
In this study, the authors use quantitative digit ratio measurements and a survey of personality traits to evaluate the potential relationship between sex and levels of conscientiousness.
Read More...The relationship between digit ratio and personality: 4D:5D digit ratio, sex, and the trait of conscientiousness

In this study, the authors use quantitative digit ratio measurements and a survey of personality traits to evaluate the potential relationship between sex and levels of conscientiousness.
Read More...Comparative screening of dose-dependent and strain-specific antimicrobial efficacy of berberine against a representative library of broad-spectrum antibiotics

We hypothesize that berberine has broad-spectrum antibacterial properties, along with potency that is comparable to current broad-spectrum antibiotics that are commercially available. Here, we screened berberine against four strains of bacteria and evaluated its antimicrobial activity against five broad-spectrum antibiotics from different classes to better quantify berberine’s antibacterial activity and compare its efficacy as an antibacterial agent to the broad-spectrum antibiotics. Our results indicated that berberine had strain-selective cytotoxic effects and was significantly less potent than most of the broad-spectrum antibiotics
Read More...The Effect of UV Treatment on the Degradation of Compostable Polylactic Acid
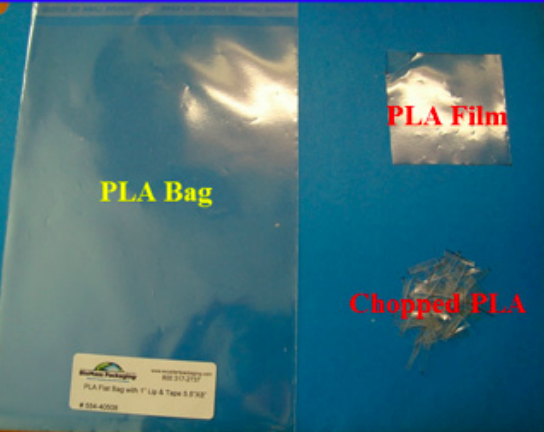

Polylactic acid (PLA) is a bio-based, compostable plastic that is comparable in cost to petroleum-based plastics. This study aims to evaluate the effects of UV treatment and mechanical chopping on the degradation of PLA. Based on their findings, the authors propose an alternative PLA degradation process that may be more time and energy efficient than current processes.
Read More...A meta-analysis on NIST post-quantum cryptographic primitive finalists
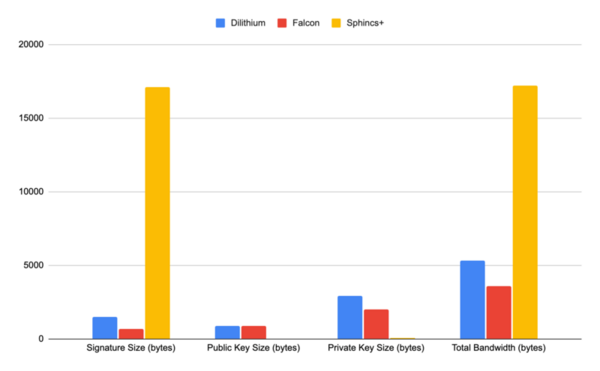
The advent of quantum computing will pose a substantial threat to the security of classical cryptographic methods, which could become vulnerable to quantum-based attacks. In response to this impending challenge, the field of post-quantum cryptography has emerged, aiming to develop algorithms that can withstand the computational power of quantum computers. This study addressed the pressing concern of classical cryptographic methods becoming vulnerable to quantum-based attacks due to the rise of quantum computing. The emergence of post-quantum cryptography has led to the development of new resistant algorithms. Our research focused on four quantum-resistant algorithms endorsed by America’s National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2022: CRYSTALS-Kyber, CRYSTALS-Dilithium, FALCON, and SPHINCS+. This study evaluated the security, performance, and comparative attributes of the four algorithms, considering factors such as key size, encryption/decryption speed, and complexity. Comparative analyses against each other and existing quantum-resistant algorithms provided insights into the strengths and weaknesses of each program. This research explored potential applications and future directions in the realm of quantum-resistant cryptography. Our findings concluded that the NIST algorithms were substantially more effective and efficient compared to classical cryptographic algorithms. Ultimately, this work underscored the need to adapt cryptographic techniques in the face of advancing quantum computing capabilities, offering valuable insights for researchers and practitioners in the field. Implementing NIST-endorsed quantum-resistant algorithms substantially reduced the vulnerability of cryptographic systems to quantum-based attacks compared to classical cryptographic methods.
Read More...Male Feminization of the Common Pillbug Armadillidium vulgare by Wolbachia bacteria
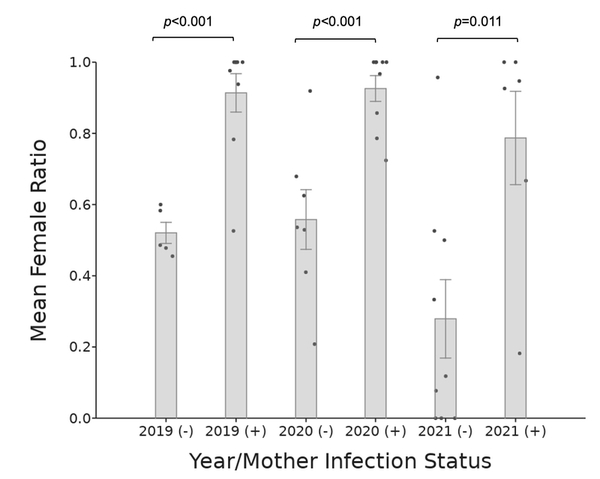
Wolbachia pipientis (Wolbachia) is a maternally inherited endosymbiotic bacterium that infects over 50% of arthropods, including pillbugs, and acts as a reproductive parasite in the host. In the common terrestrial pillbug Armadillidium vulgare (A. vulgare), Wolbachia alters the sex ratio of offspring through a phenomenon called feminization, where genetic males develop into reproductive females. Previous studies have focused on the presence or absence of Wolbachia as a sex ratio distorter in laboratory cultured and natural populations mainly from sites in Europe and Japan. Our three-year study is the first to evaluate the effects of the Wolbachia sex ratio distorter in cultured A. vulgare offspring in North America. We asked whether Wolbachia bacteria feminize A. vulgare isopod male offspring from infected mothers and if this effect can be detected in F1 offspring by comparing the male/female offspring ratios. If so, the F1 offspring ratio should show a higher number of females than males compared to the offspring of uninfected mothers. Over three years, pillbug offspring were cultured from pregnant A. vulgare females and developed into adults. We determined the Wolbachia status of mothers and counted the ratios of male and female F1 progeny to determine feminization effects. In each year sampled, significantly more female offspring were born to Wolbachia-infected mothers than those from uninfected mothers. These ratio differences suggest that the Wolbachia infection status of mothers directly impacts the A. vulgare population through the production of reproductive feminized males, which in turn provides an advantage for further Wolbachia transmission.
Read More...Which fruit peel helps retain the most soil moisture?

Here, the authors investigated the ability to use fruit peels to help soil retain moisture, a property that is essential to agriculture. Across a 96-hour observation period, orange, banana, and kiwi peel water emulsions were evaluated for their effects on soil moisture. They found that orange peels retained the most moisture, but banana and kiwi peels also offered improvements over their control sample.
Read More...Recognition of animal body parts via supervised learning
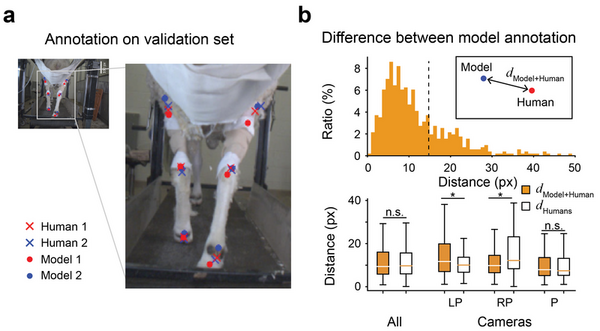
The application of machine learning techniques has facilitated the automatic annotation of behavior in video sequences, offering a promising approach for ethological studies by reducing the manual effort required for annotating each video frame. Nevertheless, before solely relying on machine-generated annotations, it is essential to evaluate the accuracy of these annotations to ensure their reliability and applicability. While it is conventionally accepted that there cannot be a perfect annotation, the degree of error associated with machine-generated annotations should be commensurate with the error between different human annotators. We hypothesized that machine learning supervised with adequate human annotations would be able to accurately predict body parts from video sequences. Here, we conducted a comparative analysis of the quality of annotations generated by humans and machines for the body parts of sheep during treadmill walking. For human annotation, two annotators manually labeled six body parts of sheep in 300 frames. To generate machine annotations, we employed the state-of-the-art pose-estimating library, DeepLabCut, which was trained using the frames annotated by human annotators. As expected, the human annotations demonstrated high consistency between annotators. Notably, the machine learning algorithm also generated accurate predictions, with errors comparable to those between humans. We also observed that abnormal annotations with a high error could be revised by introducing Kalman Filtering, which interpolates the trajectory of body parts over the time series, enhancing robustness. Our results suggest that conventional transfer learning methods can generate behavior annotations as accurate as those made by humans, presenting great potential for further research.
Read More...Do elders care about eHealth? A correlational study between eHealth consumption and literacy
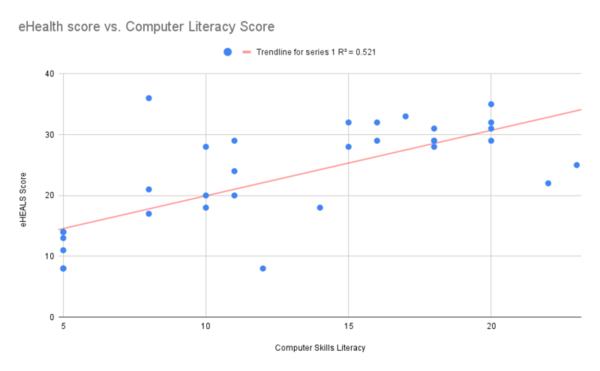
As digital tools become more prevalent in medicine, the ability for individuals to understand and take actions based on what they read on the internet is crucial. eHealth literacy is defined as as the ability to seek, find, understand, and evaluate health information from electronic sources and apply the knowledge gained to addressing or solving a health problem. In general, Americans have low eHealth literacy rates. However, limited research has been conducted to understand the eHealth literacy level among older Chinese adult immigrants in the U.S. To determine the eHealth literacy of elderly Chinese immigrants, we sent out an eHealth survey and relevant computer skills survey using a modified version of the eHEALS (eHealth Literacy Scale) health literacy test. We hypothesized that elders who consumed more electronic health content would have a higher eHealth literacy score. The results of this survey showed that there was a positive correlation between the frequency of electronic health information consumption and the participant's eHealth literacy rate. In addition, the results of our computer literacy test show that the frequency of consumption and computer literacy are positively correlated as well. There is a strong positive correlation between the level of computer skills and eHealth literacy of participants. These results reveal possible steps individuals can take to reduce health misinformation and improve their own health by attaining, understanding, and taking action on health material on the internet.
Read More...Developing anticholinergic drugs for the treatment of asthma with improved efficacy
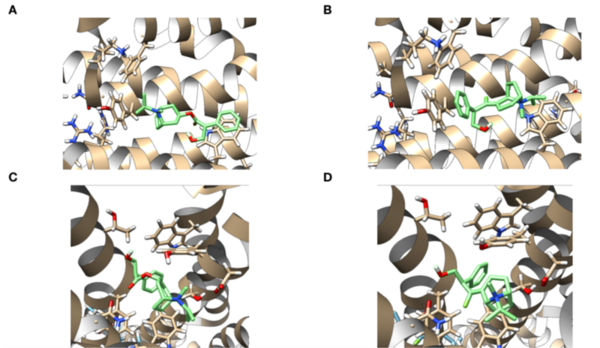
Anticholinergics are used in treating asthma, a chronic inflammation of the airways. These drugs block human M1 and M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, inhibiting bronchoconstriction. However, studies have reported complications of anticholinergic usage, such as exacerbated eosinophil production and worsened urinary retention. Modification of known anticholinergics using bioisosteric replacements to increase efficacy could potentially minimize these complications. The present study focuses on identifying viable analogs of anticholinergics to improve binding energy to the receptors compared to current treatment options. Glycopyrrolate (G), ipratropium (IB), and tiotropium bromide (TB) were chosen as parent drugs of interest, due to the presence of common functional groups within the molecules, specifically esters and alcohols. Docking score analysis via AutoDock Vina was used to evaluate the binding energy between drug analogs and the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. The final results suggest that G-A3, IB-A3, and TB-A1 are the most viable analogs, as binding energy was improved when compared to the parent drug. G-A4, IB-A4, IB-A5, TB-A3, and TB-A4 are also potential candidates, although there were slight regressions in binding energy to both muscarinic receptors for these analogs. By researching the effects of bioisosteric replacements of current anticholinergics, it is evident that there is a potential to provide asthmatics with more effective treatment options.
Read More...Analyzing honey’s ability to inhibit the growth of Rhizopus stolonifer
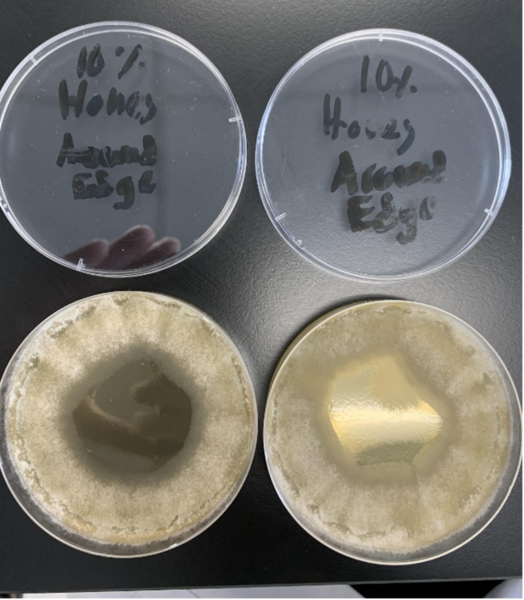

Rhizopus stolonifer is a mold commonly found growing on bread that can cause many negative health effects when consumed. Preservatives are the well-known answer to this problem; however, many preservatives are not naturally found in food, and some have negative health effects of their own. We focused on honey as a possible solution because of its natural origin and self-preservation ability. We hypothesized that honey would decrease the growth rate of R. stolonifer . We evaluated the honey with a zone of inhibition (ZOI) test on agar plates. Sabouraud dextrose agar was mixed with differing volumes of honey to generate concentrations between 10.0% and 30.0%. These plates were then inoculated with a solution of spores collected from the mold. The ZOI was measured to determine antifungal effectiveness. A statistically significant difference was found between the means of all concentrations except for 20.0% and 22.5%. Our findings support the hypothesis as we showed a positive correlation between the honey concentration and growth rate of mold. By using this data, progress could be made on an all-natural, honey-based preservative.
Read More...