
In this article, the authors investigate the RNA expression differences between groups of chronic cocaine abusers and drug-free subjects.
Read More...TNF signaling pathway upregulation as a potential pharmaceutical target for cocaine-addicted individuals

In this article, the authors investigate the RNA expression differences between groups of chronic cocaine abusers and drug-free subjects.
Read More...The Effects of Ezetimibe on Triglyceride and Alanine Transaminase Reduction in Drosophila Melanogaster Model of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)

Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a condition where a surplus of triglycerides or fat are present in the liver. In this study, ezetimibe, a cholesterol lowering drug, was used to treat flies modeling NAFLD. Compared to the coconut oil fed flies that were transferred to the control medium, the flies transferred to the control medium treated with ezetimibe showed a decrease in their triglyceride and alanine transaminase level.
Read More...Characterization of antibacterial properties of common spices
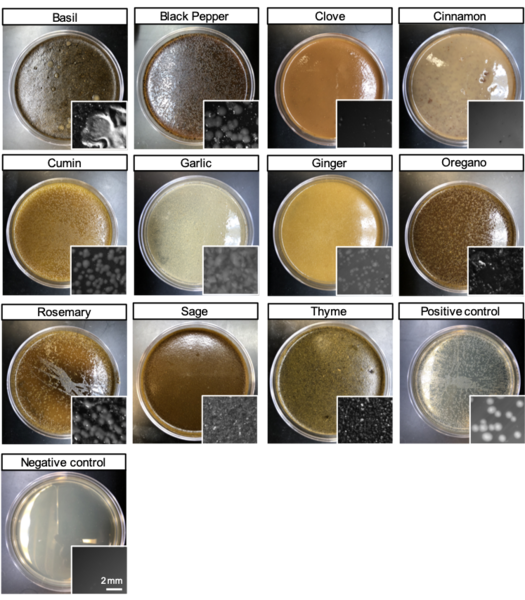

Bacterial infection is resurging as one of the most dangerous challenges facing the medical establishment. Americans spend about 55 to 70 billion dollars per year on antibiotics, yet these antibiotics are becoming increasingly ineffective as illness-causing bacteria gain resistance to the prescribed drugs. We tested if 11 commonly-used spices could inhibit growth of the gram-negative bacteria, E. coli, the main takeaway from these experiments is that certain spices and herbs have antibacterial effects that inhibit growth of E.coli , and these spices could show similarly promising activity towards other bacteria.
Read More...The effect of bioenhancers on ampicillin-sulbactam as a treatment against A. baumannii
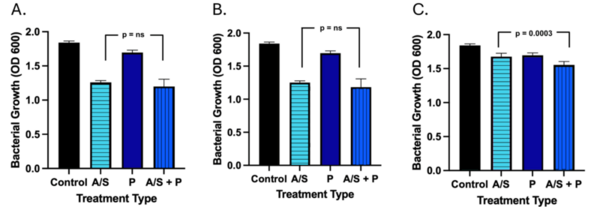
This article explores the potential of piperine, a bioenhancer from black pepper, to improve antibiotic efficacy against antibiotic-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. By combining piperine with ampicillin-sulbactam, the study demonstrated a significant reduction in bacterial growth for most strains tested, showcasing the promise of bioenhancers in combating resistant pathogens. This research highlights the possibility of reducing the required antibiotic dosage, potentially offering a new strategy in the fight against drug-resistant bacteria.
Read More...In silico modeling of emodin’s interactions with serine/threonine kinases and chitosan derivatives

Here, through protein-ligand docking, the authors investigated the effect of the interaction of emodin with serine/threonine kinases, a subclass of kinases that is overexpressed in many cancers, which is implicated in phosphorylation cascades. Through molecular dynamics theyfound that emodin forms favorable interactions with chitosan and chitosan PEG (polyethylene glycol) copolymers, which could aid in loading drugs into nanoparticles (NPs) for targeted delivery to cancerous tissue. Both polymers demonstrated reasonable entrapment efficiencies, which encourages experimental exploration of emodin through targeted drug delivery vehicles and their anticancer activity.
Read More...Assessing the Efficacy of NOX Enzyme Inhibitors as Potential Treatments for Ischemic Stroke in silico
Ischemic stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted, causing brain damage. This study investigated the effectiveness of different NOX inhibitors as treatments for ischemic stroke in silico. The results help corroborate previous in vivo and in vitro studies in an in silico format, and can be used towards developing drugs to treat ischemic stroke.
Read More...DyGS: A Dynamic Gene Searching Algorithm for Cancer Detection
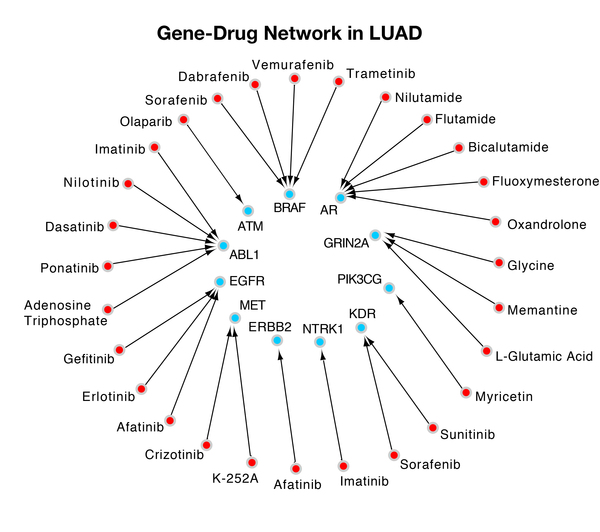
Wang and Gong developed a novel dynamic gene-searching algorithm called Dynamic Gene Search (DyGS) to create a gene panel for each of the 12 cancers with the highest annual incidence and death rate. The 12 gene panels the DyGS algorithm selected used only 3.5% of the original gene mutation pool, while covering every patient sample. About 40% of each gene panel is druggable, which indicates that the DyGS-generated gene panels can be used for early cancer detection as well as therapeutic targets in treatment methods.
Read More...Aberrant response to dexamethasone suppression test associated with inflammatory response in MDD patients
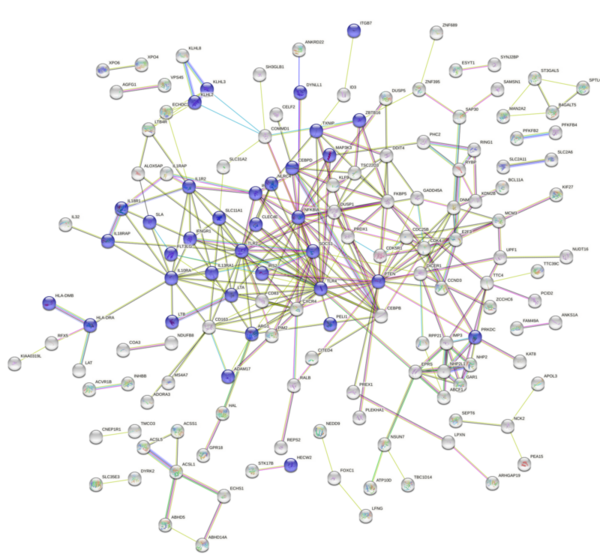
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a prevalent mood disorder. The direct causes and biological mechanisms of depression still elude understanding, though genetic factors have been implicated. This study looked to identify the mechanism behind the aberrant response to the dexamethasone suppression test (DST) displayed by MDD patients, in which they display a lack of cortisol suppression. Analysis revealed several pro-inflammatory genes that were significant and differentially expressed between affected and non-affected groups in response to the DST. Looking at ways to decrease the inflammatory response could have implications for treatment and may explain why some people treated for depression still display symptoms or may lead researchers to different classes of drugs for treatment.
Read More...Development of a Novel Treatment Strategy to Treat Parkinsonian Neurodegeneration by Targeting Both Lewy Body Aggregation and Dopaminergic Neuronal Degradation in a Drosophila melanogaster Model
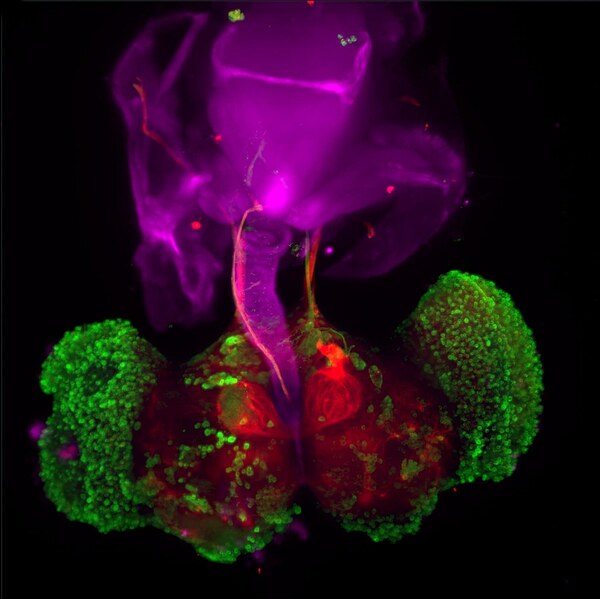
In this article the authors address the complex and life quality-diminishing neurodegenerative disease known as Parkinson's. Although genetic and/or environmental factors contribute to the etiology of the disease, the diagnostic symptoms are the same. By genetically modifying fruit flies to exhibit symptoms of Parkinson's disease, they investigate whether drugs that inhibit mitochondrial calcium uptake or activate the lysosomal degradation of proteins could improve the symptoms of Parkinson's these flies exhibit. The authors report the most promising outcome to be that when both types of drugs were used together. Their data provides encouraging evidence to support further investigation of the utility of such drugs in the treatment of human Parkinson's patients.
Read More...Survey of medication disposal: Patient views and awareness
The authors investigate how improper disposal of medication can be mitigated through community education efforts.
Read More...