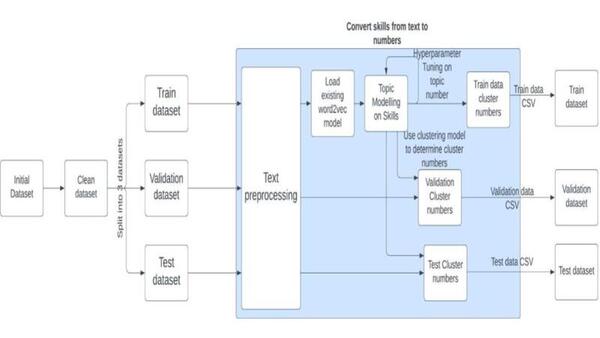
The authors looked at using machine learning to identify skills needed to apply for certain jobs, specifically looking at different techniques to parse apart the text. They found that Bidirectional Encoder Representation of Transforms (BERT) performed best.
Read More...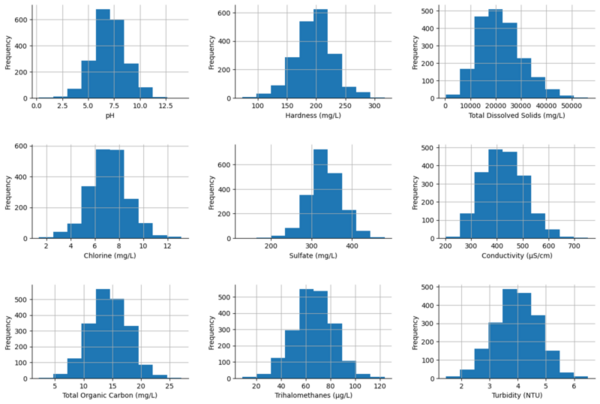
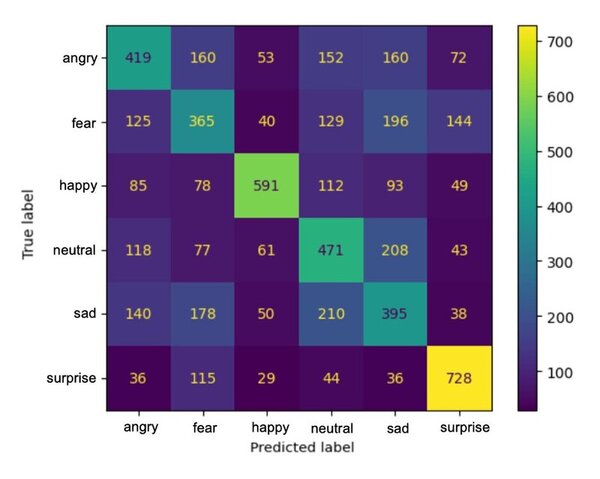
.png)
%20(1).png)

