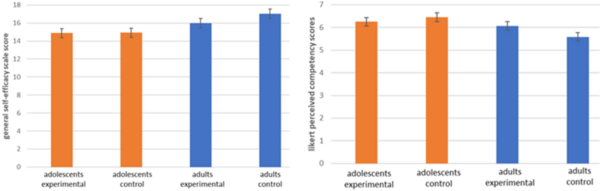
With the COVID-19 pandemic necessitating the transition to remote learning, disruption to daily school routine has impacted educational experiences on a global scale. As a result, it has potentially worsened reading achievement gaps typically exacerbated by long summer months. To address literacy skill retention and pandemic-induced social isolation, the non-profit organization ByKids4Kids has created a reading program, “Kindles4Covid Virtual Reading Buddies Program,” to instill a structure for youth to read together and connect with the convenience of Amazon Kindle devices. In this article, the authors determine the efficacy of their invaluable program by assessing changes in reading frequency and self-reported connectedness among program participants.
Read More...