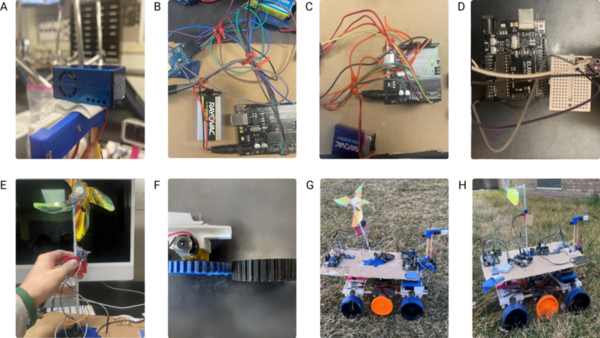
Pediatric asthma remains a significant health issue for Dallas students. This study examined the relationship between microclimatic parameters, vegetation, and pediatric asthma vulnerability (PAV) in urban schools.
Read More...Rover engineered to evaluate impacts of microclimatic parameters on pediatric asthma in Dallas schools

Pediatric asthma remains a significant health issue for Dallas students. This study examined the relationship between microclimatic parameters, vegetation, and pediatric asthma vulnerability (PAV) in urban schools.
Read More...Impact of environmental stressors on ultrasonic acoustic emissions in different species of plants
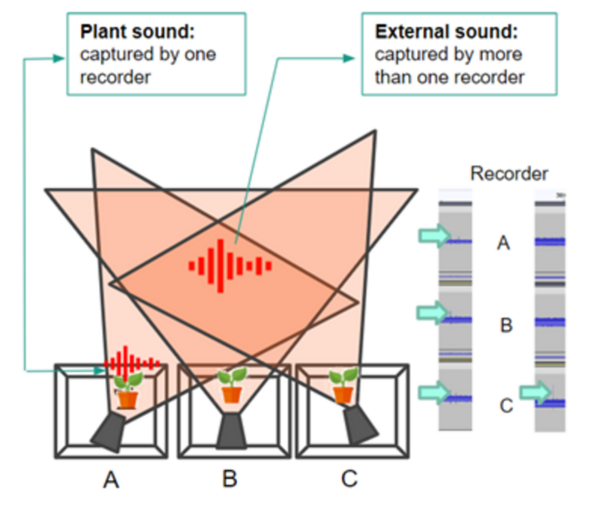
Current horticulture practices often rely on pesticides, causing environmental harm. To address this, authors explore the use of ultrasonic sound emissions to detect plant stress at an individual level.
Read More...The effect of Poisson sprinkling methods on causal sets in 1+1-dimensional flat spacetime
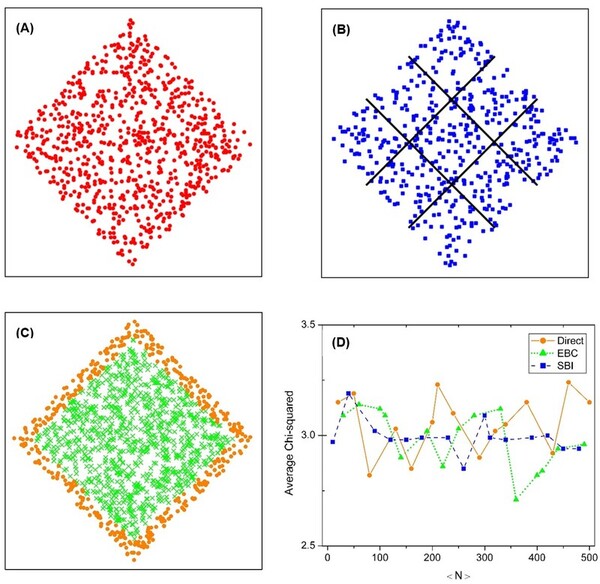
The causal set theory (CST) is a theory of the small-scale structure of spacetime, which provides a discrete approach to describing quantum gravity. Studying the properties of causal sets requires methods for constructing appropriate causal sets. The most commonly used approach is to perform a random sprinkling. However, there are different methods for sprinkling, and it is not clear how each commonly used method affects the results. We hypothesized that the methods would be statistically equivalent, but that some noticeable differences might occur, such as a more uniform distribution for the sub-interval sprinkling method compared to the direct sprinkling and edge bias compensation methods. We aimed to assess this hypothesis by analyzing the results of three different methods of sprinkling. For our analysis, we calculated distributions of the longest path length, interval size, and paths of various lengths for each sprinkling method. We found that the methods were statistically similar. However, one of the methods, sub-interval sprinkling, showed some slight advantages over the other two. These findings can serve as a point of reference for active researchers in the field of causal set theory, and is applicable to other research fields working with similar graphs.
Read More...Economic performance of solar energy systems financed with green bonds in New Jersey
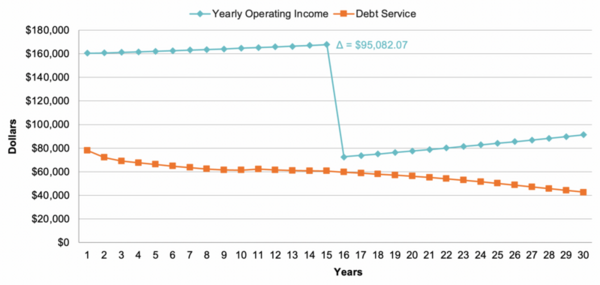
Global reliance on extractive energy sources has many downsides, among which are inconsistent supply and consequent price volatility that distress companies and consumers. It is unclear if renewable energy offers stable and affordable solutions to extractive energy sources. The cost of solar energy generation has decreased sharply in recent years, prompting a surge of installations with a range of financing options. Even so, most existing options require upfront payment, making installation inaccessible for towns with limited financial resources. The primary objective of our research is to examine the use of green bonds to finance solar energy systems, as they eliminate the need for upfront capital and enable repayment through revenue generated over time. We hypothesized that if we modeled the usage of green bonds to finance the installation of a solar energy system in New Jersey, then the revenue generated over the system’s lifetime would be enough to repay the bond. After modeling the financial performance of a proposed solar energy-producing carport in Madison, New Jersey, financed with green bonds, we found that revenue from solar energy systems successfully covered the annual green bond payments and enabled the installers to obtain over 50% of the income for themselves. Our research demonstrated green bonds as a promising option for New Jersey towns with limited financial resources seeking to install solar energy systems, thereby breaking down a financial barrier.
Read More...Recombinant preparation and characterization of ADH1C and ALDH2 in alcohol metabolism
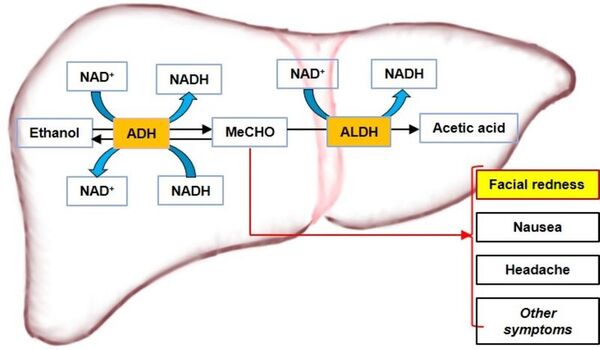
The authors test the activity of two purified human alcohol detoxification enzymes, alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase.
Read More...An exploration of western mosquitofish as the animal component in an aquaponic farming system
Aquaponics (the combination of aquatic plant farming with fish production) is an innovative farming practice, but the fish that are typically used, like tilapia, are expensive and space-consuming to cultivate. Medina and Alvarez explore other options test if mosquitofish are a viable option in the aquaponic cultivation of herbs and microgreens.
Read More...An in vitro comparative analysis of the growth factors present in FBS vs PLAY®

Here the authors performed a comparative analysis to investigate the viability of using PLAY® instead of fetal bovine serum (FBS) as a growth medium to culture cells with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Read More...Assessing the possibility of using entomopathogenic fungi for mosquito control in Hawaii
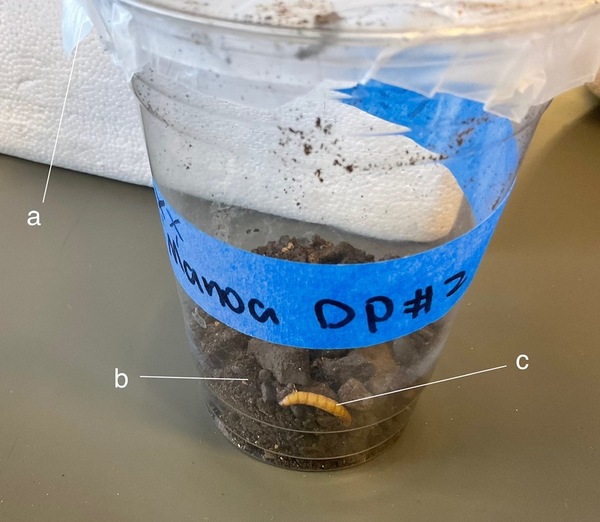

Fungi that attack and kill insects have promise for targeting mosquitoes without the harmful environmental impacts of chemicals like DDT. To find out whether fungi might be effective in controlling mosquitoes in Hawaii, Jiang and Chan test the effects of Hawaiian fungal isolates on mosquito larvae.
Read More...A natural language processing approach to skill identification in the job market
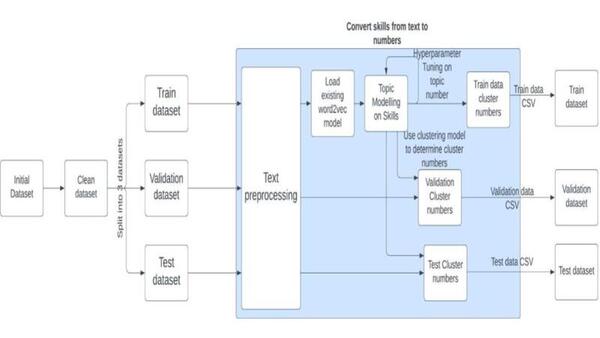
The authors looked at using machine learning to identify skills needed to apply for certain jobs, specifically looking at different techniques to parse apart the text. They found that Bidirectional Encoder Representation of Transforms (BERT) performed best.
Read More...The effect of circumference on the segregation of objects in a mixture
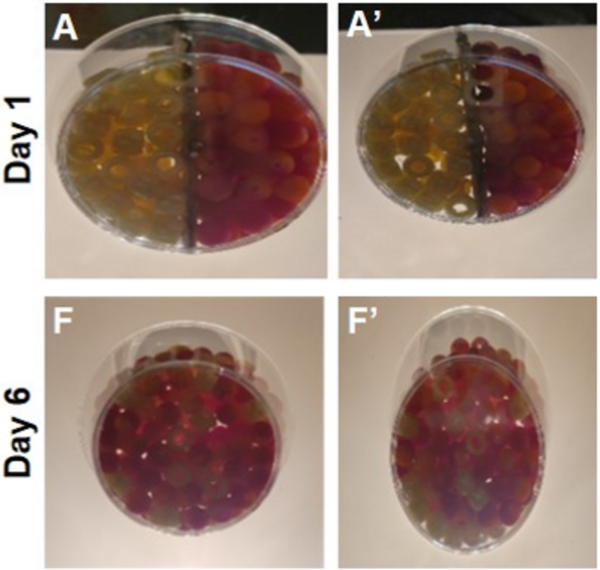
The authors test how the size-segregation theory applies to the behavior of hollow and irregular-shaped objects.
Read More...