Evaluating the effectiveness of machine learning models for detecting AI-generated art
(1) Mission San Jose High School, (2) IvyStreet
https://doi.org/10.59720/23-132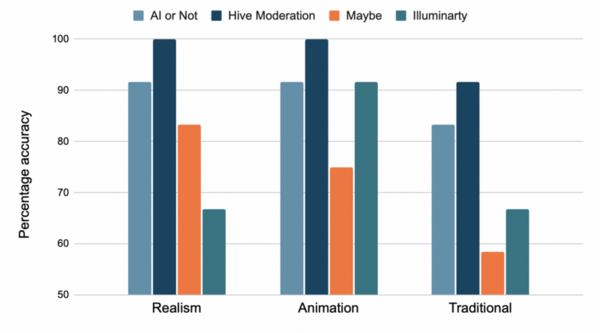
Breakthroughs in technology mean the creation of new programs that can produce results startlingly close to human creations. AI-generated art, for example, has garnered attention and debate by redefining artistic creations, originality, and the ethics of artificial intelligence. By training on existing artwork, these programs can generate images startlingly close to the intended art style and topic and can fool the ordinary person. In this paper, we examine whether the type and style of the input image will impact the accuracy of existing AI-detection machine learning models. The first part of the hypothesis is that the existing models are more accurate in classifying whether an image is AI or human-created if the image is centered around human subjects rather than the environment. The second part of the hypothesis is that the models are more accurate in classifying realistic images compared to images in animation style and traditional mediums. The data show that current models are slightly better at classifying images of the environment, with 84.7% accuracy, compared to images of human characters, with 81.9% accuracy, which doesn’t support the first part of our hypothesis. However, most models have greater success with realism style than with traditional and animation styles, which supports the second part of our hypothesis. These results may serve as suggestions for further improvements in current models. With efficient machine learning models, artists and the general public can discern between AI and human-created art, which may help improve the regulation and usage of AI-generated art.
This article has been tagged with: