
The authors survey adults to assess how childhood adversity may impact adult relationships and ways of giving or receiving affection.
Read More...Impacts of childhood adversity on relationships: Expressions of affection and social connection

The authors survey adults to assess how childhood adversity may impact adult relationships and ways of giving or receiving affection.
Read More...Specialized chicken toys are effective in relieving stagnant egg production for stressed layer hens

The authors looked at egg laying rates in chickens at two different small farms. They found when the chickens were provided homemade, colorful toys in their environment that their egg production rates increased.
Read More...Do self-expression values affect global jazz popularity? An analysis of postmaterialism and political activity
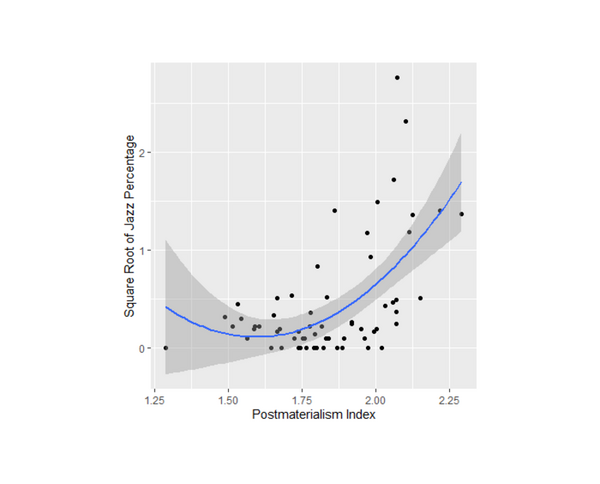
Jazz music is a unique American art form that has spread around the world. Iyer and Iyer study this spread through a computational sociology project examining how jazz popularity is correlated with postmaterialism (an ideology that values self-expression) and political activity.
Read More...Using Artificial Intelligence to Forecast Continuous Glucose Monitor(CGM) readings for Type One Diabetes
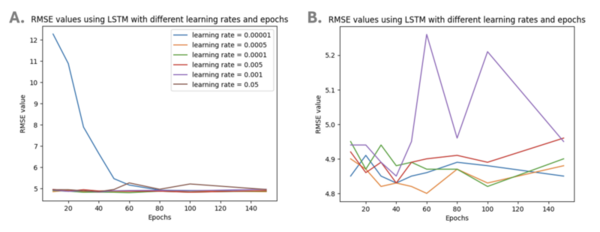
People with Type One diabetes often rely on Continuous Blood Glucose Monitors (CGMs) to track their blood glucose and manage their condition. Researchers are now working to help people with Type One diabetes more easily monitor their health by developing models that will future blood glucose levels based on CGM readings. Jalla and Ghanta tackle this issue by exploring the use of AI models to forecast blood glucose levels with CGM data.
Read More...Association between nonpharmacological interventions and dementia: A retrospective cohort study

Here, the authors investigated the role of nonpharmacological interventions in preventing or delaying cognitive impairment in individuals with and without dementia. By using a retrospective case-control study of 22 participants across two senior centers in San Diego, they found no significant differences in self-reported activities. However, they found that their results reflected activity rather than the activity itself, suggesting the need for an alternative type of study.
Read More...Studying habitability of the exoplanents Kepler-504 b, Kepler-315 b, and Kepler-315 c

The authors explore how similar exoplanets are to Earth and whether they could be inhabited by humans and other living organisms.
Read More...The effects of Helianthus Annuus on Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis using Drosophila Melanogaster
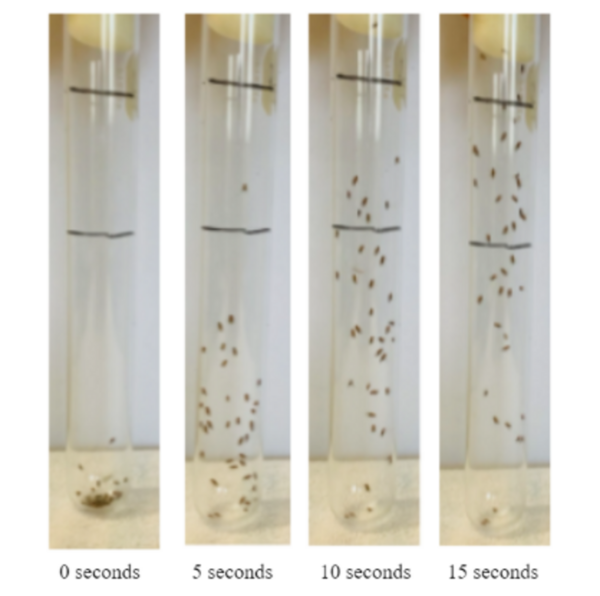

Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) affects nearly 200,000 people worldwide and there is currently no cure. The purpose of the study was to determine if Helianthus annuus seeds helped reduce nerve degeneration and increase locomotion using Drosophila melanogaster as the model organism. Through this experiment, we found a general trend suggesting that H. annuus helped increase the mobility of the D. melanogaster suggesting it could be a viable supplement for patients with ALS.
Read More...Investigating Hydrogen as a Potential Alternative to Kerosene in Fueling Commercial Aircraft
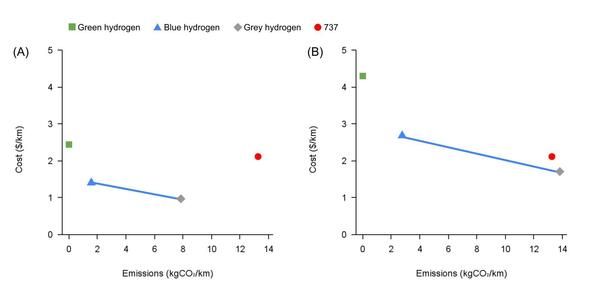
Growing climate concerns have intensified research into zero-emission transportation fuels, notably hydrogen. Hydrogen is considered a clean fuel because its only major by-product is water. This project analyzes how hydrogen compares to kerosene as a commercial aircraft fuel with respect to cost, CO2 emissions, and flight range.
Read More...The effects of different modes of vocalization and food consumption on the level of droplet transmission of bacteria
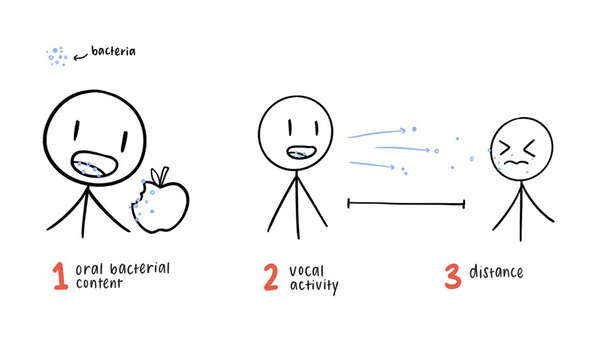
Microbial agents reposnsible for respiratory infections are often carried in spittle, which means they can be easily transmitted. Here, the authors investigate how likely certain activities are to spread microbes carried in spittle. They also investigate whether eating certain types of food might reduce the spread of spittle-borne bacteria too.
Read More...Creating a Phenology Trail Around Central Park Pond
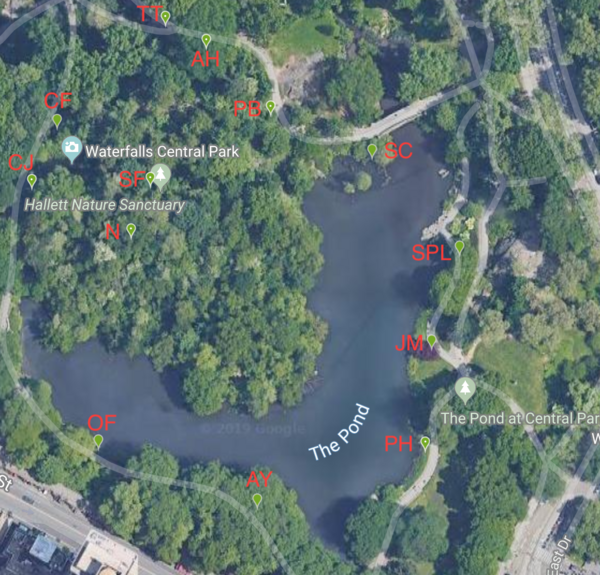
This study aimed to determine whether the life cycle stages, or phenophases, of some plants in the urban environment of Central Park, New York, differ from the typical phenophases of the same plant species. The authors hypothesized that the phenophases of the thirteen plants we studied would differ from their typical phenophases due to the urban heat island effect. Although the phenophases of five plants matched up with typical trends, there were distinct changes in the phenophases of the other eight, possibly resulting from the urban heat island effect.
Read More...