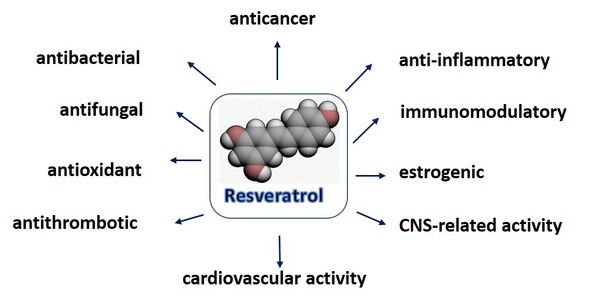
Resveratrol is a type of stillbenoid, a phenolic compound produced in plants, that is known for its anti-inflammatory and anticancer effects. Many oligomers of resveratrol have recently been isolated their bioactivities remain unknown. Here, authors compared the bioactivities of resveratrol with natural dimers (ε-viniferin and gnetin H) and trimers (suffruticosol B and C). Results provide preliminary evidence that resveratrol oligomers could be potential preventive or therapeutic agents for cancers and other immune-related diseases
Read More...





.jpg)
