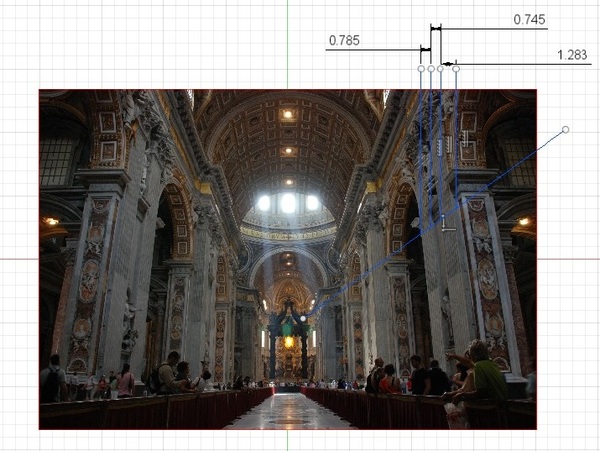

Here the authors investigate whether there are mathematical inaccuracies of perspective in artists' paintings that are undetectable with our naked eyes. Using the cross-ratio method, they find that there are three significant errors in various famous paintings which increase as the structures in the paintings recede from the viewer.
Read More...

.png)