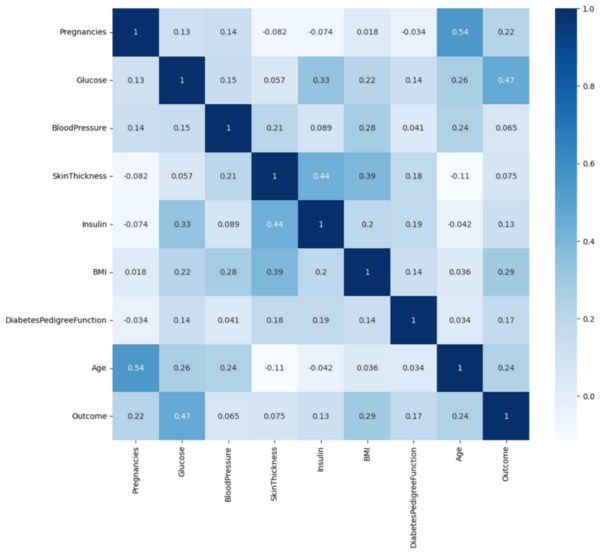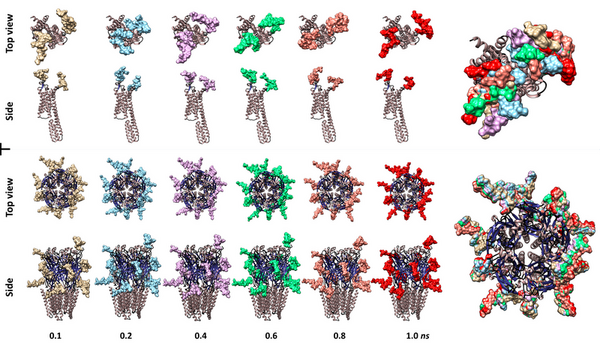
Since the discovery that thousands of different bacteria colonize our gut, many of which are important for human wellbeing, understanding the significance of balancing the different species on the human body has been intensely researched. Untangling the complexity of the gut microbiome and establishing the effect of the various strains on human health is a challenge in many circumstances, and the need for simpler systems to improve our basic understanding of microbe-host interactions seems necessary. C. elegans are a well-established laboratory animal that feed on bacteria and can thus serve as a less complex system for studying microbe-host interactions. Here the authors investigate how the choice of bacterial diet affects worm fertility. The same approach could be applied to many different outcomes, and facilitate our understanding of how the microbes colonizing our guts affect various bodily functions.
Read More...