.jpg)
In this study, the authors look into some of the implications of rising carbon dioxide levels by studying the effects of acidic pH on the ability of T. pyriformis to feed by quantifying phagosome formation and motility.
Read More...Low environmental pH inhibits phagosome formation and motility of Tetrahymena pyriformis
.jpg)
In this study, the authors look into some of the implications of rising carbon dioxide levels by studying the effects of acidic pH on the ability of T. pyriformis to feed by quantifying phagosome formation and motility.
Read More...Longer Exposure to 2% India Ink Increases Average Number of Vacuoles in Tetrahymena pyriformis
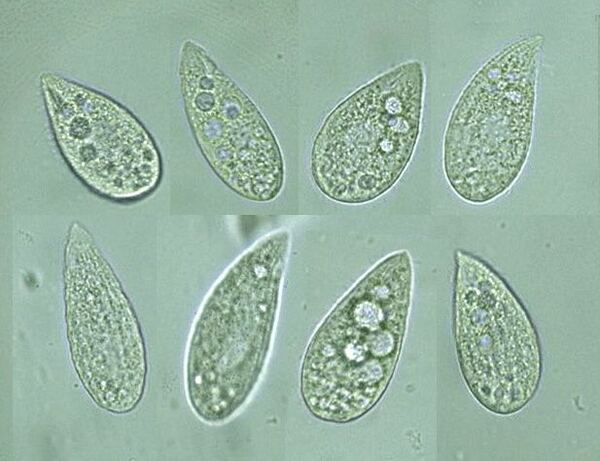
Phagocytes feed by forming food vacuoles. In this article the authors investigate the extent that exposure of non-nutritional food, such as India Ink, to Tetrahymena pyriformis affects the number of vacuole formation. These studies provide insight to how organisms budget their energy and metabolic processes during an energy shortage.
Read More...Cathodal Galvanotaxis: The Effect of Voltage on the distribution of Tetrahymena pyriformis
.png)
The surface of the unicellular eukaryote, Tetrahymena pyriformis, is covered with thousands of hair-like cilia. These cilia are very similar to cilia of the human olfactory and respiratory tracts making them model organisms for studying cilia function and pathology. The authors of this study investigated the effect of voltage on T. pyriformis galvanotaxis, the movement towards an electrical stimulus. They observed galvanotaxis towards the cathode at voltages over 4V which plateau, indicating opening of voltage gated-ion channels to trigger movement.
Read More...Increased carmine red exposure periods yields a higher number of vacuoles formed in Tetrahymena pyriformis
.jpeg)
T. pyriformis can use phagocytosis to create vacuoles of carmine red, a dye which is made using crushed insects and is full of nutrients. Establishing a relationship between vacuole formation and duration of exposure to food can demonstrate how phagocytosis occurs in T. pyriformis. We hypothesized that if T. pyriformis was incubated in a carmine red solution, then more vacuoles would form over time in each cell.
Read More...