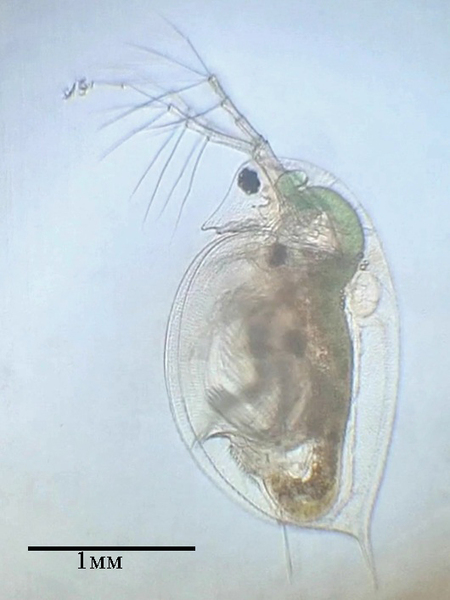
Chemical pollution can have significant effects on freshwater organisms. In this study, the effect of copper sulfate on the survival of Daphnia pulex and Ostracoda was investigated.
Read More...Differences in the effect of copper sulfate on the mortality rate of Ostracod and Daphnia

Chemical pollution can have significant effects on freshwater organisms. In this study, the effect of copper sulfate on the survival of Daphnia pulex and Ostracoda was investigated.
Read More...The effect of microplastics on the speed, mortality rate, and swimming patterns of Daphnia Magna
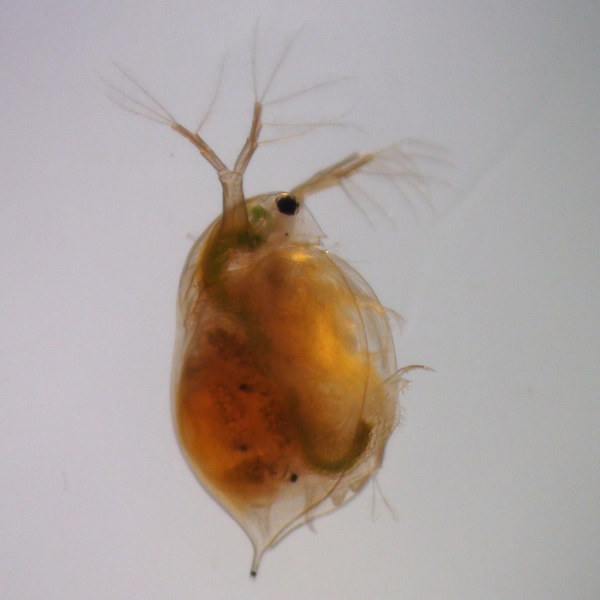

In this study, the authors investigate the effects that microplastics (which pollute fresh and saltwater ecosystems) have on plankton species Daphnia Magna by measuring their movement and viability.
Read More...Pediatric probiotic culture survival study in acidic pH using an in vitro model
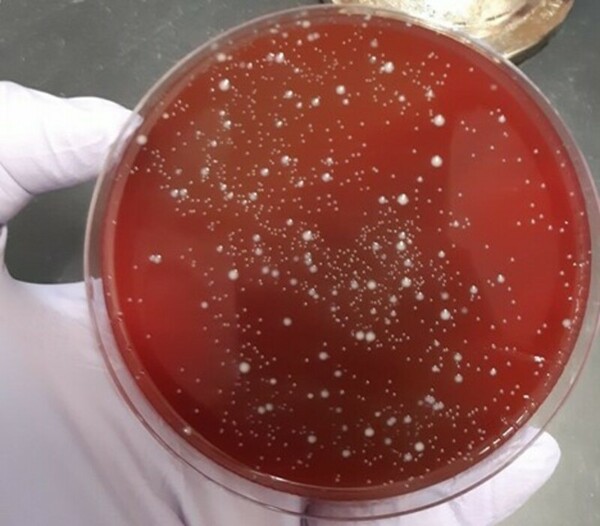
In this study, the authors investigate the effects of acidity on the survival of commercial probiotic Lovebug bacterial strains.
Read More...Effect of Increasing Concentrations of Cannabidiol (CBD) on Hatching, Survival and Development of Artemia salina
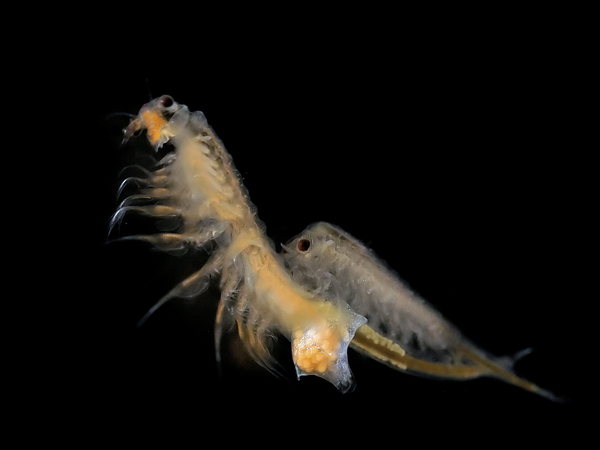

Cannabidiol, or CBD, is a widely available over the counter treatment used for various medical conditions. However, CBD exerts its effects on the endocannabinoid system, which is involved in neural maturation, and could potentially have adverse effects on brain development. Here, the impact of CBD on the development of brine shrimp (Artemia salina) was assessed. Differences in dose responses were observed.
Read More...Two Wrongs Could Make a Right: Food Waste Compost Accelerated Polystyrene Consumption of Tenebrio molitor

Expanded polystyrene (EPS) is a plastic used to make food containers and packing materials that poses a threat to the environment. Mealworms can degrade EPS, but at a slow rate. Here, researchers assessed the impact of food waste compost and oats on the speed of EPS consumption by mealworms, superworms, and waxworms. A positive correlation was found between food waste compost supplementation and EPS consumption, especially by mealworms, indicating a potential industrial application.
Read More...siRNA-dependent KCNMB2 silencing inhibits lung cancer cell proliferation and promotes cell death
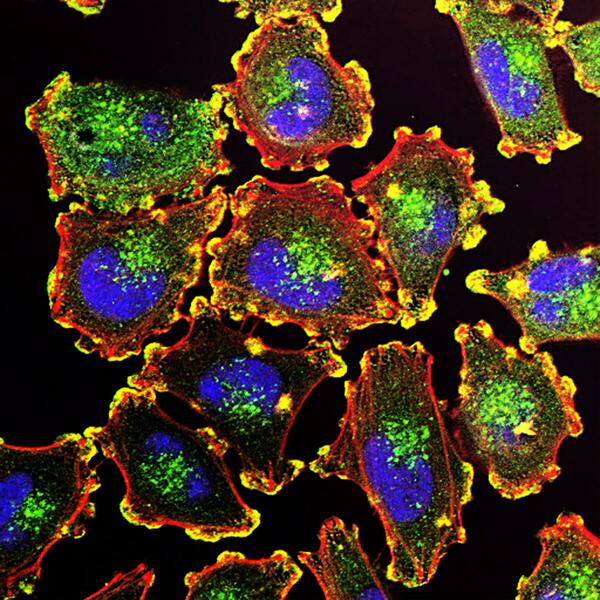
Here, seeking to better understand the genetic associations underlying non-small cell lung cancer, the authors screened hundreds of genes, identifying that KCNMB2 upregulation was significantly correlated with poor prognoses in lung cancer patients. Based on this, they used small interfering RNA to decrease the expression of KCNMB2 in A549 lung cancer cells, finding decreased cell proliferation and increased lung cancer cell death. They suggest this could lead to a new potential target for lung cancer therapies.
Read More...Characterization of Drought Tolerance in Arabidopsis Mutant fry1-6

In a world where water shortage is becoming an increasing concern, and where population increase seems inevitable, food shortage is an overwhelming concern for many. In this paper, the authors aim to characterize a drought-resistant strain of A. thaliana, investigating the cause for its water resistance. These and similar studies help us learn how plants could be engineered to improve their ability to flourish in a changing climate.
Read More...Monitoring Local Soil Toxicity by Daphnia magna Viability

In this study a student uses Daphnia magna, or water fleas, to assay the purity of local soil samples. Daphnia magna are a helpful organism to detect potentially harmful levels of toxins in water.
Read More...Longer Exposure to 2% India Ink Increases Average Number of Vacuoles in Tetrahymena pyriformis
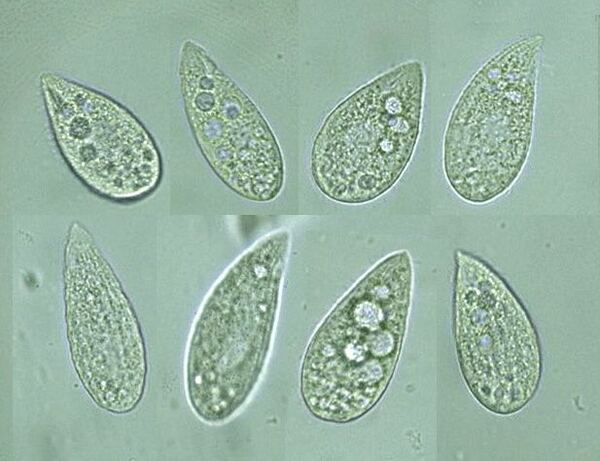
Phagocytes feed by forming food vacuoles. In this article the authors investigate the extent that exposure of non-nutritional food, such as India Ink, to Tetrahymena pyriformis affects the number of vacuole formation. These studies provide insight to how organisms budget their energy and metabolic processes during an energy shortage.
Read More...Survival of Escherichia coli K-12 in various types of drinking water

For public health, drinking water should be free of bacterial contamination. The objective of this research is to identify the fate of bacteria if drinking water becomes contaminated and inform consumers on which water type enables the least bacteria to survive. We hypothesized that bottled mineral water would provide the most sufficient conditions for E. coli to survive. We found that if water becomes contaminated, the conditions offered by the three water types at room temperature allow E. coli to survive up to three days. At 72 hours, the bottled spring water had the highest average colony forming units (CFUs), with tap and mineral water CFU values statistically lower than spring water but not significantly different from each other. The findings of this research highlight the need of implementing accessible quality drinking water for the underserved population and for the regulation of water sources.
Read More...