
Predicting antibody structures and antibody-antigen complexes using AlphaFold
Read More...Investigating AlphaFold’s handling of nanobody-antigen complex prediction

Predicting antibody structures and antibody-antigen complexes using AlphaFold
Read More...Development of novel biodegradable bioplastics for packaging film using mango peels
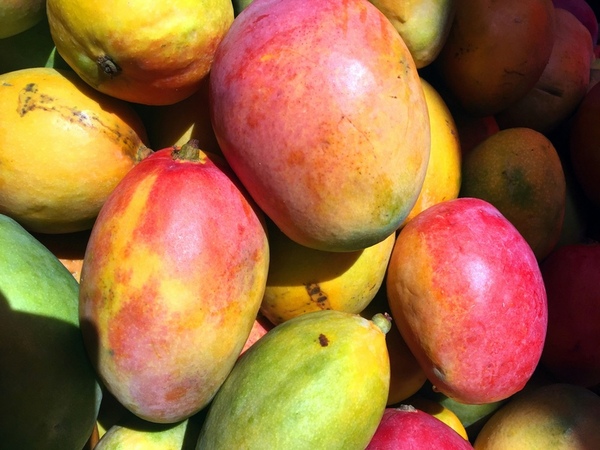

Here the authors explored the development of biodegradable bioplastic films derived from mango peels as a sustainable solution to plastic pollution and greenhouse gas emissions from fruit waste. They optimized the film's mechanical properties and water resistance through adjusting processing conditions and incorporating plasticizers and a hydrophobic coating, ultimately demonstrating its potential as a bacteriostatic and biodegradable alternative to conventional plastic food wrap.
Read More...Assessing the possibility of using entomopathogenic fungi for mosquito control in Hawaii
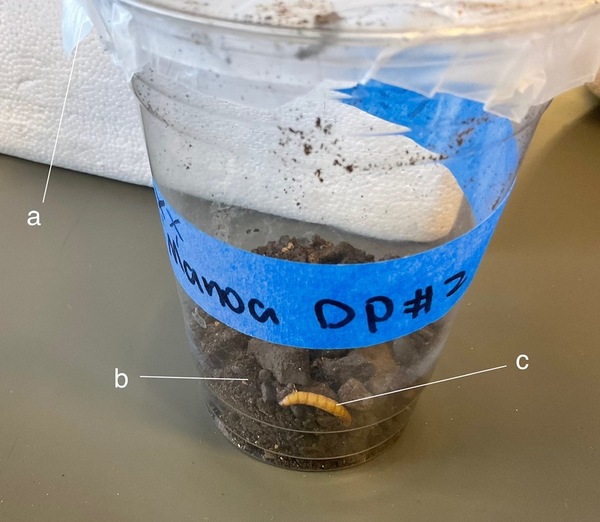

Fungi that attack and kill insects have promise for targeting mosquitoes without the harmful environmental impacts of chemicals like DDT. To find out whether fungi might be effective in controlling mosquitoes in Hawaii, Jiang and Chan test the effects of Hawaiian fungal isolates on mosquito larvae.
Read More...Generation of a magnetic field on Mars
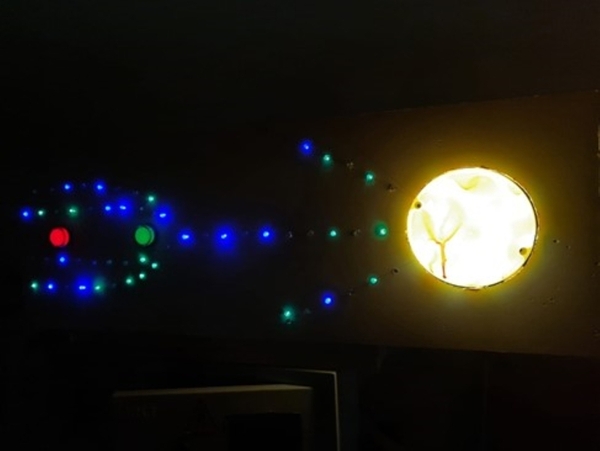

The authors propose and test a method that would allow for the generation of a magnetic field on Mars sufficient to support future colonization.
Read More...SmartZoo: A Deep Learning Framework for an IoT Platform in Animal Care
Zoos offer educational and scientific advantages but face high maintenance costs and challenges in animal care due to diverse species' habits. Challenges include tracking animals, detecting illnesses, and creating suitable habitats. We developed a deep learning framework called SmartZoo to address these issues and enable efficient animal monitoring, condition alerts, and data aggregation. We discovered that the data generated by our model is closer to real data than random data, and we were able to demonstrate that the model excels at generating data that resembles real-world data.
Read More...Investigating cross-cultural emotional responses to world music under simulated hearing loss
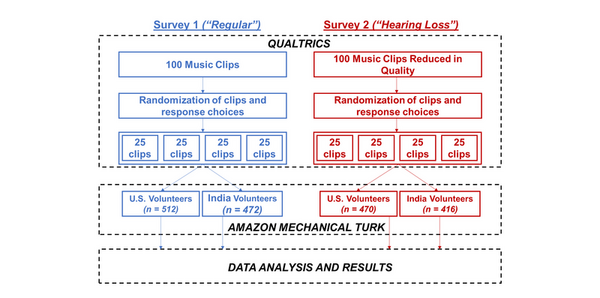
The authors survey how emotional responses to music differ across cultures and the impact of hearing loss on these emotional responses.
Read More...Transcriptomic profiling identifies differential gene expression associated with childhood abuse
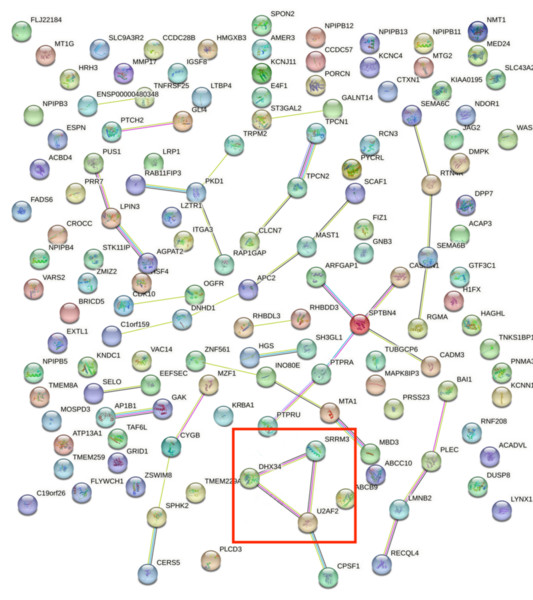
Childhood abuse has severe and lasting effects throughout an individual's life, and may even have long-term biological effects on individuals who suffer it. To learn more about the effects of abuse in childhood, Li and Yearwood analyze gene expression data to look for genes differentially expressed genes in individuals with a history of childhood abuse.
Read More...Male Feminization of the Common Pillbug Armadillidium vulgare by Wolbachia bacteria
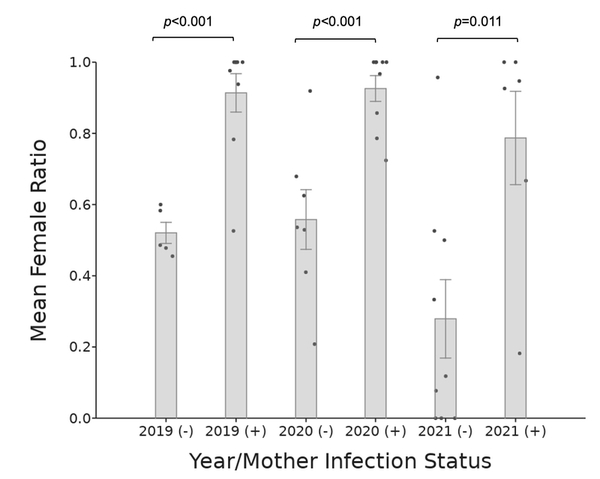
Wolbachia pipientis (Wolbachia) is a maternally inherited endosymbiotic bacterium that infects over 50% of arthropods, including pillbugs, and acts as a reproductive parasite in the host. In the common terrestrial pillbug Armadillidium vulgare (A. vulgare), Wolbachia alters the sex ratio of offspring through a phenomenon called feminization, where genetic males develop into reproductive females. Previous studies have focused on the presence or absence of Wolbachia as a sex ratio distorter in laboratory cultured and natural populations mainly from sites in Europe and Japan. Our three-year study is the first to evaluate the effects of the Wolbachia sex ratio distorter in cultured A. vulgare offspring in North America. We asked whether Wolbachia bacteria feminize A. vulgare isopod male offspring from infected mothers and if this effect can be detected in F1 offspring by comparing the male/female offspring ratios. If so, the F1 offspring ratio should show a higher number of females than males compared to the offspring of uninfected mothers. Over three years, pillbug offspring were cultured from pregnant A. vulgare females and developed into adults. We determined the Wolbachia status of mothers and counted the ratios of male and female F1 progeny to determine feminization effects. In each year sampled, significantly more female offspring were born to Wolbachia-infected mothers than those from uninfected mothers. These ratio differences suggest that the Wolbachia infection status of mothers directly impacts the A. vulgare population through the production of reproductive feminized males, which in turn provides an advantage for further Wolbachia transmission.
Read More...The influence of music on lexical decision-making in adolescents

The lexical decision task is designed to test aspects of vocabulary retrieval from short-term and long-term memory by prompting the subject to differentiate between words and non-words. From this task, researchers can determine the effects of certain stimuli on linguistic processing. Numerous studies have investigated the effects of music on various cognitive capacities, like memory and vocabulary. In the current study, we hypothesized that participants would show greater accuracy rates on the lexical decision task when exposed to a selected piece of classical music while completing the task, as compared to completing the task in silence. We tested this hypothesis on a group of 25 participants who completed the lexical decision task once in silence and once while listening to Beethoven's “Moonlight Sonata, 1st Movement”. The results suggest a positive association between the effects of classical background music and improved accuracy. Our results indicate that listening to certain types of music may enhance linguistic processes such as reading and writing. Further research with a larger group of participants is necessary to better understand the association between music and linguistic processing abilities.
Read More...Investigating ecosystem resiliency in different flood zones of south Brooklyn, New York
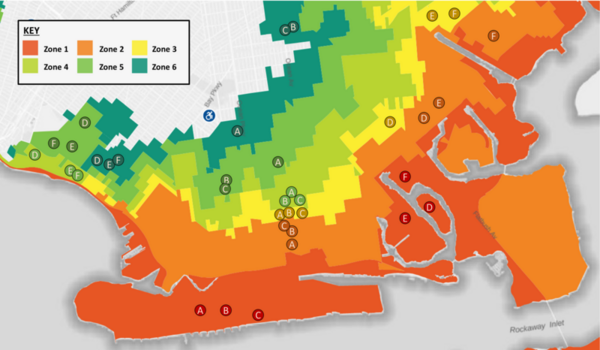
With climate change and rising sea levels, south Brooklyn is exposed to massive flooding and intense precipitation. Previous research discovered that flooding shifts plant species distribution, decreases soil pH, and increases salt concentration, nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium levels. The authors predicted a decreasing trend from Zone 1 to 6: high-pH, high-salt, and high-nutrients in more flood-prone areas to low-pH, low-salt, and low-nutrient in less flood-prone regions. They performed DNA barcoding to identify plant species inhabiting flood zones with expectations of decreasing salt tolerance and moisture uptake by plants' soil from Zones 1-6. Furthermore, they predicted an increase in invasive species, ultimately resulting in a decrease in biodiversity. After barcoding, they researched existing information regarding invasiveness, ideal soil, pH tolerance, and salt tolerance. They performed soil analyses to identify pH, nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) levels. For N and P levels, we discovered a general decreasing trend from Zone 1 to 6 with low and moderate statistical significance respectively. Previous studies found that soil moisture can increase N and P uptake, helping plants adopt efficient resource-use strategies and reduce water stress from flooding. Although characteristics of plants were distributed throughout all zones, demonstrating overall diversity, the soil analyses hinted at the possibility of a rising trend of plants adapting to the increase in flooding. Future expansive research is needed to comprehensively map these trends. Ultimately, investigating trends between flood zones and the prevalence of different species will assist in guiding solutions to weathering climate change and protecting biodiversity in Brooklyn.
Read More...