
This article describes the classification of medical text data using vector databases and text embedding. Various large language models were used to generate this medical data for the classification task.
Read More...Using text embedding models as text classifiers with medical data

This article describes the classification of medical text data using vector databases and text embedding. Various large language models were used to generate this medical data for the classification task.
Read More...Gradient boosting with temporal feature extraction for modeling keystroke log data
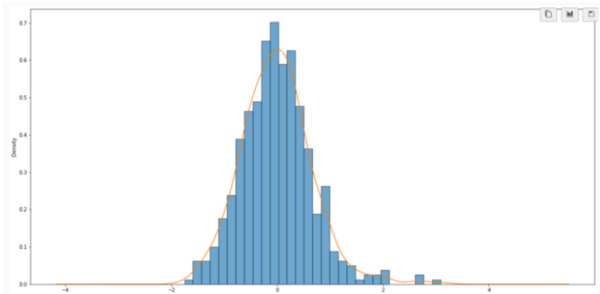
Although there has been great progress in the field of Natural language processing (NLP) over the last few years, particularly with the development of attention-based models, less research has contributed towards modeling keystroke log data. State of the art methods handle textual data directly and while this has produced excellent results, the time complexity and resource usage are quite high for such methods. Additionally, these methods fail to incorporate the actual writing process when assessing text and instead solely focus on the content. Therefore, we proposed a framework for modeling textual data using keystroke-based features. Such methods pay attention to how a document or response was written, rather than the final text that was produced. These features are vastly different from the kind of features extracted from raw text but reveal information that is otherwise hidden. We hypothesized that pairing efficient machine learning techniques with keystroke log information should produce results comparable to transformer techniques, models which pay more or less attention to the different components of a text sequence in a far quicker time. Transformer-based methods dominate the field of NLP currently due to the strong understanding they display of natural language. We showed that models trained on keystroke log data are capable of effectively evaluating the quality of writing and do it in a significantly shorter amount of time compared to traditional methods. This is significant as it provides a necessary fast and cheap alternative to increasingly larger and slower LLMs.
Read More...Exploring the effects of diverse historical stock price data on the accuracy of stock price prediction models
Algorithmic trading has been increasingly used by Americans. In this work, we tested whether including the opening, closing, and highest prices in three supervised learning models affected their performance. Indeed, we found that including all three prices decreased the error of the prediction significantly.
Read More...Model selection and optimization for poverty prediction on household data from Cambodia

Here the authors sought to use three machine learning models to predict poverty levels in Cambodia based on available household data. They found teat multilayer perceptron outperformed the other models, with an accuracy of 87 %. They suggest that data-driven approaches such as these could be used more effectively target and alleviate poverty.
Read More...Analyzing aerosol variation during the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown using satellite data
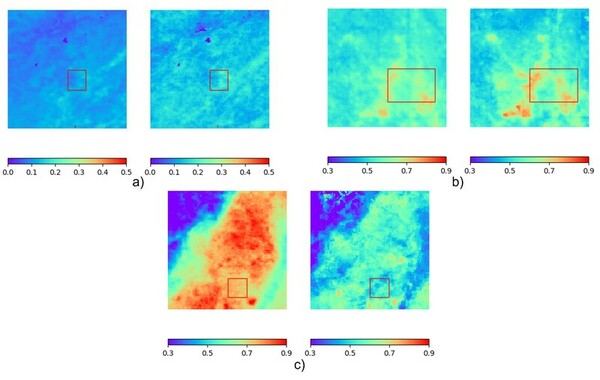
In this study, the authors use aerosol optical depth data to determine if aerosol levels were lower in major metropolitan areas around the world during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Read More...An Investigative Analysis of Climate Change Using Historical and Modern Weather Data
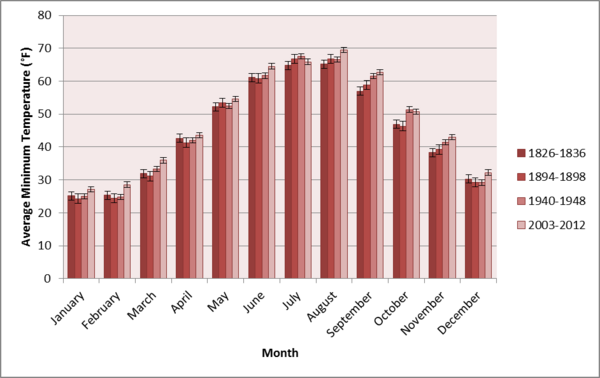
Climate change is an important and contentious issue that has far-reaching implications for our future. The authors here compare primary temperature and precipitation data from almost 200 years ago against the present day. They find that the average annual temperature in Brooklyn, NY has risen significantly over this time, as has the frequency of precipitation, though not the amount of precipitation. These data stress the need for more ecologically-conscious choices in our daily lives.
Read More...Lung cancer AI-based diagnosis through multi-modal integration of clinical and imaging data
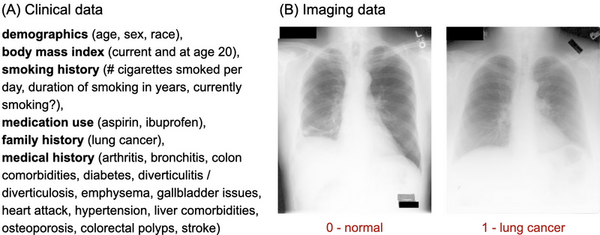
Lung cancer is highly fatal, largely due to late diagnoses, but early detection can greatly improve survival. This study developed three models to enhance early diagnosis: an MLP for clinical data, a CNN for imaging data, and a hybrid model combining both.
Read More...The characterization of quorum sensing trajectories of Vibrio fischeri using longitudinal data analytics
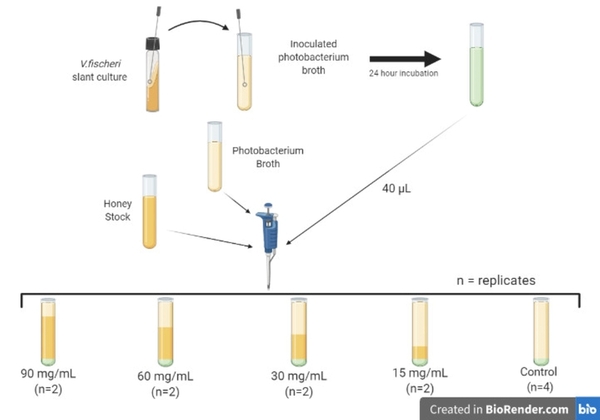
Quorum sensing (QS) is the process in which bacteria recognize and respond to the surrounding cell density, and it can be inhibited by certain antimicrobial substances. This study showed that illumination intensity data is insufficient for evaluating QS activity without proper statistical modeling. It concluded that modeling illumination intensity through time provides a more accurate evaluation of QS activity than conventional cross-sectional analysis.
Read More...Who is at Risk for a Spinal Fracture? – A Comparative Study of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data
One common age-related health problem is the loss of bone mineral density (BMD), which can lead to a variety of negative health outcomes, including increased risk of spinal fracture. In this study, the authors investigate risk factors that may be predictive of an individual's risk of spinal fracture. Their findings provide valuable information that clinicians can use in patient evaluations.
Read More...Correlation between shutdowns and CO levels across the United States.
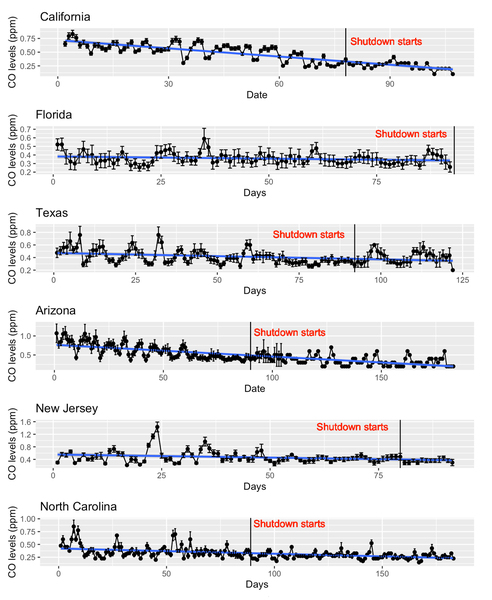
Concerns regarding the rapid spread of Sars-CoV2 in early 2020 led company and local governmental officials in many states to ask people to work from home and avoid leaving their homes; measures commonly referred to as shutdowns. Here, the authors investigate how shutdowns affected carbon monoxide (CO) levels in 15 US states using publicly available data. Their results suggest that CO levels decreased as a result of these measures over the course of 2020, a trend which started to reverse after shutdowns ended.
Read More...