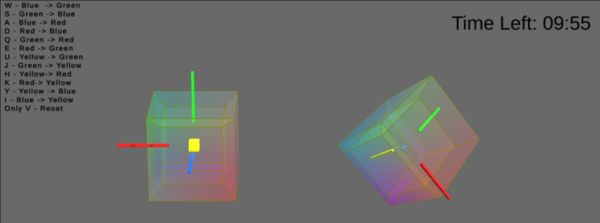
The authors looked at the ability subjects to rotation a 4D cube and how the ability to practice cube rotation impact their ability to understand 4D space.
Read More...Human comprehension of 4-dimensional rotation

The authors looked at the ability subjects to rotation a 4D cube and how the ability to practice cube rotation impact their ability to understand 4D space.
Read More...Spectrophotometric comparison of 4-Nitrophenyl carbonates & carbamates as base-labile protecting groups
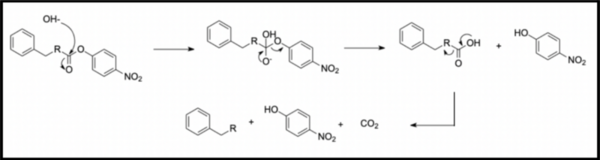
In organic synthesis, protecting groups are derivatives of reactive functionalities that play a key role in ensuring chemoselectivity of chemical transformations. To protect alcohols and amines, acid-labile tert-butyloxycarbonyl protecting groups are often employed but are avoided when the substrate is acid-sensitive. Thus, orthogonal base-labile protecting groups have been in demand to enable selective deprotection and to preserve the reactivity of acid-sensitive substrates. To meet this demand, we present 4-nitrophenyl carbonates and carbamates as orthogonal base-labile protecting group strategies.
Read More...Computational analysis and drug repositioning: Targeting the TDP-43 RRM using FDA-approved drugs
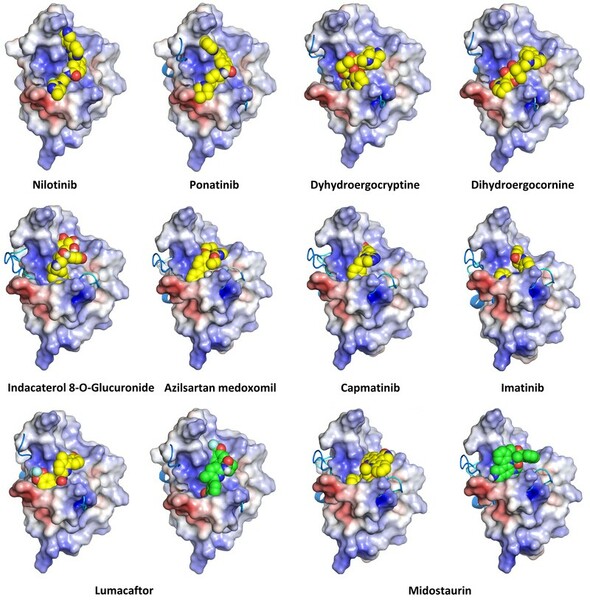
Molecules which bind to proteins that aggregate abnormally in neurodegenerative diseases could be promising drugs for these diseases. In this study, Zhang, Wu, Zhang, and Dang simulate the binding behavior of various molecules to screen for candidates which could be promising candidates for drug development.
Read More...The impact of Red 40 artificial food dye on the heart rate of Daphnia magna
.jpg)
In this study, potential physiological effects of Red 40 food dye, found in many different food products, are tested using Daphnia magna, a small freshwater crustacean.
Read More...The relationship between digit ratio and personality: 4D:5D digit ratio, sex, and the trait of conscientiousness

In this study, the authors use quantitative digit ratio measurements and a survey of personality traits to evaluate the potential relationship between sex and levels of conscientiousness.
Read More...Indoor near-field target detection characteristics under radio and radar joint operation at 2.4 GHz ISM band
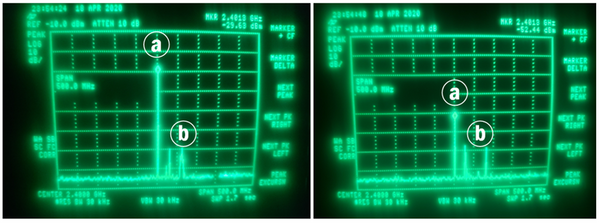
In our modern age, the burgeoning use of radios and radars has resulted in competition for electromagnetic spectrum resources. With recent research highlighting solutions to radio and radar mutual interference, there is a desperate need for a cost-effective configuration that permits a radar-radio joint system. In this study, the authors have set out to determine the feasibility of using single-tone continuous-wave radars in a radar-joint system. With this system, they aim to facilitate cost-effective near-field target detection by way of the popularized 2.4-GHz industrial, scientific, and medical (ISM) band.
Read More...Temperature and Precipitation Responses to a Stratospheric Aerosol Geoengineering Experiment Using the Community Climate System Model 4
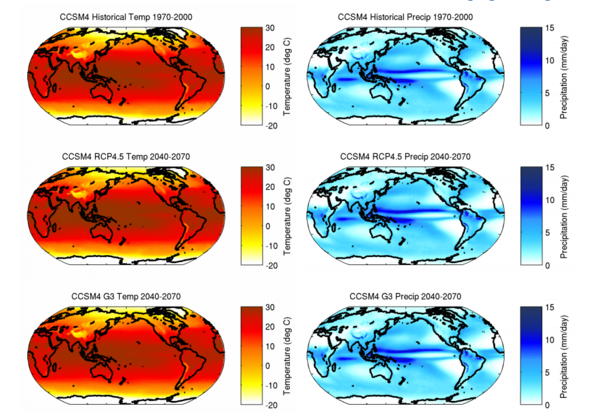
We are changing our environment with steadily increasing carbon dioxide emissions, but we might be able to help. The authors here use a computer program called Community Climate System Model 4 to predict the effects of spraying small particles into the atmosphere to reflect away some of the sun's rays. The software predicts that this could reduce the amount of energy the Earth's atmosphere absorbs and may limit but will not completely counteract our carbon dioxide production.
Read More...Comparative singlet oxygen photosensitizer efficiency of berberine, rose bengal, and methylene blue by time course nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) monitoring of a photochemical 4+2 cycloaddition endoperoxide formation

Berberine, a natural product alkaloid, has been shown to exert biological activity via in situ production of singlet oxygen when photo irradiated. Berberine utilizes singlet oxygen in its putative mechanism of action, wherein it forms an activated complex with DNA and photosensitizes triplet oxygen to singlet oxygen to specifically oxidize guanine residues, thereby halting cell replication and leading to cell death. This has potential application in photodynamic therapy, alongside other such compounds which also act as photosensitizers and produce singlet oxygen in situ. The quantification of singlet oxygen in various photosensitizers, including berberine, is essential for determining their photosensitizer efficiencies. We postulated that the singlet oxygen produced by photoirradiation of berberine would be superior in terms of singlet oxygen production to the aforementioned photosensitizers when irradiated with UV light, but inferior under visible light conditions, due to its strong absorbance of UV wavelengths.
Read More...Luteolin's positive inhibition of melanoma cell lines.

Luteolin (3′,4′,5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone) is a flavonoid that occurs in fruits, vegetables, and herbs. Research suggests that luteolin is effective against various forms of cancer by triggering apoptosis pathways. This experiment analyzes the effects of luteolin on the cell viability of malignant melanoma cells using an in vitro experiment to research alternative melanoma treatments and hopefully to help further cancer research as a whole.
Read More...Creating a drought prediction model using convolutional neural networks
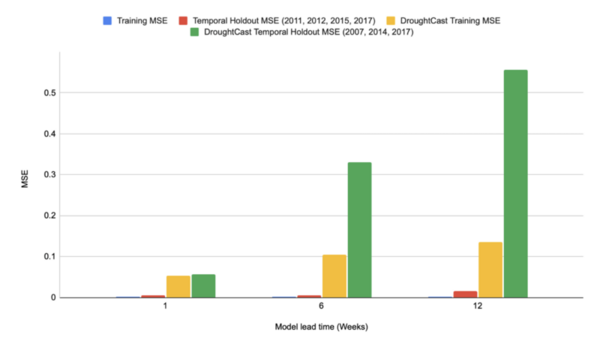
Droughts kill over 45,000 people yearly and affect the livelihoods of 55 million others worldwide, with climate change likely to worsen these effects. However, unlike other natural disasters (hurricanes, etc.), there is no early detection system that can predict droughts far enough in advance to be useful. Bora, Caulkins, and Joycutty tackle this issue by creating a drought prediction model.
Read More...